
Concept explainers
(b)
The null and alternative hypotheses for the consumption of proteins.
(b)
Answer to Problem 72E
Solution: The null and alternative hypotheses are formulated as
Explanation of Solution
Therefore, the hypotheses are formulated as:
In the above hypotheses
To find: The null and alternative hypotheses for the consumption of carbohydrates.
Answer to Problem 72E
Solution: The null and alternative hypotheses are formulated as
Explanation of Solution
Calculation: The significance test is to compare the two groups in terms of consumption of carbohydrates. Hence, the hypothesis is that the consumption of carbohydrates in the two groups is the same against the alternative that the consumption of carbohydrates in the two groups is not the same.
Therefore, the hypotheses are formulated as
In the above hypothesis
(c)
To find: The test statistic with the degrees of freedom and the p-value for consumption of proteins.
(c)
Answer to Problem 72E
Solution: The t – test statistic is obtained as 2.47 and p – value as 0.0144 for 199 degrees of freedom for consumption of proteins.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation: The two-sample t – test statistic for the hypothesis formulated in part (a) is defined as:
Where,
The difference of means is considered as 0 in the null hypothesis. Substitute the provided values in the above defined formula to compute the two sample t statistic. So,
The p-value for the provided one–sided test is calculated as
So, the degrees of freedom are 199. The Excel function to determine the p- value from t-test statistic is displayed in the attached screenshot,
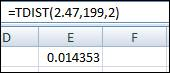
Therefore, the p-value is obtained as 0.0144.
To explain: The conclusion of the performed significance test.
Answer to Problem 72E
Solution: There is significant difference between the early eaters and late eaters in terms of consumption of proteins.
Explanation of Solution
To find: The test statistic with the degrees of freedom and the p-value for the consumption of carbohydrates.
Answer to Problem 72E
Solution: The t – test statistic is obtained as 0.29 and p – value as 0.772 for 199 degrees of freedom for carbohydrates consumption.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation: The two-sample t – test statistic for the hypothesis formulated in part (a) is defined as:
Where,
The difference of true means is considered as 0 according to the null hypothesis. Substitute the provided values in the above defined formula to compute the two sample t statistic. So,
The p-value for the provided one-sided test is calculated as
So, the degrees of freedom are 199. The Excel function to determine the p- value from t-test statistic is displayed in the attached screenshot,
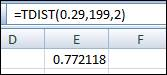
Therefore, the p-value is obtained as 0.772.
The conclusion of the performed significance test.
Answer to Problem 72E
Solution: There is no significant difference between the early eaters and late eaters in terms of consumption of carbohydrates.
Explanation of Solution
(d)
To find: A 95% confidence interval for the difference of means between early eaters and late eaters in terms of consumption of proteins.
(d)
Answer to Problem 72E
Solution: A required 95% confidence interval is
Explanation of Solution
Calculation: The formula for confidence interval for the difference between the means is defined as:
where
According to the Table D provided in the Appendix, the critical value for a two-tailed test at 95% confidence level is 1.962 for 199 degrees of freedom. Substitute the provided values in the above-defined formula to determine the 95% confidence interval for the difference between the early eaters and late eaters in terms of consumption of proteins. So,
Therefore, the 95% confidence interval for the difference between the means is obtained as
To explain: The comparison of information from the obtained confidence interval with the information given by the significance test.
Answer to Problem 72E
Solution: The information provided by both confidence interval and the significance test shows that there is a significant difference between the two means of proteins.
Explanation of Solution
To find: A 95% confidence interval for the difference of means between early eaters and late eaters in terms of consumption of carbohydrates.
Answer to Problem 72E
Solution: A required confidence interval is
Explanation of Solution
Calculation: The formula for confidence interval for the difference between the means is defined as:
where
According to the Table D provided in the Appendix, the critical value for a two-tailed test at 95% confidence level is 1.962 for 199 degrees of freedom. Substitute the provided values in the above defined formula to determine the 95% confidence interval for the difference between the early eaters and late eaters in terms of consumption of carbohydrates. So,
Interpretation: Therefore, the 95% confidence interval for the difference between the means is obtained as
To explain: The comparison of information from obtained confidence interval with the information given by the significance test.
Answer to Problem 72E
Solution: The information provided by both confidence interval and the significance test shows that there is no significant difference between the two means of carbohydrates.
Explanation of Solution
The obtained confidence interval
To explain: A short summary on the results of the performed significance test and obtained confidence intervals for three dietary compositions.
