
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The equilibrium picture of 10 molecules of HA and HCl acid in their two separate aqueous solutions needs to be drawn.
Concept Introduction: An acid is the substance that gives H+ or
On the contrary, a weak acid ionized partially and reaches to equilibrium.
(a)
Answer to Problem 6DQ
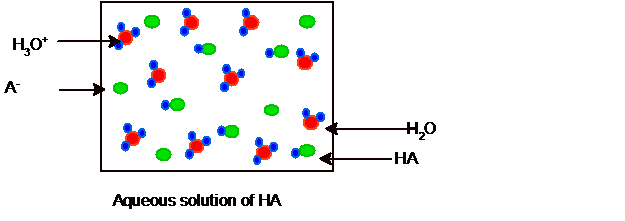
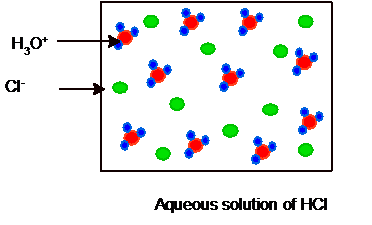
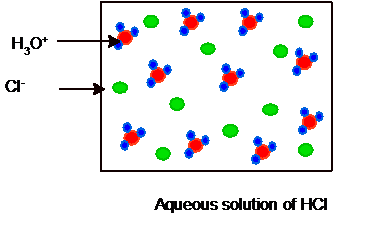
Explanation of Solution
HA is weak acid and HCl is a strong acid. For a weak acid HA, the ionization reaction can be written as:
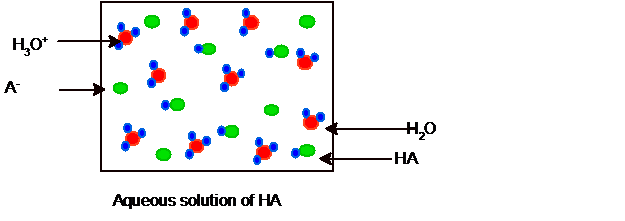
Since it is partial ionization hence some molecules of HCl and water must be present in the solution and the picture of equilibrium can be shown as:
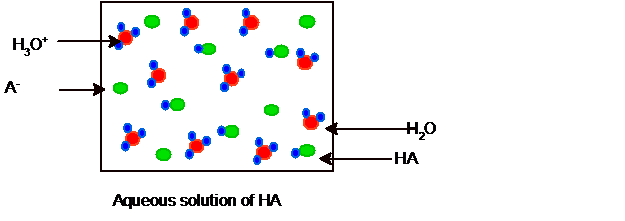 Whereas HCl is a strong acid so it will ionize completely as given below. Hence no HCl and water molecules must be present in the solution.
Whereas HCl is a strong acid so it will ionize completely as given below. Hence no HCl and water molecules must be present in the solution.
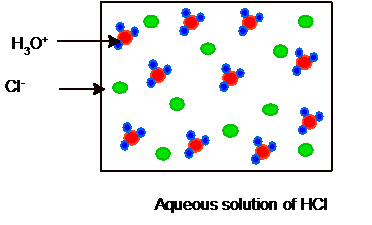
Hence the picture of equilibrium can be shown as:
(b)
Interpretation: The major species in the two separate aqueous solution of HA and HCl acid needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction: An acid is the substance that gives H+ or
On the contrary, a weak acid ionized partially and reaches to equilibrium.
(b)
Answer to Problem 6DQ
Explanation of Solution
HA is weak acid and HCl is a strong acid. For a weak acid HA, the ionization reaction can be written as:
Whereas HCl is a strong acid so it will ionize completely as given below:
Hence the major species in both acids must be:
(c)
Interpretation: The Ka value from the equilibrium picture of 10 molecules of HA and HCl acid in their two separate aqueous solution needs to be calculated.
 Concept Introduction: An acid is the substance that gives H+ or
Concept Introduction: An acid is the substance that gives H+ or
On the contrary, a weak acid ionized partially and reaches to equilibrium.
(c)
Answer to Problem 6DQ
Explanation of Solution
The Kaexpression for both acids can be written as given :
Substitute the values of number of molecules from each picture:
(d)
Interpretation: The order from strongest to weakest base for
Concept Introduction: An acid is the substance that gives H+ or
On the contrary, a weak acid ionized partially and reaches to equilibrium.
(d)
Answer to Problem 6DQ
Explanation of Solution
HA is weak acid and HCl is a strong acid. For a weak acid HA, the ionization reaction can be written as:
Whereas HCl is a strong acid so it will ionize completely as given below:
According to the Bronsted-Lowery acid-base theory, a strong acid gives H+ ions and form weak conjugate base whereas a strong base accepts H+ ion to form weak conjugate acid of it. Since HA is weak acid and forms
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Chemical Principles
- Synthesize 2-Ethyl-3-methyloxirane from dimethyl(propyl)sulfonium iodide using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize 2-Hydroxy-2-phenylacetonitrile from phenylmethanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- Synthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardIf possible, please provide the formula of the compound 3,3-dimethylbut-2-enal.arrow_forwardSynthesize 1,4-dibromobenzene from acetanilide (N-phenylacetamide) using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained by mixing (3-oxo-3-phenylpropyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide with sodium hydride.arrow_forwardWe mix N-ethyl-2-hexanamine with excess methyl iodide and followed by heating with aqueous Ag2O. Indicate the major products obtained.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing acetophenone with iodine and NaOH.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained by mixing 2-Propanone and ethyllithium and performing a subsequent acid hydrolysis.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained if (E)-2-butenal and 3-oxo-butanenitrile are mixed with sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forwardQuestion 3 (4 points), Draw a full arrow-pushing mechanism for the following reaction Please draw all structures clearly. Note that this intramolecular cyclization is analogous to the mechanism for halohydrin formation. COH Br + HBr Brarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning





