
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
10th Edition
ISBN: 9780134319650
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 7.3, Problem 7.43P
The box beam is constructed from four boards that are fastened together using nails spaced along the beam every 2 in. If each nail can resist a shear force of 50 lb, determine the largest force P that can be applied to the beam without causing failure of the nails.
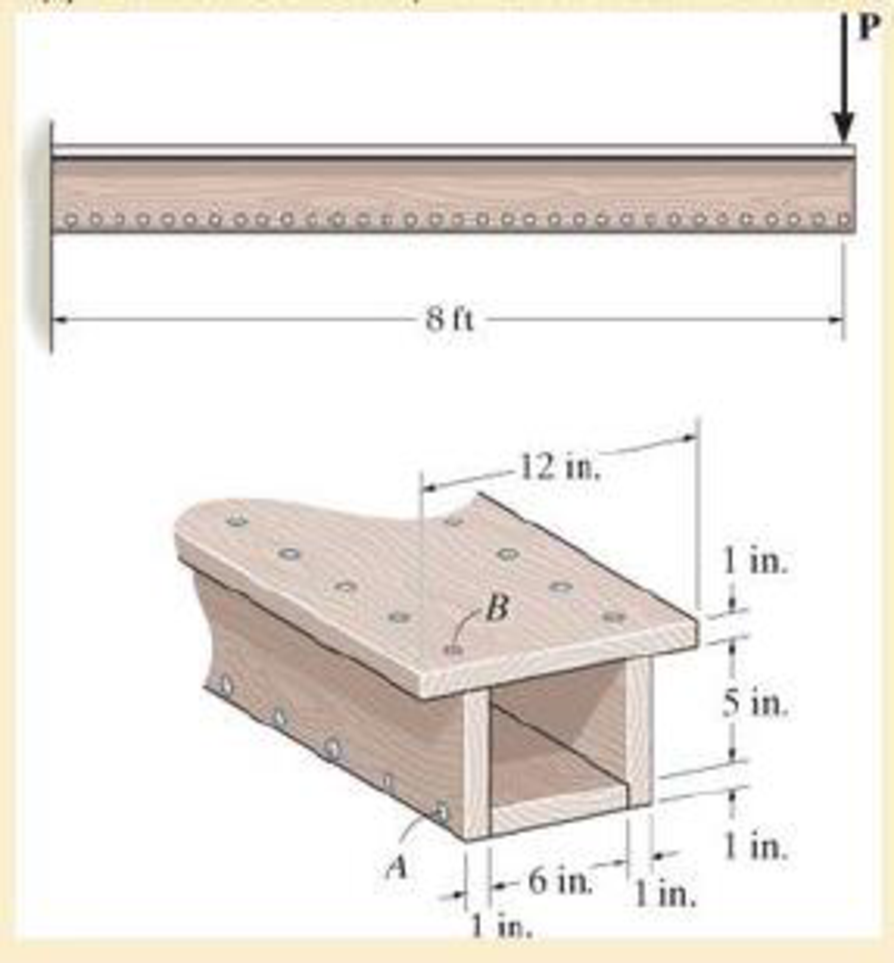
Probs. 7–43/44
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
what is heat exchanger, what are formulas, and their importance, define the diagram, and give me a script on how to explain the design of heat exchanger, and how did values end up in that number. based on standards . what is dshell
FIGURE P1.37
1.38 WP As shown in Figure P1.38, an inclined manometer is used
to measure the pressure of the gas within the reservoir, (a) Using data
on the figure, determine the gas pressure, in lbf/in.² (b) Express the
pressure as a gage or a vacuum pressure, as appropriate, in lbf/in.²
(c) What advantage does an inclined manometer have over the U-tube
manometer shown in Figure 1.7?
Patm = 14.7 lbf/in.²
L
I
C
i
Gas
a
Oil (p = 54.2 lb/ft³)
140°
8=32.2 ft/s²
15 in.
what is an low pressure Heater, what are formulas, and their importance, define the diagram, and give me a script on how to explain the design of an air preheater, and how did values end up in that number. based on standards
Chapter 7 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Ch. 7.2 - In each case, calculate the value of Q and t that...Ch. 7.2 - If the beam is subjected to a shear force of V =...Ch. 7.2 - Determine the shear stress at points A and B if...Ch. 7.2 - Determine the absolute maximum shear stress in the...Ch. 7.2 - If the beam is subjected to a shear force of V =20...Ch. 7.2 - If the beam is made from four plates and subjected...Ch. 7.2 - If the wide-flange beam is subjected to a shear of...Ch. 7.2 - If the wide-flange beam is subjected to a shear of...Ch. 7.2 - If the wide-flange beam is subjected to a shear of...Ch. 7.2 - If the beam is subjected to a shear of V = 30 kN,...
