
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Synthesis method of the given compound has to be given from the compound which have the same number of carbon atoms.
Concept Introduction:
Addition of water to
Under acidic conditions, alkyne reacts with water to produce an enol which then immediately converts into
The formed enol and ketone are called keto-enol tautomers.
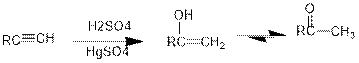
Tautomerization: It is the process of inter conversion of tautomers and therefore the process can also be called as keto-enol tautomerization.
Hydroboration reaction:
It is the reaction in which an internal alkyne is converted into ketone. The reagents used for the hydroboration oxidation reaction is either
(b)
Interpretation:
Synthesis method of the given compound has to be given from the compound which have the same number of carbon atoms.
Concept Introduction:
Addition of water to alkynes in presence of acid:
Under acidic conditions, alkyne reacts with water to produce an enol which then immediately converts into ketone. For terminal alkynes, there is a need of catalyst which is mercury.
The formed enol and ketone are called keto-enol tautomers.
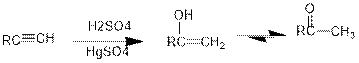
Tautomerization: It is the process of inter conversion of tautomers and therefore the process can also be called as keto-enol tautomerization.
Hydroboration reaction:
It is the reaction in which an internal alkyne is converted into ketone. The reagents used for the hydroboration oxidation reaction is either
(c)
Interpretation:
Synthesis method of the given compound has to be given from the compound which have the same number of carbon atoms.
Concept Introduction:
Addition of water to alkynes in presence of acid:
Under acidic conditions, alkyne reacts with water to produce an enol which then immediately converts into ketone. For terminal alkynes, there is a need of catalyst which is mercury.
The formed enol and ketone are called keto-enol tautomers.
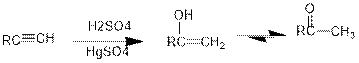
Tautomerization: It is the process of inter conversion of tautomers and therefore the process can also be called as keto-enol tautomerization.
Hydroboration reaction:
It is the reaction in which an internal alkyne is converted into ketone. The reagents used for the hydroboration oxidation reaction is either
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 7 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- 8:16 PM Sun Mar 30 K Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Proble 1. CH3MgBr 2. H3O+ F Drawingarrow_forwardо но оarrow_forwardName the major organic product of the following action of 4-chloro-4-methyl-1-pentanol in neutral pollution 10+ Now the product. The product has a molecular formula f b. In a singly hain, the starting, material again converts into a secule with the molecular kormula CIO. but with comply Draw the major organic structure inhalationarrow_forward
- Macmillan Learning Alcohols can be oxidized by chromic acid derivatives. One such reagent is pyridinium chlorochromate, (C,H,NH*)(CICTO3), commonly known as PCC. Draw the proposed (neutral) intermediate and the organic product in the oxidation of 1-butanol by PCC when carried out in an anhydrous solvent such as CH₂C₁₂. PCC Intermediate OH CH2Cl2 Draw the intermediate. Select Draw Templates More с H Cr о Product Draw the product. Erase Select Draw Templates More H о Erasearrow_forwardIf I have 1-bromopropene, to obtain compound A, I have to add NaOH and another compound. Indicate which compound that would be. A C6H5 CH3arrow_forwardProvide the reagents for the following reactions.arrow_forward
- If I have 1-bromopropene, to obtain compound Z, I have to add two compounds A1 and A2. Indicate which compounds are needed. P(C6H5)3arrow_forwardDraw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Assume that the water side product is continuously removed to drive the reaction toward products. O CH3CH2NH2, TSOH Select to Draw >arrow_forwardPredict the major organic product(s) for the following reaction.arrow_forward
- Predict the major organic product(s) for the following reactions.arrow_forwardProvide the complete mechanism for the reactions below. You must include appropriate arrows,intermediates, and formal charges.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by reacting fluorobenzene with a sulfonitric mixture.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning





