
(a)
Interpretation:
Stereo selectivity of the given reaction should be explained under given basic condition.
Concept Introduction:
Elimination Reaction: It is just reverse reaction of addition where substituent from the given molecule is removed via
E1 reaction is a unimolecular elimination reaction to produce
E2 reaction is a bimolecular elimination reaction in which alkene compounds formed in a single step.
Elimination of compound in presence of bulky base leads to less substituted alkene, in presence of strong base (not bulky) leads to more substituted alkene.
Stereoisomers: These types of isomers that have same molecular formula and connectivity but differ in the way of atoms are oriented space. For example the difference between two stereoisomers lies only in the three dimensional arrangement of atoms.
Stereospecific reaction: reaction undergoes from a stereoisomer to a unique stereo isomeric product.
Newman projection: Newman projection of molecule is one type of representations for the
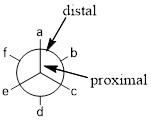
From the angle of observer the front carbon is proximal and second carbon is distal.
In wedge-dash line representation wedge is coming out of the plane and dash is going behind the plane, the wedge line and the dash line of front carbon in Newman projection are pointing up and the wedge line and the dash line of back carbon in Newman projection are pointing down.
(b)
Interpretation:
Stereo selectivity of the given reaction should be explained under given basic condition.
Concept Introduction:
Elimination Reaction: It is just reverse reaction of addition where substituent from the given molecule is removed via
E1 reaction is a unimolecular elimination reaction to produce alkene compounds in which carbocation is formed as an intermediate and it has stepwise mechanism.
E2 reaction is a bimolecular elimination reaction in which alkene compounds formed in a single step.
Elimination of compound in presence of bulky base leads to less substituted alkene, in presence of strong base (not bulky) leads to more substituted alkene.
Stereoisomers: These types of isomers that have same molecular formula and connectivity but differ in the way of atoms are oriented space. For example the difference between two stereoisomers lies only in the three dimensional arrangement of atoms.
Stereospecific reaction: reaction undergoes from a stereoisomer to a unique stereo isomeric product.
Newman projection: Newman projection of molecule is one type of representations for the alkanes, where the projection visualization from one carbon to another carbon. In this Newman projection, front carbon which represented with dot is called proximal and the back carbon which represented with circle is called distal.

From the angle of observer the front carbon is proximal and second carbon is distal.
In wedge-dash line representation wedge is coming out of the plane and dash is going behind the plane, the wedge line and the dash line of front carbon in Newman projection are pointing up and the wedge line and the dash line of back carbon in Newman projection are pointing down.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 7 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRYPKGDRL+MLCRL MDL
- The reaction Q(g) + R(g) → Z(l) is shown to be exothermic. Which of the following is true concerning the reactionarrow_forwardWhich of the following has the largest standard molar entropy, S° (298.15 K) He H2 NaCl KBr Hgarrow_forwardWhich of the following is true for a particular reaction if ∆G° is -40.0 kJ/mol at 290 K and –20.0 kJ/mol at 390 K?arrow_forward
- Choose the major product of the reaction with correct regio- and stereochemistry. Br2 H₂O O "Br Br & O 'Br OH Br 吡 O OH OH Br "OH Brarrow_forwardSelect the major product of the following reaction. & Br (CH)CONa (CH₂),COH 0 OC(CH) O &arrow_forwardDraw the products of the hydrolysis reaction between the ester molecule and water. Determine the products of the following reaction.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