Ch. 7.2 - If the wide-flange beam is subjected to a shear of...Ch. 7.2 - The wood beam has an allowable shear stress of...Ch. 7.2 - The shaft is supported by a thrust bearing at A...Ch. 7.2 - The shaft is supported by a thrust bearing at A...Ch. 7.2 - Determine the largest shear force V that the...Ch. 7.2 - If the applied shear force V = 18 kip, determine...Ch. 7.2 - The overhang beam is subjected to the uniform...Ch. 7.2 - The beam is made from a polymer and is subjected...Ch. 7.2 - Determine the maximum shear stress in the strut if...Ch. 7.2 - Determine the maximum shear force V that the strut...Ch. 7.2 - Sketch the intensity of the shear-stress...Ch. 7.2 - Plot the shear-stress distribution over the cross...Ch. 7.2 - If the beam is subjected to a shear of V=15 kN,...Ch. 7.2 - If the wide-flange beam is subjected to a shear of...Ch. 7.2 - If the wide-flange beam is subjected to a shear of...Ch. 7.2 - Determine the length of the cantilevered beam so...Ch. 7.2 - If the beam is made from wood having an allowable...Ch. 7.2 - Determine the largest intensity w of the...Ch. 7.2 - If w=800 lb/ft, determine the absolute maximum...Ch. 7.2 - Determine the shear stress at point B on the web...Ch. 7.2 - Determine the maximum shear stress acting at...Ch. 7.2 - Railroad ties must be designed to resist large...Ch. 7.2 - The beam is slit longitudinally along both sides....Ch. 7.2 - The beam is to be cut longitudinally along both...Ch. 7.2 - The composite beam is constructed from wood and...Ch. 7.2 - The beam has a rectangular cross section and is...Ch. 7.2 - The beam in Fig.6-48f is subjected to a fully...Ch. 7.3 - The two identical boards are bolted together to...Ch. 7.3 - Two identical 20-mm-thick plates are bolted to the...Ch. 7.3 - The boards are bolted together to form the...Ch. 7.3 - The boards are bolted together to form the...Ch. 7.3 - The beam is constructed from two boards fastened...Ch. 7.3 - The beam is constructed from two boards fastened...Ch. 7.3 - The beam is constructed from three boards. If it...Ch. 7.3 - The beam is constructed from three boards....Ch. 7.3 - The double T-beam is fabricated by welding the...Ch. 7.3 - The double T-beam is fabricated by welding the...Ch. 7.3 - The beam is constructed from three boards....Ch. 7.3 - A beam is constructed from three boards bolted...Ch. 7.3 - The simply supported beam is built up from three...Ch. 7.3 - The simply supported beam is built up from three...Ch. 7.3 - The T-beam is constructed as shown. If each nail...Ch. 7.3 - The box beam is constructed from four boards that...Ch. 7.3 - The box beam is constructed from four boards that...Ch. 7.3 - The member consists of two plastic channel strips...Ch. 7.3 - The member consists of two plastic channel strips...Ch. 7.3 - The beam is made from four boards nailed together...Ch. 7.3 - The beam is made from three polystyrene strips...Ch. 7.5 - A shear force of V=300 kN is applied to the box...Ch. 7.5 - A shear force of V=450 kN is applied to the box...Ch. 7.5 - A shear force of V = 18 kN is applied to the box...Ch. 7.5 - A shear force of V = 18 kN is applied to the box...Ch. 7.5 - The aluminum strut is 10 mm thick and has the...Ch. 7.5 - The aluminum strut is 10 mm thick and has the...Ch. 7.5 - The beam is subjected to a shear force of V=50...Ch. 7.5 - The beam is subjected to a shear force of V=50...Ch. 7.5 - The H-beam is subjected to a shear of V=80 kN...Ch. 7.5 - The H-beam is subjected to a shear of V=80 kN...Ch. 7.5 - The built-up beam is formed by welding together...Ch. 7.5 - The assembly is subjected to a vertical shear of V...Ch. 7.5 - The box girder is subjected to a shear of V=15 kN....Ch. 7.5 - Determine the location e of the shear center,...Ch. 7.5 - Determine the location e of the shear center,...Ch. 7.5 - The beam supports a vertical shear of V=7 kip....Ch. 7.5 - The stiffened beam is constructed from plates...Ch. 7.5 - The pipe is subjected to a shear force of V=8 kip....Ch. 7.5 - Determine the location e of the shear center,...Ch. 7.5 - A thin plate of thickness t is bent to form the...Ch. 7.5 - Determine the location e of the shear center,...Ch. 7 - The beam is fabricated from four boards nailed...Ch. 7 - The T-beam is subjected to a shear of V = 150 kN....Ch. 7 - The member is subject to a shear force of V = 2...Ch. 7 - Determine the shear stress at points B and C on...Ch. 7 - Determine the maximum shear stress acting at...