
(a)
Interpretation:
The major product of the given reaction should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Addition of halides to
Halogens like chlorine and bromine adds to the alkyne compounds. The general form of the reaction is given below.
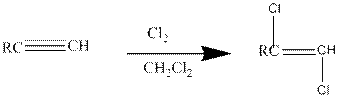
If excess halides are present, a second addition reaction also occurs.
(b)
Interpretation:
The major product of the given reaction should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Addition of halides to alkynes:
Halogens like chlorine and bromine adds to the alkyne compounds. The general form of the reaction is given below.

If excess halides are present, a second addition reaction also occurs.
(c)
Interpretation:
The major product of the given reaction should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Addition of halides to alkynes:
Halogens like chlorine and bromine adds to the alkyne compounds. The general form of the reaction is given below.

If excess halides are present, a second addition reaction also occurs.
(d)
Interpretation:
The major product of the given reaction should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Addition of halides to alkynes:
Halogens like chlorine and bromine adds to the alkyne compounds. The general form of the reaction is given below.

If excess halides are present, a second addition reaction also occurs.
(e)
Interpretation:
The major product of the given reaction should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Addition of halides to alkynes:
Halogens like chlorine and bromine adds to the alkyne compounds. The general form of the reaction is given below.

If excess halides are present, a second addition reaction also occurs.
(f)
Interpretation:
The major product of the given reaction should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Addition of halides to alkynes:
Halogens like chlorine and bromine adds to the alkyne compounds. The general form of the reaction is given below.

If excess halides are present, a second addition reaction also occurs.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 7 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- In the decomposition reaction in solution B → C, only species C absorbs UV radiation, but neither B nor the solvent absorbs. If we call At the absorbance measured at any time, A0 the absorbance at the beginning of the reaction, and A∞ the absorbance at the end of the reaction, which of the expressions is valid? We assume that Beer's law is fulfilled.arrow_forward> You are trying to decide if there is a single reagent you can add that will make the following synthesis possible without any other major side products: 1. ☑ CI 2. H3O+ O Draw the missing reagent X you think will make this synthesis work in the drawing area below. If there is no reagent that will make your desired product in good yield or without complications, just check the box under the drawing area and leave it blank. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Explanation Check ? DO 18 Ar B © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibilityarrow_forwardDon't use ai to answer I will report you answerarrow_forward
- Consider a solution of 0.00304 moles of 4-nitrobenzoic acid (pKa = 3.442) dissolved in 25 mL water and titrated with 0.0991 M NaOH. Calculate the pH at the equivalence pointarrow_forwardWhat is the name of the following compound? SiMe3arrow_forwardK Draw the starting structure that would lead to the major product shown under the provided conditions. Drawing 1. NaNH2 2. PhCH2Br 4 57°F Sunny Q Searcharrow_forward
- 7 Draw the starting alkyl bromide that would produce this alkyne under these conditions. F Drawing 1. NaNH2, A 2. H3O+ £ 4 Temps to rise Tomorrow Q Search H2arrow_forward7 Comment on the general features of the predicted (extremely simplified) ¹H- NMR spectrum of lycopene that is provided below. 00 6 57 PPM 3 2 1 0arrow_forwardIndicate the compound formula: dimethyl iodide (propyl) sulfonium.arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
