
(a)
Interpretation:
The systematic name and common name for the given set of molecules should be identified.
Concept introduction:
Systematic Name: It is a standardized name given for a chemical compound in systematic manner. Any organic molecule can be named by using IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry) rules. IUPAC name consists of three parts in major namely Prefix suffix and root word.
Prefix represents the substituent present in the molecule. It can be any alkyl group and carboxy, amino, cyano etc…
Suffix represents the substituent present in the molecule. It can be any
Root word represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton present in the organic molecule.
When a molecule consists of cyclic structure, the root word of the molecule is prefixed with cyclo.
Common Name: It is quiet opposite to systematic name which is used for branched groups.
Chirality: It refers to a Carbon atom in a molecule that contains four different substituents.
Enantiomers: they are chiral molecules whose mirror images are not superimposable.
R and S nomenclature: it is used to assign the molecule using CIP rules.
The CIP rules are as follows:
Select the chiral carbon and assign the numbers according to the decreasing
If the numbering follows clockwise direction then the molecule is termed as R and if it follows anti-clockwise direction then molecule is termed as S.
(a)
Answer to Problem 47PP
Systematic name: 2-choloropropane and the common name: iso-propylchloride.
Explanation of Solution
To identify: The systematic name and the common name for the given molecules.
Find the longest carbon chain in the given molecule and assign number accordingly so that the substituent in the molecule present in the least
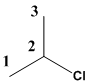
The given molecule is drawn. In the given molecule the parent carbon skeleton is 3 membered linear chain and the root name for this molecule is propane.
The carbon chain should be numbered such that the substituent present in the molecule should be given the least number in the carbon chain.
The substituent present in the molecule should be termed as chloro which is the prefix part should be written along with the number to where it is attached.
Therefore the systematic name is 2-choloropropane.
Find the common name for the given molecule by considering the position of carbon atoms attached.
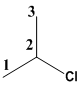
The given molecule contains two methyl groups bonded to same carbon atom in the second position and also it consists one Choloro group which should be suffixed using ide.
Therefore the common name for the given molecule is iso-propylchloride.
Conclusion
The systematic name and the common name for the given molecules are identified by using the atoms attached to the respective carbon with the help of using
(b)
Interpretation:
The systematic name and common name for the given set of molecules should be identified.
Concept introduction:
Systematic Name: It is a standardized name given for a chemical compound in systematic manner. Any organic molecule can be named by using IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry) rules. IUPAC name consists of three parts in major namely Prefix suffix and root word.
Prefix represents the substituent present in the molecule. It can be any alkyl group and carboxy, amino, cyano etc…
Suffix represents the substituent present in the molecule. It can be any alkene, alkyne, alcohol, carboxylic acid, alcohol etc...
Root word represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton present in the organic molecule.
When a molecule consists of cyclic structure, the root word of the molecule is prefixed with cyclo.
Common Name: It is quiet opposite to systematic name which is used for branched groups.
Chirality: It refers to a Carbon atom in a molecule that contains four different substituents.
Enantiomers: they are chiral molecules whose mirror images are not superimposable.
R and S nomenclature: it is used to assign the molecule using CIP rules.
The CIP rules are as follows:
Select the chiral carbon and assign the numbers according to the decreasing atomic mass of atoms attached to it.
If the numbering follows clockwise direction then the molecule is termed as R and if it follows anti-clockwise direction then molecule is termed as S.
(b)
Answer to Problem 47PP
Systematic name: 2-bromo-2-methylpropane and the common name: tert-butylbromide.
Explanation of Solution
Find the longest carbon chain in the given molecule and number it accordingly so that the substituent in the molecule present in the least numbered carbon atoms.
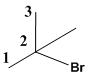
The given molecule is drawn. In the given molecule the parent carbon skeleton is 3 membered linear chain and the root name for this molecule should be termed as propane.
The carbon chain should be numbered such that the substituent present in the molecule should given the least number in the carbon chain.
The substituents Br and CH3 present in the molecule should be termed as bromo and methyl respectively according to their alphabetical order which is the prefix part should be written along with the number to which position it is attached.
Therefore the systematic name is 2-bromo-2-methylpropane.
Find the common name for the given molecule. By considering the number of carbon atoms attached.
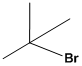
It contains
Therefore the common name for the given molecule is tert-butylbromide.
Conclusion
The systematic name and the common name for the given molecules are identified by using the atoms attached to the respective carbon with the help of using IUPAC nomenclature rules and R,S- configurations.
(c)
Interpretation:
The systematic name and common name for the given set of molecules should be identified.
Concept introduction:
Systematic Name: It is a standardized name given for a chemical compound in systematic manner. Any organic molecule can be named by using IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry) rules. IUPAC name consists of three parts in major namely Prefix suffix and root word.
