
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The structure of all products formed in the given reaction is to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
The compounds which have same molecular formula but different connectivity of atoms are known as constitutional isomers. Chiral compounds are those compounds which contain an asymmetric carbon atom. Chiral molecules are optically active molecules. Stereocentre can be an atom, bond, or any point in molecule at which interchange of two groups form a stereoisomer.
Answer:
(1) The structures of all products formed in the given reactions are shown below.
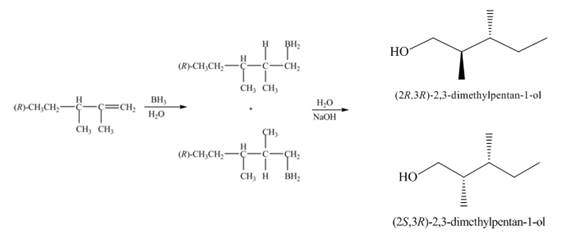
(2) The structures of all products formed in the given reactions are shown below.
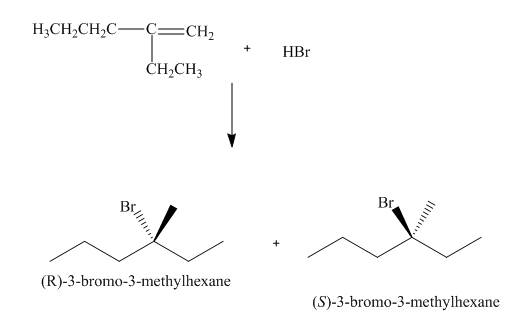
(3) The structures of all products formed in the given reactions are shown below.
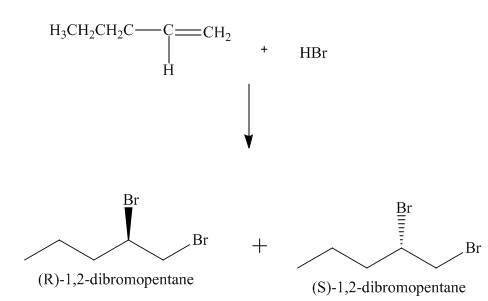
(4) The structures of all products formed in the given reactions are shown below.
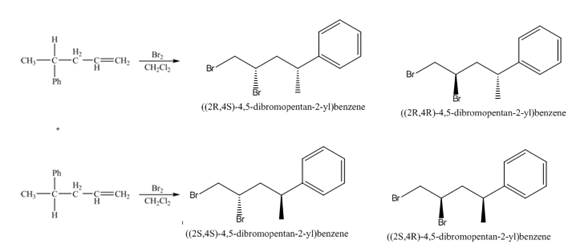
(5) The structures of all products formed in the given reactions are shown below.
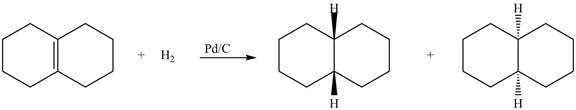
(6) The structures of all products formed in the given reactions are shown below.
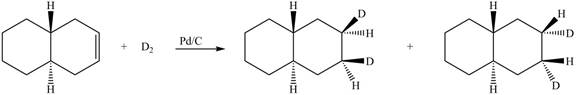
Explanation:
(1) The
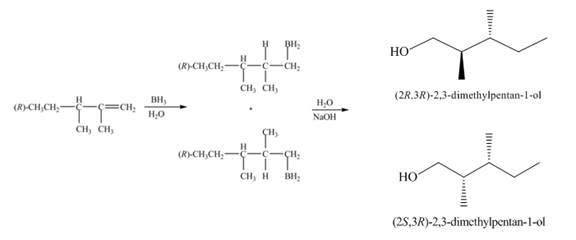
Figure 1
(2) The electrophilic addition of hydrogen bromide takes place on the carbon-carbon double bond of the alkene. The addition follows markonikov’s rule, the hydrogen atom goes to the less substituted carbon atom. The products formed in the given reaction are shown below.

Figure 2
(3) The addition reaction of bromine on the alkene takes place. The addition of bromine on alkene is anti addition. The cyclic bromonium ion intermediate is formed in the reaction. The product formed in the given reaction is shown below.

Figure 3
(4) The addition reaction of bromine on the alkene takes place. The addition of bromine on alkene is anti addition. The cyclic bromonium ion intermediate is formed in the reaction. The product formed in the given reaction is shown below.
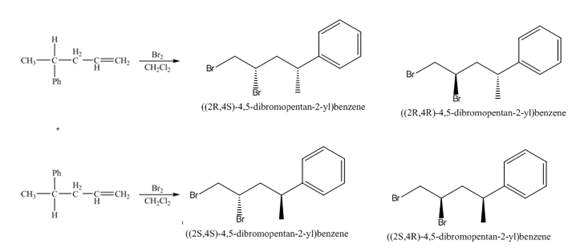
Figure 4
(5) In the reduction reaction of alkene in presence of palladium metal the hydrogen gets adsorbed on the metal surface. Alkene reduction to form
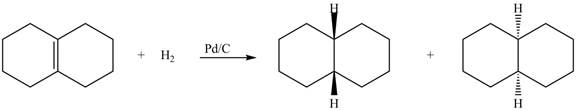
Figure 5
(6) In the reduction reaction of alkene in presence of palladium metal,
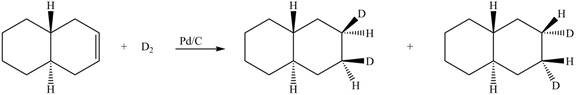
Figure 6
Conclusion:
The products formed in the given reactions are shown in Figure 1, Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5 and Figure 6.
Answer to Problem 7.42AP
(1) The structures of all products formed in the given reactions are shown below.

(2) The structures of all products formed in the given reactions are shown below.

(3) The structures of all products formed in the given reactions are shown below.

(4) The structures of all products formed in the given reactions are shown below.

(5) The structures of all products formed in the given reactions are shown below.

(6) The structures of all products formed in the given reactions are shown below.

Explanation of Solution
(1) The alkene undergoes hydroboration-oxidation reaction to form alcohol compounds. The borane gets added to the double bond. Then it will undergo oxidation reaction to form the alcohol compound. The products formed in the given reaction are shown below.

Figure 1
(2) The electrophilic addition of hydrogen bromide takes place on the carbon-carbon double bond of the alkene. The addition follows markonikov’s rule, the hydrogen atom goes to the less substituted carbon atom. The products formed in the given reaction are shown below.

Figure 2
(3) The addition reaction of bromine on the alkene takes place. The addition of bromine on alkene is anti addition. The cyclic bromonium ion intermediate is formed in the reaction. The product formed in the given reaction is shown below.

Figure 3
(4) The addition reaction of bromine on the alkene takes place. The addition of bromine on alkene is anti addition. The cyclic bromonium ion intermediate is formed in the reaction. The product formed in the given reaction is shown below.

Figure 4
(5) In the reduction reaction of alkene in presence of palladium metal the hydrogen gets adsorbed on the metal surface. Alkene reduction to form alkane takes place forming syn addition product. The products formed in the given reaction are shown below.

