
University Physics with Modern Physics (14th Edition)
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780321973610
Author: Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 7.2, Problem 7.2TYU
Consider the situation in Example 7.9 at the instant when the elevator is still moving downward and the spring is compressed by 1.00 m. Which of the energy bar graphs in the figure most accurately shows the kinetic energy K. gravitational potential energy Ugrav, and elastic potential energy Uel at this instant?
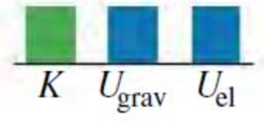
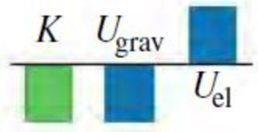
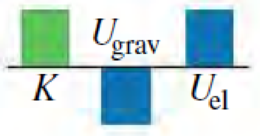
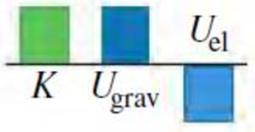
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Statistical thermodynamics. The number of imaginary replicas of a system of N particlesa) cannot be greater than Avogadro's numberb) must always be greater than Avogadro's number.c) has no relation to Avogadro's number.
Lab-Based Section
Use the following information to answer the lab based scenario.
A student performed an experiment in an attempt to determine the index of refraction of glass.
The student used a laser and a protractor to measure a variety of angles of incidence and
refraction through a semi-circular glass prism. The design of the experiment and the student's
results are shown below.
Angle of
Incidence (°)
Angle of
Refraction (º)
20
11
30
19
40
26
50
31
60
36
70
38
2a) By hand (i.e., without using computer software), create a linear graph on graph paper
using the student's data. Note: You will have to manipulate the data in order to achieve a
linear function.
2b) Graphically determine the index of refraction of the semi-circular glass prism, rounding your
answer to the nearest hundredth.
Use the following information to answer the next two questions.
A laser is directed at a prism made of zircon (n = 1.92) at an incident angle of 35.0°, as shown in
the diagram.
3a) Determine the critical angle of zircon.
35.0°
70°
55
55°
3b) Determine the angle of refraction when the laser beam leaves the prism.
Chapter 7 Solutions
University Physics with Modern Physics (14th Edition)
Ch. 7.1 - The figure shows two friction-less ramps. The...Ch. 7.2 - Consider the situation in Example 7.9 at the...Ch. 7.3 - In a hydroelectric generating station, falling...Ch. 7.4 - A particle moving along the x-axis is acted on by...Ch. 7.5 - The curve in Fig. 7.24b has a maximum at a point...Ch. 7 - A baseball is thrown straight up with initial...Ch. 7 - A projectile has the same initial kinetic energy...Ch. 7 - An object is released from rest at the top of a...Ch. 7 - An egg is released from rest from the roof of a...Ch. 7 - A physics teacher had a howling hall suspended...
Ch. 7 - Is it possible for a friction force to increase...Ch. 7 - A woman bounces on a trampoline, going a little...Ch. 7 - Fractured Physics. People often call their...Ch. 7 - (a) A book is lifted upward a vertical distance of...Ch. 7 - (a) A block of wood is pushed against a spring,...Ch. 7 - A 1.0-kg stone and a 10.0-kg stone are released...Ch. 7 - Two objects with different masses are launched...Ch. 7 - When people are cold, they often rub their hands...Ch. 7 - A box slides down a ramp and work is done on the...Ch. 7 - In physical terms, explain why friction is a...Ch. 7 - Since only changes in potential energy are...Ch. 7 - Figure 7.22a shows the potential-energy function...Ch. 7 - Figure 7.22b shows the potential-energy function...Ch. 7 - For a system of two particles we often let the...Ch. 7 - Explain why the points x = A and x = A in Fig....Ch. 7 - A particle is in neutral equilibrium if the net...Ch. 7 - The net force on a particle of mass m has the...Ch. 7 - The potential-energy function for a force F is...Ch. 7 - In one day, a 75-kg mountain climber ascends from...Ch. 7 - BIO How High Can We Jump? The maximum height a...Ch. 7 - CP A 90.0-kg mail bag hangs by a vertical rope 3.5...Ch. 7 - BIO Food Calories. The food calorie, equal to 4186...Ch. 7 - A baseball is thrown from the roof of a...Ch. 7 - A crate of mass M starts from rest at the top of a...Ch. 7 - BIO Human Energy vs. Insect Energy. For its size,...