
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
10th Edition
ISBN: 9780134319650
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 7.5, Problem 7.59P
The H-beam is subjected to a shear of V=80 kN Sketch the shear-stress distribution acting along one of its side segments Indicate all peak values
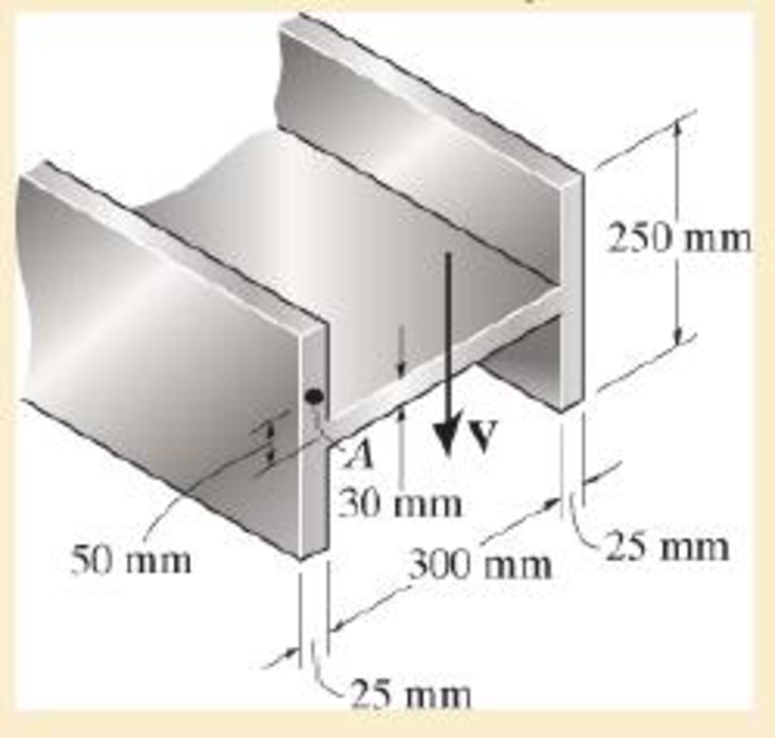
Probs. 7–58/59
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Cushioning: (Q1)
A cylinder is used to clamp onto rubber tires on an assembly line. The cylinder quickly extends and clamps onto the tire and robot
puts a label onto the tire. The cylinder then retracts quickly to unclamp the tire.
Which of these four cylinders is best for the job?
A
0
A Selection A is best
B Selection B is best
(C) Selection C is best
D) Selection D is best
B
D
Bourdon Gauges: (Q4) - True of False
"A Bourdon gauge is used to measure high pressures above 500 psi"
Weight of Air:
If you could collect the air in a square inch column of air starting at sea level going all the way to space, how much would it weigh?
Answer with one decimal. Do not write the unit.
Chapter 7 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Ch. 7.2 - In each case, calculate the value of Q and t that...Ch. 7.2 - If the beam is subjected to a shear force of V =...Ch. 7.2 - Determine the shear stress at points A and B if...Ch. 7.2 - Determine the absolute maximum shear stress in the...Ch. 7.2 - If the beam is subjected to a shear force of V =20...Ch. 7.2 - If the beam is made from four plates and subjected...Ch. 7.2 - If the wide-flange beam is subjected to a shear of...Ch. 7.2 - If the wide-flange beam is subjected to a shear of...Ch. 7.2 - If the wide-flange beam is subjected to a shear of...Ch. 7.2 - If the beam is subjected to a shear of V = 30 kN,...
Ch. 7.2 - If the wide-flange beam is subjected to a shear of...Ch. 7.2 - The wood beam has an allowable shear stress of...Ch. 7.2 - The shaft is supported by a thrust bearing at A...Ch. 7.2 - The shaft is supported by a thrust bearing at A...Ch. 7.2 - Determine the largest shear force V that the...Ch. 7.2 - If the applied shear force V = 18 kip, determine...Ch. 7.2 - The overhang beam is subjected to the uniform...Ch. 7.2 - The beam is made from a polymer and is subjected...Ch. 7.2 - Determine the maximum shear stress in the strut if...Ch. 7.2 - Determine the maximum shear force V that the strut...Ch. 7.2 - Sketch the intensity of the shear-stress...Ch. 7.2 - Plot the shear-stress distribution over the cross...Ch. 7.2 - If the beam is subjected to a shear of V=15 kN,...Ch. 7.2 - If the wide-flange beam is subjected to a shear of...Ch. 7.2 - If the wide-flange beam is subjected to a shear of...Ch. 7.2 - Determine the length of the cantilevered beam so...Ch. 7.2 - If the beam is made from wood having an allowable...Ch. 7.2 - Determine the largest intensity w of the...Ch. 7.2 - If w=800 lb/ft, determine the absolute maximum...Ch. 7.2 - Determine the shear stress at point B on the web...Ch. 7.2 - Determine the maximum shear stress acting at...Ch. 7.2 - Railroad ties must be designed to resist large...Ch. 7.2 - The beam is slit longitudinally along both sides....Ch. 7.2 - The beam is to be cut longitudinally along both...Ch. 7.2 - The composite beam is constructed from wood and...Ch. 7.2 - The beam has a rectangular cross section and is...Ch. 7.2 - The beam in Fig.6-48f is subjected to a fully...Ch. 7.3 - The two identical boards are bolted together to...Ch. 7.3 - Two identical 20-mm-thick plates are bolted to the...Ch. 7.3 - The boards are bolted together to form the...Ch. 7.3 - The boards are bolted together to form the...Ch. 7.3 - The beam is constructed from two boards fastened...Ch. 7.3 - The beam is constructed from two boards fastened...Ch. 7.3 - The beam is constructed from three boards. If it...Ch. 7.3 - The beam is constructed from three boards....Ch. 7.3 - The double T-beam is fabricated by welding the...Ch. 7.3 - The double T-beam is fabricated by welding the...Ch. 7.3 - The beam is constructed from three boards....Ch. 7.3 - A beam is constructed from three boards bolted...Ch. 7.3 - The simply supported beam is built up from three...Ch. 7.3 - The simply supported beam is built up from three...Ch. 7.3 - The T-beam is constructed as shown. If each nail...Ch. 7.3 - The box beam is constructed from four boards that...Ch. 7.3 - The box beam is constructed from four boards that...Ch. 7.3 - The member consists of two plastic channel strips...Ch. 7.3 - The member consists of two plastic channel strips...Ch. 7.3 - The beam is made from four boards nailed together...Ch. 7.3 - The beam is made from three polystyrene strips...Ch. 7.5 - A shear force of V=300 kN is applied to the box...Ch. 7.5 - A shear force of V=450 kN is applied to the box...Ch. 7.5 - A shear force of V = 18 kN is applied to the box...Ch. 7.5 - A shear force of V = 18 kN is applied to the box...Ch. 7.5 - The aluminum strut is 10 mm thick and has the...Ch. 7.5 - The aluminum strut is 10 mm thick and has the...Ch. 7.5 - The beam is subjected to a shear force of V=50...Ch. 7.5 - The beam is subjected to a shear force of V=50...Ch. 7.5 - The H-beam is subjected to a shear of V=80 kN...Ch. 7.5 - The H-beam is subjected to a shear of V=80 kN...Ch. 7.5 - The built-up beam is formed by welding together...Ch. 7.5 - The assembly is subjected to a vertical shear of V...Ch. 7.5 - The box girder is subjected to a shear of V=15 kN....Ch. 7.5 - Determine the location e of the shear center,...Ch. 7.5 - Determine the location e of the shear center,...Ch. 7.5 - The beam supports a vertical shear of V=7 kip....Ch. 7.5 - The stiffened beam is constructed from plates...Ch. 7.5 - The pipe is subjected to a shear force of V=8 kip....Ch. 7.5 - Determine the location e of the shear center,...Ch. 7.5 - A thin plate of thickness t is bent to form the...Ch. 7.5 - Determine the location e of the shear center,...Ch. 7 - The beam is fabricated from four boards nailed...Ch. 7 - The T-beam is subjected to a shear of V = 150 kN....Ch. 7 - The member is subject to a shear force of V = 2...Ch. 7 - Determine the shear stress at points B and C on...Ch. 7 - Determine the maximum shear stress acting at...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Piston Area: (Q2) A cylinder applies a force of 400 pounds in extension. If the pressure in the cylinder is 39 psi what is the area of the piston in square inches? Use πon your calculator Answer with two decimals. Do not write the unit.arrow_forwardA 2D incompressible flow has velocitycomponents u= X^2 - 2y^2 and v=aX^b y^c ,where a, b, and c are numbers. Find the values of a, b, and c Find the stream functionarrow_forwardPlease can you assist with the attached question please?arrow_forward