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- what is an air preheater, what are formulas, and their importance, define the diagram, and give me a script on how to explain the design of an air preheater, and how did values end up in that number. based on standardsarrow_forwardQf, Qa,Qm, Qcon,Qfg, Qbd, Qref,Qloss ( meaning, formula, percentage, and importance of higher value na qf, qa etc)arrow_forwardThe beam is supported by a fixed support at point C and a roller at point A. It also has an internal hinge at point B. The beam supports a point load at point D, a moment at point A and a distributed load on segment BC. a. calculate the support reactions at points A and C b. calculate the internal resultant loadings (N, V, M) at points E and F, which lies in the middle between points A and D P = 4 kip Ma = 5 kip-ft w1 = 3 kip/ft and w2 = 4 kip/ft a = 3 ftarrow_forward
- From the image of the pyramid, I want to find what s1 hat, s2 hat, and s3 hat are. I think s3 hat is just equal to e3 hat right? What about the others?arrow_forward(a) What kind of equation is it?(b) Is it linear or non-linear?(c) Is it a coupled system or uncoupled?arrow_forwardWhat kind of system is presented in Figure 2? Open loop or closed loop?arrow_forward
- What are the control hardware shown in the Figure?arrow_forwardQuestion 1. A tube rotates in the horizontal ry plane with a constant angular velocity w about the z-axis. A particle of mass m is released from a radial distance R when the tube is in the position shown. This problem is based on problem 3.2 in the text. R m 2R Figure 1 x a) Draw a free body diagram of the particle if the tube is frictionless. b) Draw a free body diagram of the particle if the coefficient of friction between the sides of the tube and the particle is = k = p. c) For the case where the tube is frictionless, what is the radial speed at which the particle leaves the tube? d) For the case where there is friction, derive a differential equation that would allow you to solve for the radius of the particle as a function of time. I'm only looking for the differential equation. DO NOT solve it. 1 e) If there is no friction, what is the angle of the tube when the particle exits? • Hint: You may need to solve a differential equation for the last part. The "potentially useful…arrow_forwardQuestion 2. A smooth uniform sphere of mass m and radius r is squeezed between two massless levers, each of length 1, which are inclined at an angle with the vertical. A mechanism at pivot point O ensures that the angles & remain the same at all times so that the sphere moves straight upward. This problem is based on Problem 3-1 in the text. P P r Figure 2 a) Draw appropriate freebody diagrams of the system assuming that there is no friction. b) Draw appropriate freebody diagrams of the system assuming that there is a coefficient of friction between the sphere and the right lever of μ. c) If a force P is applied between the ends of the levers (shown in the diagram), and there is no friction, what is the acceleration of the sphere when = 30°arrow_forward
- If you had a matrix A = [1 2 3; 4 5 6; 7 8 9] and a matrix B = [1 2 3], how would you cross multiply them i.e. what is the cross product of AxB. what would be the cross product of a dyadic with a vector?arrow_forwardProblem 3: The inertia matrix can be written in dyadic form which is particularly useful when inertia information is required in various vector bases. On the next page is a right rectangular pyramid of total mass m. Note the location of point Q. (a) Determine the inertia dyadic for the pyramid P, relative to point Q, i.e., 7%, for unit vectors ₁₁, 2, 3.arrow_forwardCan you solve for v? Also, what is A x uarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Mechanics of Materials Lecture: Beam Design; Author: UWMC Engineering;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-wVs5pvQPm4;License: Standard Youtube License