Answer to Problem 72E
Solution: From the calculated value of the test statistic from the previous exercise for the consumption of fats, the null hypothesis is not rejected and it is concluded that there is no significant difference between the consumption of fats. The obtained confidence interval
Explanation of Solution
From the calculated value of the test statistic for the consumption of proteins, the null hypothesis is rejected and it is concluded that there is a significant difference between the consumption of proteins. The obtained confidence interval
From the calculated value of the test statistic for the consumption of carbohydrates, the null hypothesis is not rejected and it is concluded that there is no significant difference between the consumption of carbohydrates. The obtained confidence interval
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
- Q.3.2 A sample of consumers was asked to name their favourite fruit. The results regarding the popularity of the different fruits are given in the following table. Type of Fruit Number of Consumers Banana 25 Apple 20 Orange 5 TOTAL 50 Draw a bar chart to graphically illustrate the results given in the table.arrow_forwardQ.2.3 The probability that a randomly selected employee of Company Z is female is 0.75. The probability that an employee of the same company works in the Production department, given that the employee is female, is 0.25. What is the probability that a randomly selected employee of the company will be female and will work in the Production department? Q.2.4 There are twelve (12) teams participating in a pub quiz. What is the probability of correctly predicting the top three teams at the end of the competition, in the correct order? Give your final answer as a fraction in its simplest form.arrow_forwardQ.2.1 A bag contains 13 red and 9 green marbles. You are asked to select two (2) marbles from the bag. The first marble selected will not be placed back into the bag. Q.2.1.1 Construct a probability tree to indicate the various possible outcomes and their probabilities (as fractions). Q.2.1.2 What is the probability that the two selected marbles will be the same colour? Q.2.2 The following contingency table gives the results of a sample survey of South African male and female respondents with regard to their preferred brand of sports watch: PREFERRED BRAND OF SPORTS WATCH Samsung Apple Garmin TOTAL No. of Females 30 100 40 170 No. of Males 75 125 80 280 TOTAL 105 225 120 450 Q.2.2.1 What is the probability of randomly selecting a respondent from the sample who prefers Garmin? Q.2.2.2 What is the probability of randomly selecting a respondent from the sample who is not female? Q.2.2.3 What is the probability of randomly…arrow_forward
- Test the claim that a student's pulse rate is different when taking a quiz than attending a regular class. The mean pulse rate difference is 2.7 with 10 students. Use a significance level of 0.005. Pulse rate difference(Quiz - Lecture) 2 -1 5 -8 1 20 15 -4 9 -12arrow_forwardThe following ordered data list shows the data speeds for cell phones used by a telephone company at an airport: A. Calculate the Measures of Central Tendency from the ungrouped data list. B. Group the data in an appropriate frequency table. C. Calculate the Measures of Central Tendency using the table in point B. D. Are there differences in the measurements obtained in A and C? Why (give at least one justified reason)? I leave the answers to A and B to resolve the remaining two. 0.8 1.4 1.8 1.9 3.2 3.6 4.5 4.5 4.6 6.2 6.5 7.7 7.9 9.9 10.2 10.3 10.9 11.1 11.1 11.6 11.8 12.0 13.1 13.5 13.7 14.1 14.2 14.7 15.0 15.1 15.5 15.8 16.0 17.5 18.2 20.2 21.1 21.5 22.2 22.4 23.1 24.5 25.7 28.5 34.6 38.5 43.0 55.6 71.3 77.8 A. Measures of Central Tendency We are to calculate: Mean, Median, Mode The data (already ordered) is: 0.8, 1.4, 1.8, 1.9, 3.2, 3.6, 4.5, 4.5, 4.6, 6.2, 6.5, 7.7, 7.9, 9.9, 10.2, 10.3, 10.9, 11.1, 11.1, 11.6, 11.8, 12.0, 13.1, 13.5, 13.7, 14.1, 14.2, 14.7, 15.0, 15.1, 15.5,…arrow_forwardPEER REPLY 1: Choose a classmate's Main Post. 1. Indicate a range of values for the independent variable (x) that is reasonable based on the data provided. 2. Explain what the predicted range of dependent values should be based on the range of independent values.arrow_forward
- In a company with 80 employees, 60 earn $10.00 per hour and 20 earn $13.00 per hour. Is this average hourly wage considered representative?arrow_forwardThe following is a list of questions answered correctly on an exam. Calculate the Measures of Central Tendency from the ungrouped data list. NUMBER OF QUESTIONS ANSWERED CORRECTLY ON AN APTITUDE EXAM 112 72 69 97 107 73 92 76 86 73 126 128 118 127 124 82 104 132 134 83 92 108 96 100 92 115 76 91 102 81 95 141 81 80 106 84 119 113 98 75 68 98 115 106 95 100 85 94 106 119arrow_forwardThe following ordered data list shows the data speeds for cell phones used by a telephone company at an airport: A. Calculate the Measures of Central Tendency using the table in point B. B. Are there differences in the measurements obtained in A and C? Why (give at least one justified reason)? 0.8 1.4 1.8 1.9 3.2 3.6 4.5 4.5 4.6 6.2 6.5 7.7 7.9 9.9 10.2 10.3 10.9 11.1 11.1 11.6 11.8 12.0 13.1 13.5 13.7 14.1 14.2 14.7 15.0 15.1 15.5 15.8 16.0 17.5 18.2 20.2 21.1 21.5 22.2 22.4 23.1 24.5 25.7 28.5 34.6 38.5 43.0 55.6 71.3 77.8arrow_forward
- In a company with 80 employees, 60 earn $10.00 per hour and 20 earn $13.00 per hour. a) Determine the average hourly wage. b) In part a), is the same answer obtained if the 60 employees have an average wage of $10.00 per hour? Prove your answer.arrow_forwardThe following ordered data list shows the data speeds for cell phones used by a telephone company at an airport: A. Calculate the Measures of Central Tendency from the ungrouped data list. B. Group the data in an appropriate frequency table. 0.8 1.4 1.8 1.9 3.2 3.6 4.5 4.5 4.6 6.2 6.5 7.7 7.9 9.9 10.2 10.3 10.9 11.1 11.1 11.6 11.8 12.0 13.1 13.5 13.7 14.1 14.2 14.7 15.0 15.1 15.5 15.8 16.0 17.5 18.2 20.2 21.1 21.5 22.2 22.4 23.1 24.5 25.7 28.5 34.6 38.5 43.0 55.6 71.3 77.8arrow_forwardBusinessarrow_forward
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman





