
Interpretation:
An equation that relates λ1 to λ2 and λ3 in which an electron in an excited state in a hydrogen atom can return to the ground state either by direct transition or by an intermediate excited state should be derived.
Concept Introduction:
A wave is a disturbance or variation that travels through a medium transporting energy without transporting matter. The wavelength is the distance between identical points on successive waves. The frequency is the number of waves that pass through any particular point in 1 second.
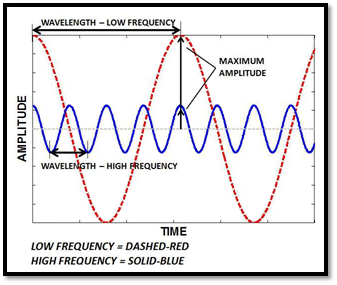
Figure 1
The speed, wavelength and frequency of a wave are related by the equation: c = λν where λ and ν are expressed in meters (m) and reciprocal seconds (s−1) respectively. Hence, rearranging the equation for getting frequency is
ν = cλ
Planck’s quantum theory
- 1. Different atoms and molecules can emit or absorb energy in discreet quantities only. The smallest amount of energy that can be emitted or absorbed in the form of electromagnetic radiation is known as quantum.
- 2. The energy of the radiation absorbed or emitted is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation. The energy of radiation is expressed in terms of frequency as,
E = hν
Where,
E = energy of the radiation
h = Planck’s constant (6.626 × 10–34 Js)
ν = Frequency of radiation
Substituting the frequency formula in this equation,
E = hcλ
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 7 Solutions
EBK GENERAL CHEMISTRY: THE ESSENTIAL CO
- From the following reduction potentials I2 (s) + 2e- = 2I- (aq) E0= 0.535 V I2 (aq) + 2e- = 2I- (aq) E0= 0.620 V I3- (aq) + 2e- = 3I- (aq) E0= 0.535 V a) Calculate the equilibrium constant for I2 (aq) + I- (aq) = I3- (aq). b) Calculate the equilibrium constant for I2 (s) + I- (aq) = I3- (aq). c) Calculate the solubility of I2 (s) in water.arrow_forward2. (3 pts) Consider the unit cell for the spinel compound, CrFe204. How many total particles are in the unit cell? Also, show how the number of particles and their positions are consistent with the CrFe204 stoichiometry - this may or may not be reflected by the particle colors in the diagram. (HINT: In the diagram, the blue particle is in an interior position while each red particle is either in a corner or face position.)arrow_forwardFrom the following potentials, calculate the activity of Cl- in saturated KCl. E0 (calomel electrode)= 0.268 V E (calomel electrode, saturated KCl)= 0.241 Varrow_forward
- Calculate the voltage of each of the following cells. a) Fe(s)/Fe2+ (1.55 x 10-2 M)//Cu2+ (6.55 x 10-3 M)/Cu(s) b) Pt, H2 (0.255 bar)/HCl (4.55 x 10-4 M), AgCl (sat'd)/Ag Fe2+ +2e- = Fe E0= -0.44 V Cu2+ + 2e- = Cu E0= 0.337 V Ag+ + e- = Ag E0= 0.799 V AgCl(s) + e- = Ag(s) + Cl- E0= 0.222 V 2H+ + 2e- = H2 E0= 0.000 Varrow_forwardA solution contains 0.097 M Ce3+, 1.55x10-3 M Ce4+, 1.55x10-3 M Mn2+, 0.097 M MnO4-, and 1.00 M HClO4 (F= 9.649 x 104 C/mol). a) Write a balanced net reaction that can occur between species in this solution. b) Calculate deltaG0 and K for the reaction. c) Calculate E and deltaG for the conditions given. Ce4+ + e- = Ce3+ E0= 1.70 V MnO4- + 8H+ + 5e- = Mn2+ + 4H2O E0= 1.507 Varrow_forward1. Provide a step-by-step mechanism for formation of ALL STEREOISOMERS in the following reaction. Na HCO3 (Sodium bicarbonate, baking soda) is not soluble in CH2Cl2. The powder is a weak base used to neutralize strong acid (pKa < 0) produced by the reaction. Redraw the product to show the configuration(s) that form at C-2 and C-4. Br2 OH CH2Cl2 Na* HCO3 Br HO OH + Na Br +arrow_forward
- 2. Specify the solvent and reagent(s) required to carry out each of the following FGI. If two reagent sets must be used for the FGI, specify the solvent and reagent(s) for each reagent set. If a reaction cannot be carried out with reagents (sets) class, write NP (not possible) in the solvent box for reagent set #1. Use the letter abbreviation for each solvent; use a number abbreviation for reagent(s). Solvents: CH2Cl2 (A); H₂O (B); Reagents: HBr (1); R₂BH (6); H2SO4 (2); CH3OH (C); Br₂ (3); CH3CO₂H (D) NaHCO3 (4); Hg(OAc)2 (5); H₂O2/HO (7); NaBH4 (8) Reagent Set #1 Reagent Set #2 FGI + enant OH Solvent Reagent(s) Solvent Reagent(s)arrow_forwardGermanium (Ge) is a semiconductor with a bandgap of 2.2 eV. How could you dope Ge to make it a p-type semiconductor with a larger bandgap? Group of answer choices It is impossible to dope Ge and have this result in a larger bandgap. Dope the Ge with silicon (Si) Dope the Ge with gallium (Ga) Dope the Ge with phosphorus (P)arrow_forwardWhich of the following semiconductors would you choose to have photons with the longest possible wavelengths be able to promote electrons to the semiconductor's conduction band? Group of answer choices Si Ge InSb CdSarrow_forward
- Which of the following metals is the only one with all of its bands completely full? Group of answer choices K Na Ca Alarrow_forward2. Specify the solvent and reagent(s) required to carry out each of the following FGI. If two reagent sets must be used for the FGI, specify the solvent and reagent(s) for each reagent set. If a reaction cannot be carried out with reagents (sets) class, write NP (not possible) in the solvent box for reagent set #1. Use the letter abbreviation for each solvent; use a number abbreviation for reagent(s). Solvents: CH2Cl2 (A); Reagents: H₂O (B); CH3CO₂H (D) NaHCO3 (4); Hg(OAc)2 (5); HBr (1); R₂BH (6); H2SO4 (2); CH3OH (C); Br₂ (3); H₂O₂ / HO- (7); NaBH4 (8) Reagent Set #1 Reagent Set #2 FGI OH - α-α Br + enant Solvent Reagent(s) Solvent Reagent(s)arrow_forwardBased on concepts from Lecture 3-5, which of the following ionic compounds should be most soluble in water? Group of answer choices MgO BeO CaO BaOarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





