
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
A model of chair cyclohexane corresponding to the leftmost model in the given figure is to be drawn. The two reasons corresponding to the fact that the half-chair conformation is less stable than the chair or twist-boat conformation is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
The conformation of cyclohexane is a type of
Answer to Problem 7.1P
A model of chair cyclohexane corresponding to the leftmost model in the given figure is shown below.
The half-chair conformation is less stable than the chair or twist-boat conformation because half-chair conformation has maximum ring strain and the presence of angle strain in half-chair conformation of cyclohexane molecule.
Explanation of Solution
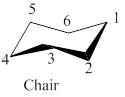
The given leftmost figure of chair conformation of cyclohexane is shown as,
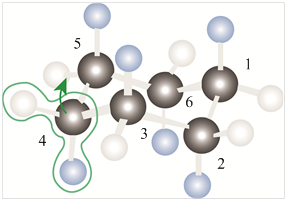
Figure 1
The model of chair conformation of cyclohexane corresponding to the leftmost model is shown as,
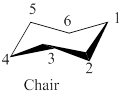
Figure 2
If the carbon-4 in order to locate carbons 2-5 in a common plane then the above model chair conformation of cyclohexane is shown as,
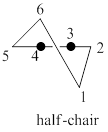
Figure 3
Thus, the raising of carbon-4 in order to locate carbons 2-5 in a common plane forms the half-chair conformation of cyclohexane molecule. This half-chair conformation of cyclohexane molecule is a transition state for the conversion into the chair and twist boat conformations.
The two reasons which explain that the half-chair conformation is less stable than the chair or twist-boat conformation are as follows.
• The ring strain in half chair conformation is more as compared to the chair or twist-boat conformation.
• The angle strain of
A model of chair cyclohexane corresponding to the leftmost model in the given figure has been shown above. The two reasons corresponding to the fact that the half-chair conformation is less stable than the chair or twist-boat conformations has been stated above.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- What is the product of the reaction? F3C. CF3 OMe NaOH / H₂Oarrow_forwardWhat would you expect to be the major product obtained from the following reaction? Please explain what is happening here. Provide a detailed explanation and a drawing showing how the reaction occurs. The correct answer to this question is V.arrow_forwardPlease answer the question for the reactions, thank youarrow_forward
- What is the product of the following reaction? Please include a detailed explanation of what is happening in this question. Include a drawing showing how the reagent is reacting with the catalyst to produce the correct product. The correct answer is IV.arrow_forwardPlease complete the reactions, thank youarrow_forwardConsider the synthesis. What is compound Y? Please explain what is happening in this question. Provide a detailed explanation and a drawing to show how the compound Y creates the product. The correct answer is D.arrow_forward
- What would be the major product of the following reaction? Please include a detailed explanation of what is happening in this question. Include steps and a drawing to show this reaction proceeds and how the final product is formed. The correct answer is B. I put answer D and I don't really understand what is going on in the question.arrow_forwardWhat is the product of the following reaction? Please explain what is happening in this question. Provide a detailed explanation and a drawing showing how the reagent is reacting with the catalysts to product the correct product. The correct answer is B.arrow_forwardWhat is the missing intermediate 1 and the final product 2. Please include a detailed explanation explaining the steps of malonic ester synthesis. Please include drawings of the intermediate and how it occurs and how the final product is former.arrow_forward
- What would be the reagents and conditions above and below the arrow that will complete the proposed acetoacetic ester synthesis? If it cannot be done efficiently, then I will choose that answer. There could be 2 or 4 reagents involved. Please provide a detailed explanation and drawings showing how it would proceed with the correct reagents.arrow_forwardFor benzene, the ∆H° of vaporization is 30.72 kJ/mol and the ∆S° of vaporization is 86.97 J/mol・K. At 1.00 atm and 228.0 K, what is the ∆G° of vaporization for benzene, in kJ/mol?arrow_forwardThe reaction Q(g) + R(g) → Z(l) is shown to be exothermic. Which of the following is true concerning the reaction. it is spontaneous only at High T, it is spontaneous at low T it is nonspontaneous at all T it is spontanrous at all T. it is non spontaneous only at low T.arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