Prefix represents the substituent present in the molecule. It can be any alkyl group and carboxy, amino, cyano etc…
Suffix represents the substituent present in the molecule. It can be any alkene, alkyne, alcohol, carboxylic acid, alcohol etc...
Root word represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton present in the organic molecule.
When a molecule consists of cyclic structure, the root word of the molecule is prefixed with cyclo.
Common Name: It is quiet opposite to systematic name which is used for branched groups.
Chirality: It refers to a Carbon atom in a molecule that contains four different substituents.
Enantiomers: they are chiral molecules whose mirror images are not superimposable.
R and S nomenclature: it is used to assign the molecule using CIP rules.
The CIP rules are as follows:
Select the chiral carbon and assign the numbers according to the decreasing atomic mass of atoms attached to it.
If the numbering follows clockwise direction then the molecule is termed as R and if it follows anti-clockwise direction then molecule is termed as S.
(c)
Answer to Problem 47PP
Systematic name: 1-iodopropane and the common name: propyl iodide.
Explanation of Solution
Find the longest carbon chain in the given molecule and number it accordingly so that the substituent in the molecule present in the least numbered carbon atoms.
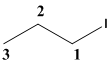
The given molecule is drawn. In the given molecule the parent carbon skeleton is 3 membered linear chain and the root name for this molecule should be termed as propane.
The carbon chain should be numbered such that the substituent present in the molecule should be given the least number in the carbon chain.
The substituent I present in the molecule should be termed as iodo which is the prefix part should be written along with the number to which it is attached.
Therefore the systematic name for the given molecule is 1-iodopropane.
Find the common name for the given molecule.

It is termed as propyl since it contains –CH2CH2CH3 and also it contains one iodine group which should be suffixed using ide.
Therefore the common name for the given molecule is propyl-iodide.
Conclusion
The systematic name and the common name for the given molecules are identified by using the atoms attached to the respective carbon with the help of using IUPAC nomenclature rules and R,S- configurations.
(d)
Interpretation:
The systematic name and common name for the given set of molecules should be identified.
Concept introduction:
Systematic Name: It is a standardized name given for a chemical compound in systematic manner. Any organic molecule can be named by using IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry) rules. IUPAC name consists of three parts in major namely Prefix suffix and root word.
Prefix represents the substituent present in the molecule. It can be any alkyl group and carboxy, amino, cyano etc…
Suffix represents the substituent present in the molecule. It can be any alkene, alkyne, alcohol, carboxylic acid, alcohol etc...
Root word represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton present in the organic molecule.
When a molecule consists of cyclic structure, the root word of the molecule is prefixed with cyclo.
Common Name: It is quiet opposite to systematic name which is used for branched groups.
Chirality: It refers to a Carbon atom in a molecule that contains four different substituents.
Enantiomers: they are chiral molecules whose mirror images are not superimposable.
R and S nomenclature: it is used to assign the molecule using CIP rules.
The CIP rules are as follows:
Select the chiral carbon and assign the numbers according to the decreasing atomic mass of atoms attached to it.
If the numbering follows clockwise direction then the molecule is termed as R and if it follows anti-clockwise direction then molecule is termed as S.
(d)
Answer to Problem 47PP
Systematic name: (R)-2-bromobutane and the common name: (R)-sec-butyl bromide.
Explanation of Solution
Find the longest carbon chain in the given molecule and number it accordingly so that the substituent in the molecule present in the least numbered carbon atoms.
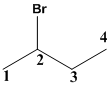
The given molecule is drawn. In the given molecule the parent carbon skeleton is 4 membered linear chain and the root name for this molecule should be termed as butane.
The substituent
This molecule contains chiral carbon so the atoms around the carbon atoms are numbered and the numbering results in clockwise direction termed as R which is to be placed in first part of the name.
Therefore the systematic name for the given molecule is (R)-2-bromobutane.
Find the common name for the given molecule.
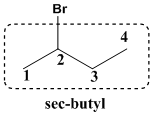
It is termed as sec-butyl since it contains
This molecule contains one chiral carbon so the atoms around the carbon atoms are numbered and the numbering results in clockwise direction termed as R which is to be placed in first part of the name.
Therefore the common name for the given molecule is (R)-sec-butylbromide.
Conclusion
The systematic name and the common name for the given molecules are identified by using the atoms attached to the respective carbon with the help of using IUPAC nomenclature rules and R,S- configurations.
(e)
Interpretation:
The systematic name and common name for the given set of molecules should be identified.
Concept introduction:
Systematic Name: It is a standardized name given for a chemical compound in systematic manner. Any organic molecule can be named by using IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry) rules. IUPAC name consists of three parts in major namely Prefix suffix and root word.
Prefix represents the substituent present in the molecule. It can be any alkyl group and carboxy, amino, cyano etc…
Suffix represents the substituent present in the molecule. It can be any alkene, alkyne, alcohol, carboxylic acid, alcohol etc...
Root word represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton present in the organic molecule.
When a molecule consists of cyclic structure, the root word of the molecule is prefixed with cyclo.
Common Name: It is quiet opposite to systematic name which is used for branched groups.
Chirality: It refers to a Carbon atom in a molecule that contains four different substituents.
Enantiomers: they are chiral molecules whose mirror images are not superimposable.
R and S nomenclature: it is used to assign the molecule using CIP rules.
The CIP rules are as follows:
Select the chiral carbon and assign the numbers according to the decreasing atomic mass of atoms attached to it.
If the numbering follows clockwise direction then the molecule is termed as R and if it follows anti-clockwise direction then molecule is termed as S.
(e)
Answer to Problem 47PP
Systematic name: 1-choloro-2, 2-dimethylpropane and the common name: neo-pentylchloride.
Explanation of Solution
Find the longest carbon chain in the given molecule and number it accordingly so that the substituent in the molecule present in the least numbered carbon atoms.
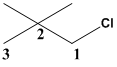
The given molecule is drawn.
In the given molecule the parent carbon skeleton is 3 membered linear chain and the root name for this molecule should be termed as propane.
The substituents Cl and two methyl groups present in the molecule should be termed as chloro and dimethyl respectively according to their alphabetical order which serves as the prefix part should be written along with the number to where it is attached.
Therefore the systematic name for the given molecule is 1-choloro-2,2dimethylpropane.
Find the common name for the given molecule.

It is termed as neo-pentyl since it is doubly branched and contains five carbon atoms. The substituent
Therefore the common name for the given molecule is neo-pentylchloride.
Conclusion
The systematic name and the common name for the given molecules are identified by using the atoms attached to the respective carbon with the help of using IUPAC nomenclature rules and R,S- configurations.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRYPKGDRL+MLCRL MDL
- Provide the semi-developed formula of isooxazole obtained by reacting acetylacetone and hydroxylamine.arrow_forwardGiven a 1,3-dicarbonyl compound (R1-CO-CH2-CO-R2), indicate the formula of the compound obtaineda) if I add hydroxylamine (NH2OH) to give an isooxazole.b) if I add thiosemicarbazide (NH2-CO-NH-NH2) to give an isothiazole.arrow_forwardAn orange laser has a wavelength of 610 nm. What is the energy of this light?arrow_forward
- The molar absorptivity of a protein in water at 280 nm can be estimated within ~5-10% from its content of the amino acids tyrosine and tryptophan and from the number of disulfide linkages (R-S-S-R) between cysteine residues: Ε280 nm (M-1 cm-1) ≈ 5500 nTrp + 1490 nTyr + 125 nS-S where nTrp is the number of tryptophans, nTyr is the number of tyrosines, and nS-S is the number of disulfide linkages. The protein human serum transferrin has 678 amino acids including 8 tryptophans, 26 tyrosines, and 19 disulfide linkages. The molecular mass of the most dominant for is 79550. Predict the molar absorptivity of transferrin. Predict the absorbance of a solution that’s 1.000 g/L transferrin in a 1.000-cm-pathlength cuvet. Estimate the g/L of a transferrin solution with an absorbance of 1.50 at 280 nm.arrow_forwardIn GC, what order will the following molecules elute from the column? CH3OCH3, CH3CH2OH, C3H8, C4H10arrow_forwardBeer’s Law is A = εbc, where A is absorbance, ε is the molar absorptivity (which is specific to the compound and wavelength in the measurement), and c is concentration. The absorbance of a 2.31 × 10-5 M solution of a compound is 0.822 at a wavelength of 266 nm in a 1.00-cm cell. Calculate the molar absorptivity at 266 nm.arrow_forward
- How to calculate % of unknown solution using line of best fit y=0.1227x + 0.0292 (y=2.244)arrow_forwardGiven a 1,3-dicarbonyl compound, state the (condensed) formula of the compound obtaineda) if I add hydroxylamine (NH2OH) to give an isooxazole.b) if I add thiosemicarbazide (NH2-CO-NH-NH2) to give an isothiazole.arrow_forwardComplete the following acid-base reactions and predict the direction of equilibrium for each. Justify your prediction by citing pK values for the acid and conjugate acid in each equilibrium. (a) (b) NHs (c) O₂N NH NH OH H₁PO₁arrow_forward
- 23.34 Show how to convert each starting material into isobutylamine in good yield. ཅ ནད ཀྱི (b) Br OEt (c) (d) (e) (f) Harrow_forwardPlease help me Please use https://app.molview.com/ to draw this. I tried, but I couldn't figure out how to do it.arrow_forwardPropose a synthesis of 1-butanamine from the following: (a) a chloroalkane of three carbons (b) a chloroalkane of four carbonsarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





