
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
8th Edition
ISBN: 8220102744127
Author: Bruice
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Chapter 7.6, Problem 13P
(a)
Interpretation Introduction
Interpretation:
The mechanism for the reaction of 2-butyne with one equivalent of bromine should be given.
Concept Introduction:
Addition of halides to
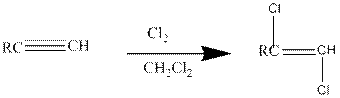
If excess halides are present, a second addition reaction also occurs.
(b)
Interpretation Introduction
Interpretation:
The configuration of the product obtained in the above reaction should be identified.
Concept Introduction:
Addition of halides to alkynes: Halogens like chlorine and bromine adds to the alkyne compounds. The general form of the reaction is given below.

If excess halides are present, a second addition reaction also occurs.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
For each reaction below, decide if the first stable organic product that forms in solution will create a new CC bond, and check
the appropriate box.
Next, for each reaction to which you answered "Yes" to in the table, draw this product in the drawing area below.
Note for advanced students: for this problem, don't worry if you think this product will continue to react under the current conditions
- just focus on the first stable product you expect to form in solution.
?
NH2
MgBr
Will the first product that forms in this reaction
create a new CC bond?
○ Yes
○ No
MgBr
?
Will the first product that forms in this reaction
create a new CC bond?
O Yes
O No
Click and drag to start drawing a
structure.
:☐
G
x
c
olo
Ar
HE
Predicting
As the lead product manager at OrganometALEKS Industries, you are trying to decide if the following reaction will make a molecule
with a new C - C bond as its major product:
H₂N
O
H
1.
?
2. H3O+
If this reaction will work, draw the major organic product or products you would expect in the drawing area below. If there's more
than one major product, you can draw them in any arrangement you like. Be sure you use wedge and dash bonds if necessary, for
example to distinguish between major products with different stereochemistry.
0
If the major products of this reaction won't have a new CC bond, just check the box under the drawing area and leave it blank.
فا
Explanation
Check
Click and drag to start drawing a
structure.
Highlight the chirality (or stereogenic) center(s) in the given compound. A compound may have one or more stereogenic centers.
OH
OH
OH
OH
OH
OH
Chapter 7 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
Ch. 7.1 - Prob. 1PCh. 7.1 - Name the following:Ch. 7.1 - What is the molecular formula for a monocyclic...Ch. 7.1 - Draw the condensed and skeletal structures for...Ch. 7.1 - Draw the structure and give the common and...Ch. 7.2 - Prob. 6PCh. 7.2 - Name the following:Ch. 7.3 - What orbitals are used to form the carbon-carbon ...Ch. 7.4 - Prob. 9PCh. 7.4 - Why does cis-2-butene have a higher boiling point...
Ch. 7.6 - Prob. 12PCh. 7.6 - Prob. 13PCh. 7.7 - Prob. 14PCh. 7.7 - Which alkyne should be used for the synthesis of...Ch. 7.7 - Prob. 16PCh. 7.8 - Prob. 17PCh. 7.8 - Only one alkyne forms an aldehyde when it...Ch. 7.9 - Describe the alkyne you should start with and the...Ch. 7.9 - Prob. 20PCh. 7.10 - Prob. 21PCh. 7.10 - Prob. 22PCh. 7.10 - Prob. 23PCh. 7.10 - Rank the following from strongest base to weakest...Ch. 7.10 - Prob. 26PCh. 7.12 - Prob. 28PCh. 7 - What is the major product obtained from the...Ch. 7 - Draw a condensed structure for each of the...Ch. 7 - A student was given the structural formula of...Ch. 7 - Prob. 32PCh. 7 - What is each compounds systematic name?Ch. 7 - What reagents should be used to carry out the...Ch. 7 - Prob. 35PCh. 7 - Draw the mechanism for the following reaction:Ch. 7 - Prob. 37PCh. 7 - Prob. 38PCh. 7 - What is the major product of the reaction of 1 mol...Ch. 7 - Answer Problem 39, parts a-b, using 2-butyne as...Ch. 7 - What is each compounds systematic name? a....Ch. 7 - What is the molecular formula of a hydrocarbon...Ch. 7 - a. Starting with 3-methyl 1-butyne, how can you...Ch. 7 - Prob. 44PCh. 7 - Which of the following pairs are keto-enol...Ch. 7 - Prob. 46PCh. 7 - Do the equilibria of the following acid-base...Ch. 7 - What is each compounds systematic name?Ch. 7 - What stereoisomers are obtained when 2-butyne...Ch. 7 - Prob. 50PCh. 7 - Draw the keto tautomer for each of the following:Ch. 7 - Show how each of the following compounds can be...Ch. 7 - A chemist is planning to synthesize 3-octyne by...Ch. 7 - Prob. 54PCh. 7 - What stereoisomers are obtained from the following...Ch. 7 - Prob. 56PCh. 7 - Prob. 57PCh. 7 - Prob. 58PCh. 7 - Show how the following compound can be prepared...Ch. 7 - Prob. 60P
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Using wedge-and-dash bonds, modify the bonds on the chiral carbon in the molecule below so the molecule has R stereochemical configuration. NH H Br X टेarrow_forwardProvide photos of models of the following molecules. (Include a key for identification of the atoms) 1,2-dichloropropane 2,3,3-trimethylhexane 2-bromo-3-methybutanearrow_forwardPlease draw the structure in the box that is consistent with all the spectral data and alphabetically label all of the equivalent protons in the structure (Ha, Hb, Hc....) in order to assign all the proton NMR peaks. The integrations are computer generated and approximate the number of equivalent protons. Molecular formula: C13H1802 14 13 12 11 10 11 (ppm) Structure with assigned H peaks 2.08 3.13arrow_forward
- A 0.10 M solution of acetic acid (CH3COOH, Ka = 1.8 x 10^-5) is titrated with a 0.0250 M solution of magnesium hydroxide (Mg(OH)2). If 10.0 mL of the acid solution is titrated with 10.0 mL of the base solution, what is the pH of the resulting solution?arrow_forwardFirefly luciferin exhibits three rings. Identify which of the rings are aromatic. Identify which lone pairs are involved in establishing aromaticity. The lone pairs are labeled A-D below.arrow_forwardA 0.10 M solution of acetic acid (CH3COOH, Ka = 1.8 x 10^-5) is titrated with a 0.0250 M solution of magnesium hydroxide (Mg(OH)2). If 10.0 mL of the acid solution is titrated with 10.0 mL of the base solution, what is the pH of the resulting solution?arrow_forward
- Given a complex reaction with rate equation v = k1[A] + k2[A]2, what is the overall reaction order?arrow_forwardPlease draw the structure in the box that is consistent with all the spectral data and alphabetically label all of the equivalent protons in the structure (Ha, Hb, Hc....) in order to assign all the proton NMR peaks. The integrations are computer generated and approximate the number of equivalent protons. Molecular formula: C13H1802 14 13 12 11 10 11 (ppm) Structure with assigned H peaks 2.08 3.13arrow_forwardCHEMICAL KINETICS. One of the approximation methods for solving the rate equation is the steady-state approximation method. Explain what it consists of.arrow_forward
- CHEMICAL KINETICS. One of the approximation methods for solving the rate equation is the limiting or determining step approximation method. Explain what it consists of.arrow_forwardCHEMICAL KINETICS. Indicate the approximation methods for solving the rate equation.arrow_forwardTRANSMITTANCE เบบ Please identify the one structure below that is consistent with the 'H NMR and IR spectra shown and draw its complete structure in the box below with the protons alphabetically labeled as shown in the NMR spectrum and label the IR bands, including sp³C-H and sp2C-H stretch, indicated by the arrows. D 4000 OH LOH H₂C CH3 OH H₂C OCH3 CH3 OH 3000 2000 1500 HAVENUMBERI-11 1000 LOCH3 Draw your structure below and label its equivalent protons according to the peak labeling that is used in the NMR spectrum in order to assign the peaks. Integrals indicate number of equivalent protons. Splitting patterns are: s=singlet, d=doublet, m-multiplet 8 3Hb s m 1Hd s 3Hf m 2Hcd 2Had 1He 鄙视 m 7 7 6 5 4 3 22 500 T 1 0arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning


Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:Cengage Learning