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.8ECh. 7 - Prob. 7.9ECh. 7 - A 25.0-kg child plays on a swing having support...Ch. 7 - You are testing a new amusement park roller...Ch. 7 - Tarzan and Jane. Tarzan, in one tree, sights Jane...Ch. 7 - CP A 10.0-kg microwave oven is pushed 6.00 m up...Ch. 7 - An ideal spring of negligible mass is 12.00 cm...Ch. 7 - A force of 520 N keeps a certain spring stretched...Ch. 7 - BIO Tendons. Tendons are strong elastic fibers...Ch. 7 - A spring stores potential energy U0 when it is...Ch. 7 - A slingshot will shoot a 10-g pebble 22.0 m...Ch. 7 - A spring of negligible mass has force constant k =...Ch. 7 - A 1.20-kg piece of cheese is placed on a vertical...Ch. 7 - A spring of negligible mass has force constant k =...Ch. 7 - (a) For the elevator of Example 7.9 (Section 7.2),...Ch. 7 - A 2.50-kg mass is pushed against a horizontal...Ch. 7 - A 2.50-kg block on a horizontal floor is attached...Ch. 7 - You are asked to design a spring that will give a...Ch. 7 - A 75-kg roofer climbs a vertical 7.0-m ladder to...Ch. 7 - A 0.60-kg book slides on a horizontal table. The...Ch. 7 - CALC In an experiment, one of the forces exerted...Ch. 7 - A 62.0-kg skier is moving at 6.50 m/s on a...Ch. 7 - Vector A is in the direction 34.0 clockwise from...Ch. 7 - CALC A force parallel to the .v-axis acts on a...Ch. 7 - CALC The potential energy of a pair of hydrogen...Ch. 7 - CALC A small block with mass 0.0400 kg is moving...Ch. 7 - CALC An object moving in the xy-plane is acted on...Ch. 7 - CALC The potential energy of two atoms in a...Ch. 7 - A marble moves along the x-axis. The...Ch. 7 - At a construction site, a 65.0-kg bucket of...Ch. 7 - Two blocks with different masses are attached to...Ch. 7 - A block with mass 0.50 kg is forced against a...Ch. 7 - A 2.00-kg block is pushed against a spring with...Ch. 7 - A 2.00-kg block is pushed against a spring with...Ch. 7 - CP Riding a Loop-the- Loop. A car in an amusement...Ch. 7 - A 2.0-kg piece of wood slides on a curved surface...Ch. 7 - Up and Down the Hill. A 28-kg rock approaches the...Ch. 7 - A 15.0-kg stone slides down a snow-covered hill...Ch. 7 - CP A 2.8-kg block slides over the smooth, icy hill...Ch. 7 - Bungee Jump. A bungee cord is 30.0 m long and,...Ch. 7 - You are designing a delivery ramp for crates...Ch. 7 - The Great Sandini is a 60-kg circus performer who...Ch. 7 - A 1500-kg rocket is to be launched with an initial...Ch. 7 - A system of two paint buckets connected by a...Ch. 7 - These results are from a computer simulation for a...Ch. 7 - CP A 0.300-kg potato is tied to a string with...Ch. 7 - A 60.0-kg skier starts from rest at the top of a...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.55PCh. 7 - A ball is thrown upward with an initial velocity...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.57PCh. 7 - A truck with mass m has a brake failure while...Ch. 7 - CALC A certain spring found not to obey Hookes law...Ch. 7 - CP A sled with rider having a combined mass of 125...Ch. 7 - CALC A conservative force F is in the +x-direction...Ch. 7 - A 3.00-kg block is connected to two ideal...Ch. 7 - A 0.150-kg block of ice is placed against a...Ch. 7 - If a fish is attached to a vertical spring and...Ch. 7 - CALC You are an industrial engineer with a...Ch. 7 - A basket of negligible weight hangs from a...Ch. 7 - CALC A 3.00-kg fish is attached to the lower end...Ch. 7 - You are designing an amusement park ride. A cart...Ch. 7 - A 0.500-kg block, attached to a spring with length...Ch. 7 - CP A small block with mass 0.0400 kg slides in a...Ch. 7 - CP A small block with mass 0.0500 kg slides in a...Ch. 7 - CP Pendulum. A small rock with mass 0.12 kg is...Ch. 7 - A wooden block with mass 1.50 kg is placed against...Ch. 7 - CALC A small object with mass m = 0.0900 kg moves...Ch. 7 - CALC A cutting tool under microprocessor control...Ch. 7 - A particle moves along the x-axis while acted on...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.77PCh. 7 - DATA A long ramp made of cast iron is sloped at a...Ch. 7 - DATA A single conservative force F(x) acts on a...Ch. 7 - CALC A proton with mass m moves in one dimension....Ch. 7 - BIO THE DNA SPRING. A DNA molecule, with its...Ch. 7 - BIO THE DNA SPRING. A DNA molecule, with its...Ch. 7 - BIO THE DNA SPRING. A DNA molecule, with its...Ch. 7 - BIO THE DNA SPRING. A DNA molecule, with its...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
33. Consider the reaction:
The tabulated data were collected for the concentration of C4H8 as a function...