Figure 5
(6) In the reduction reaction of alkene in presence of palladium metal,

Figure 6
The products formed in the given reactions are shown in Figure 1, Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5 and Figure 6.
(b)
Interpretation:
The stereochemical relationship between products formed is to be stated.
Concept Introduction:
Stereoisomers which are non-superimposable and not mirror image are known as diastereomer. The compound must contain two or more than two stereocentre. Diastereomer are non identical stereoisomers. The pair of stereoisomer which are mirror image of each other are known as enantiomers. Enantiomers are non-congruent mirror images. If the molecules are placed on top of each other they will not give same molecule.
Answer to Problem 7.42AP
(1) The products formed are diastereomers.
(2) The products formed are enantiomers.
(3) The products formed are enantiomers.
(4) The two pairs of products formed are diastereomers.
(5) Only one product is formed.
(6) Only one product is formed.
Explanation of Solution
(1) The products formed are non-congruent and not mirror image of each other. Hence they are diastereomers.
(2) The products formed are non-congruent mirror image of each other. Therefore, they are enantiomers.
(3) The products formed are non-congruent mirror image of each other. Therefore, they are enantiomers.
(4) The products formed are non-congruent and not mirror image of each other. Hence they are diastereomers.
(5) Only one product is formed.
(6) Only one product is formed.
The stereochemical relationship between products formed in reaction (1) and (4) are diastereomers and reaction (2) and (3) are enantiomers.
(c)
Interpretation:
The products are formed in identical or different amount is to be stated.
Concept Introduction:
The electrophilic addition reaction on the alkene can takes place from any side of alkene. The electrophile can attack the carbon double bond from above or below the plane. The probability of attack from both sides is equal.
Answer to Problem 7.42AP
(1) The products are formed in equal amount.
(2) The products are formed in equal amount.
(3) The products are formed in equal amount.
(4) The products are formed in equal amount.
(5) Only one product is formed.
(6) Only one product is formed.
Explanation of Solution
(1) The alkene is a planar molecule. The reaction on the carbon-carbon double bond of alkene can takes place from above or below the plane. Therefore, products are formed in equal amount.
(2) The alkene is a planar molecule. The reaction on the carbon-carbon double bond of alkene can takes place from above or below the plane. Therefore, products are formed in equal amount.
(3) The alkene is a planar molecule. The reaction on the carbon-carbon double bond of alkene can takes place from above or below the plane. Therefore, products are formed in equal amount.
(4) The alkene is a planar molecule. The reaction on the carbon-carbon double bond of alkene can takes place from above or below the plane. Therefore, products are formed in equal amount.
(5) Only one product is formed.
(6) Only one product is formed.
The products are formed in equal amount in reaction (1), (2), (3), (4) and only one product is formed in reaction (5) and (6).
(d)
Interpretation:
The products which have different physical properties is to be stated.
Concept Introduction:
Stereoisomers which are non-superimposable and not mirror image are known as diastereomer. The compound must contain two or more than two stereocentre. Diastereomer are non identical stereoisomers. The pair of stereoisomer which are mirror image of each other are known as enantiomers. Enantiomers are non-congruent mirror images. Diastereomers shows different physical properties and enantiomers show same physical properties.
Answer to Problem 7.42AP
(1) The products formed in the given reaction will have different physical properties.
(2) The products formed in the given reaction will have identical physical properties.
(3) The products formed in the given reaction will have identical physical properties.
(4) The products formed in the given reaction will have different physical properties.
(5) Only one product is formed.
(6) Only one product is formed.
Explanation of Solution
(1) The products formed in the given reaction are diastereomer. Diastereomers show different physical properties. Therefore, the products formed in the given reaction will have different physical properties.
(2) The products formed in the given reaction are enantiomers. Enantiomers show identical physical properties. Therefore, the products formed in the given reaction will have identical physical properties.
(3) The products formed in the given reaction are enantiomers. Enantiomers show identical physical properties. Therefore, the products formed in the given reaction will have identical physical properties.
(4) The products formed in the given reaction are diastereomer. Diastereomers show different physical properties. Therefore, the products formed in the given reaction will have different physical properties.
(5) Only one product is formed.
(6) Only one product is formed.
The products formed in the reaction (1) and reaction (4) will have different physical properties. The products formed in the reaction (2) and reaction (3) will have identical physical properties. In reaction (5) and (6) only one product is formed.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Indicate the products obtained by reacting fluorobenzene with a sulfonitric mixture.arrow_forwardIf I have 1-bromopropene, to obtain compound A, I have to add NaOH and another compound. Indicate which compound that would be. C6H5 CH3arrow_forwardIf I have 1-bromopropene and I want to obtain (1,1-dipropoxyethyl)benzene, indicate the compound that I should add in addition to NaOH.arrow_forward
- Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Ο HSCH2CH2CH2SH, BF3 Select to Draw I Submitarrow_forwardFeedback (7/10) Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Assume that the water side product is continuously removed to drive the reaction toward products. Incorrect, 3 attempts remaining Ο (CH3CH2)2NH, TSOH Select to Draw V N. 87% Retryarrow_forwardIf I want to obtain (1,1-dipropoxyethyl)benzene from 1-bromopropene, indicate the product that I have to add in addition to NaOH.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained when fluorobenzene reacts with a sulfonitric acid mixture (HNO3 + H2SO4). Indicate the majority if necessary.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained when chlorobenzene acid reacts with a sulfonitric acid mixture (HNO3 + H2SO4). Indicate the majority if necessary.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by reacting benzenesulfonic acid with a sulfonitric acid mixture (HNO3 + H2SO4). Indicate the majority if necessary.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