- (a) Find a second-order homogeneous linear ODE for which the given functions are solutions. (b) Show linear independence by the Wronskian. (c) Solve the initial value problem. a. cos(5x), sin(5x), y(0) = 3, y'(0) = −5 b. e-2.5x cos(0.3x), e-2.5x sin(0.3x), y(0) = 3, y'(0) = -7.5arrow_forwardSolve the IVP. a. y" 16y 17e* ; = y(0) = 6, y'(0) = -2 b. (D² + 41)y = sin(t) + ½ sin(3t) + sin(t) ; y(0) = 0, y'(0) : = 35 31arrow_forwardFind the general solution. a. y' 5y = 3ex - 2x + 1 - b. y" +4y' + 4y = e¯*cos(x) c. (D² + I)y = cos(wt), w² # 1arrow_forward
- handwritten solutions, please!!arrow_forward> Homework 4 - Spring 2025.pdf Spring 2025.pdf k 4 - Spring 2025.pdf (447 KB) Due: Thursday, February 27 Page 1 > of 2 ZOOM 1. A simply supported shaft is shown in Figure 1 with wo = 25 N/cm and M = 20 N cm. Use singularity functions to determine the reactions at the supports. Assume EI = 1000 kN cm². M Wo 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 cm Figure 1 - Problem 1 2. A support hook was formed from a rectangular bar. Find the stresses at the inner and outer surfaces at sections just above and just below O-B. 210 mmarrow_forwardA distillation column with a total condenser and a partial reboiler is separating ethanol andwater at 1.0 atm. Feed is 0.32 mol fraction ethanol and it enters as a saturated liquid at 100mol/s on the optimum plate. The distillate product is a saturated liquid with 80 mol% ethanol.The condenser removes 5615 kW. The bottoms product is 0.05 mol fraction ethanol. AssumeCMO is valid.(a) Find the number of equilibrium stages for this separation. [6 + PR](b) Find how much larger the actual reflux ratio, R, used is than Rmin, i.e. R/Rmin. [3]Note: the heats of vaporization of ethanol and water are λe = 38.58 and λw = 40.645 arrow_forward
- We have a feed that is a binary mixture of methanol and water (60.0 mol% methanol) that issent to a system of two flash drums hooked together. The vapor from the first drum is cooled,which partially condenses the vapor, and then is fed to the second flash drum. Both drumsoperate at 1.0 atm and are adiabatic. The feed to the first drum is 1000 kmol/hr. We desire aliquid product from the first drum that is 35.0 mol% methanol. The second drum operates at afraction vaporized of (V/F)2 = 0.25.(a) Find the liquid flow rate leaving the first flash drum, L1 (kmol/hr). [286 kmol/hr](b) Find the vapor composition leaving the second flash drum, y2. [0.85]arrow_forward= The steel curved bar shown has rectangular cross-section with a radial height h = 6 mm and thickness b = 4mm. The radius of the centroidal axis is R = 80 mm. A force P = 10 N is applied as shown. Assume the steel modulus of 207,000 MPa and G = 79.3(103) MPa, repectively. elasticity and shear modulus E = Find the vertical deflection at point B. Use Castigliano's method for a curved flexural member and since R/h > 10, neglect the effect of shear and axial load, thereby assuming that deflection is due to merely the bending moment. Note the inner and outer radii of the curves bar are: r = 80 + ½ (6) = 83 mm, r₁ = 80 − ½ (6) = 77 mm 2 2 Sπ/2 sin² 0 d = √π/² cos² 0 d0 = Π 0 4 大 C R B Parrow_forwardThe steel eyebolt shown in the figure is loaded with a force F = 75 lb. The eyebolt is formed from round wire of diameter d = 0.25 in to a radius R₁ = 0.50 in in the eye and at the shank. Estimate the stresses at the inner and outer surfaces at section A-A. Notice at the section A-A: r₁ = 0.5 in, ro = 0.75 in rc = 0.5 + 0.125 = 0.625 in Ri 200 F FAarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Everything About TRANSVERSE SHEAR in 10 Minutes!! - Mechanics of Materials; Author: Less Boring Lectures;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4x0E9yvzfCM;License: Standard Youtube License