
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
Among the given options, which one belongs to changes of state is the final state that of solid has to be chosen.
Concept Introduction:
A change of state is a cycle in that a substance is transformed from one physical state to another physical sate. The physical changes of a substance occurs by either heating or cooling. There are six possible changes of state and they are freezing, melting, evaporation, condensation, sublimation, and deposition. The below mentioned figure will represent each of the physical changes of a substance from starting stage to final stage via intermediate stage.
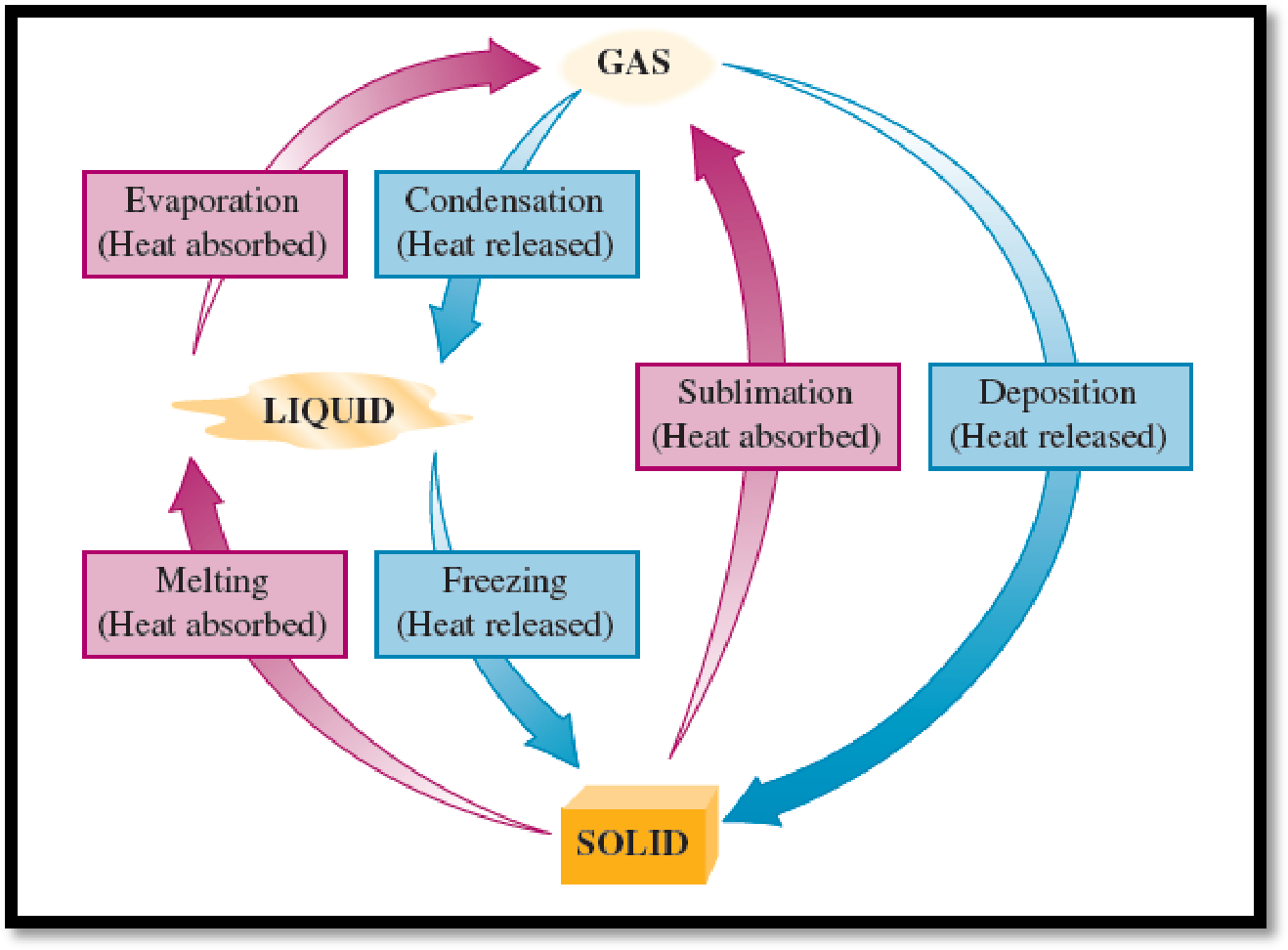
Figure 1
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 7 Solutions
Bundle: General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry, 7th + OWLv2 Quick Prep for General Chemistry, 4 terms (24 months) Printed Access Card
- What is the preparation of 1 Liter of 0.1M NH4Cl buffer at pH 9.0 with solid NH4Cl and 0.1M NaOH. How would I calculate the math to describe this preparation? How would I use Henderson-Hasselbach equation?arrow_forwardC Predict the major products of this organic reaction. Be sure you use wedge and dash bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products with different stereochemistry. : ☐ + x G C RCO₂H Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forwardFill in the blanks by selecting the appropriate term from below: For a process that is non-spontaneous and that favors products at equilibrium, we know that a) ΔrG∘ΔrG∘ _________, b) ΔunivSΔunivS _________, c) ΔsysSΔsysS _________, and d) ΔrH∘ΔrH∘ _________.arrow_forward
- Highest occupied molecular orbital Lowest unoccupied molecular orbital Label all nodes and regions of highest and lowest electron density for both orbitals.arrow_forwardRelative Intensity Part VI. consider the multi-step reaction below for compounds A, B, and C. These compounds were subjected to mass spectrometric analysis and the following spectra for A, B, and C was obtained. Draw the structure of B and C and match all three compounds to the correct spectra. Relative Intensity Relative Intensity 20 NaоH 0103 Br (B) H2504 → (c) (A) 100- MS-NU-0547 80 40 20 31 10 20 100- MS2016-05353CM 80 60 100 MS-NJ-09-3 80 60 40 20 45 J.L 80 S1 84 M+ absent राग 135 137 S2 62 164 166 11 S3 25 50 75 100 125 150 175 m/zarrow_forwardDon't used hand raiting and don't used Ai solutionarrow_forward
- Don't used hand raitingarrow_forwardDon't used hand raitingarrow_forwardA composite material reinforced with aligned fibers, consisting of 20% by volume of silicon carbide (SiC) fibers and 80% by volume of polycarbonate (PC) matrix. The mechanical characteristics of the 2 materials are in the table. The stress of the matrix when the fiber breaks is 45 MPa. Calculate the longitudinal strength? SiC PC Elastic modulus (GPa) Tensile strength (GPa) 400 2,4 3,9 0,065arrow_forward
 General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning