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
MAKE CONNECTIONS Review the description of meiosis (see Figure 10.8) and Mendels laws of segregation and indepe...
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
Distinguish between microevolution, speciation, and macroevolution.
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
Pure oxygen gas can be prepared in the laboratory by the decomposition of solid potassium chlorate to form soli...
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
As genetic testing becomes widespread, medical records will contain the results of such testing. Who should hav...
Concepts of Genetics (12th Edition)
41. A hollow metal sphere has 6 cm and 10 cm inner and outer radii, respectively. The surface charge density on...
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Use the following information to answer the next two questions. A laser is directed at a prism made of zircon (n = 1.92) at an incident angle of 35.0°, as shown in the diagram. 3a) Determine the critical angle of zircon. 35.0° 70° 55 55° 3b) Determine the angle of refraction when the laser beam leaves the prism.arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardA beam of alpha-particles of energy 7.3MeV is used.The protons emitted at an angle of zero degree are found to have energy of 9.34MeV.Find the Q-value of this reaction .arrow_forward
- An aluminum rod and a copper rod have the same length of 100cm at 5C. At what temperatures would one of the rods be 0.5 mm longer than the other? Which rod is longer at such temperature?arrow_forwardROTATIONAL DYNAMICS Question 01 A solid circular cylinder and a solid spherical ball of the same mass and radius are rolling together down the same inclined. Calculate the ratio of their kinetic energy. Assume pure rolling motion Question 02 A sphere and cylinder of the same mass and radius start from ret at the same point and more down the same plane inclined at 30° to the horizontal Which body gets the bottom first and what is its acceleration b) What angle of inclination of the plane is needed to give the slower body the same acceleration Question 03 i) Define the angular velocity of a rotating body and give its SI unit A car wheel has its angular velocity changing from 2rads to 30 rads seconds. If the radius of the wheel is 400mm. calculate ii) The angular acceleration iii) The tangential linear acceleration of a point on the rim of the wheel Question 04 in 20arrow_forwardQuestion B3 Consider the following FLRW spacetime: t2 ds² = -dt² + (dx² + dy²+ dz²), t2 where t is a constant. a) State whether this universe is spatially open, closed or flat. [2 marks] b) Determine the Hubble factor H(t), and represent it in a (roughly drawn) plot as a function of time t, starting at t = 0. [3 marks] c) Taking galaxy A to be located at (x, y, z) = (0,0,0), determine the proper distance to galaxy B located at (x, y, z) = (L, 0, 0). Determine the recessional velocity of galaxy B with respect to galaxy A. d) The Friedmann equations are 2 k 8πG а 4πG + a² (p+3p). 3 a 3 [5 marks] Use these equations to determine the energy density p(t) and the pressure p(t) for the FLRW spacetime specified at the top of the page. [5 marks] e) Given the result of question B3.d, state whether the FLRW universe in question is (i) radiation-dominated, (ii) matter-dominated, (iii) cosmological-constant-dominated, or (iv) none of the previous. Justify your answer. f) [5 marks] A conformally…arrow_forward
- SECTION B Answer ONLY TWO questions in Section B [Expect to use one single-sided A4 page for each Section-B sub question.] Question B1 Consider the line element where w is a constant. ds²=-dt²+e2wt dx², a) Determine the components of the metric and of the inverse metric. [2 marks] b) Determine the Christoffel symbols. [See the Appendix of this document.] [10 marks] c) Write down the geodesic equations. [5 marks] d) Show that e2wt it is a constant of geodesic motion. [4 marks] e) Solve the geodesic equations for null geodesics. [4 marks]arrow_forwardPage 2 SECTION A Answer ALL questions in Section A [Expect to use one single-sided A4 page for each Section-A sub question.] Question A1 SPA6308 (2024) Consider Minkowski spacetime in Cartesian coordinates th = (t, x, y, z), such that ds² = dt² + dx² + dy² + dz². (a) Consider the vector with components V" = (1,-1,0,0). Determine V and V. V. (b) Consider now the coordinate system x' (u, v, y, z) such that u =t-x, v=t+x. [2 marks] Write down the line element, the metric, the Christoffel symbols and the Riemann curvature tensor in the new coordinates. [See the Appendix of this document.] [5 marks] (c) Determine V", that is, write the object in question A1.a in the coordinate system x'. Verify explicitly that V. V is invariant under the coordinate transformation. Question A2 [5 marks] Suppose that A, is a covector field, and consider the object Fv=AAμ. (a) Show explicitly that F is a tensor, that is, show that it transforms appropriately under a coordinate transformation. [5 marks] (b)…arrow_forwardHow does boiling point of water decreases as the altitude increases?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:9780534408961
Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanical work done (GCSE Physics); Author: Dr de Bruin's Classroom;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OapgRhYDMvw;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY