
(a)
Interpretation: The explanation for poor nucleophilicity of the solvent should be suggested.
Concept introduction:Carbocation formation is relatively slower than acid-base reactions. Carbocations generated from
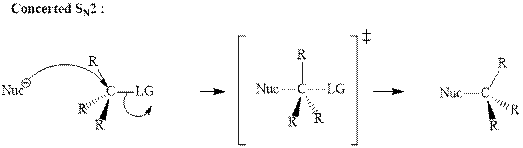
Bimolecular substitution or
A general
Unimolecular substitution or
A general

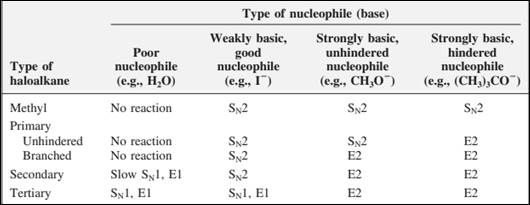
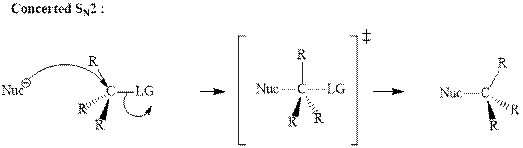
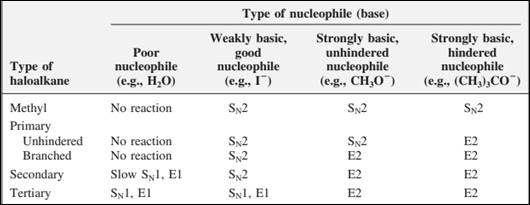
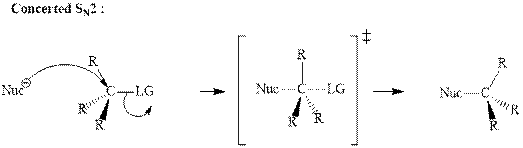
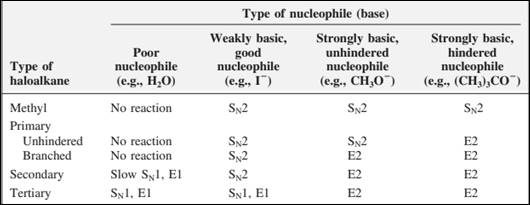
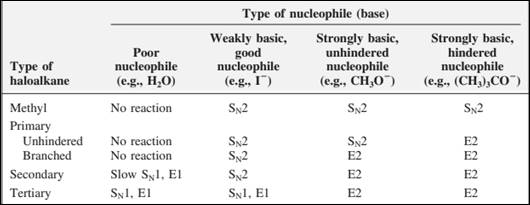
The most likely mechanisms for different kinds of alkyl halides reactions with various nucleophiles is given as follows:
(b)
Interpretation: The relative rates of the two steps should be found and compared to usual
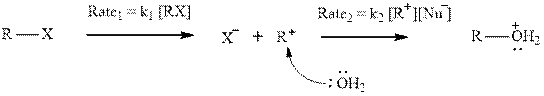
Concept introduction: Carbocation formation is relatively slower than acid-base reactions. Carbocations generated from alkyl halides have two fates; they can be either trapped by nucleophiles to give substitution product or may deprotonate to yield a small amount of alkene.
Bimolecular substitution or
A general
Unimolecular substitution or
A general

The most likely mechanisms for different kinds of alkyl halides reactions with various nucleophiles is given as follows:
(c)
Interpretation: The manner carbocation stability and decreasing solvent nucleophilicity might affect the relative magnitudes of
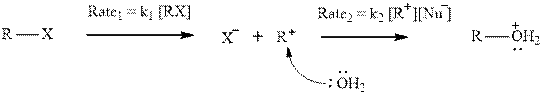
Concept introduction: Carbocation formation is relatively slower than acid-base reactions. Carbocations generated from alkyl halides have two fates; they can be either trapped by nucleophiles to give substitution product or may deprotonate to yield a small amount of alkene.
Bimolecular substitution or
A general
Unimolecular substitution or
A general

The most likely mechanisms for different kinds of alkyl halides reactions with various nucleophiles is given as follows:
(d)
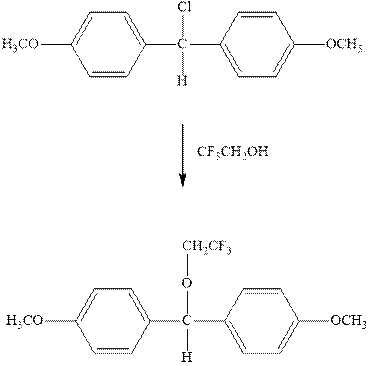
Interpretation: The complete mechanism for the indicated reaction should be written.
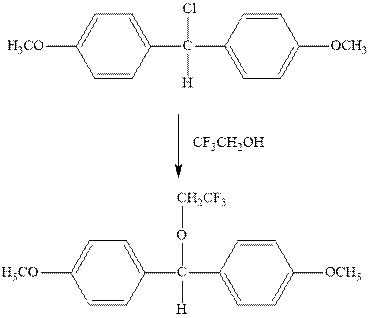
Concept introduction: Carbocation formation is relatively slower than acid-base reactions. Carbocations generated from alkyl halides have two fates; they can be either trapped by nucleophiles to give substitution product or may deprotonate to yield a small amount of alkene.
Unimolecular substitution or
A general

The most likely mechanisms for different kinds of alkyl halides reactions with various nucleophiles is given as follows:
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 7 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Structure and Function
- Assign the functional group bands on the IR spectra.arrow_forwardFind the pH of a 0.120 M solution of HNO2. Find the pH ignoring activity effects (i.e., the normal way). Find the pH in a solution of 0.050 M NaCl, including activityarrow_forwardPlease help me answer these three questions. Required info should be in data table.arrow_forward
- Draw the major organic substitution product or products for (2R,3S)-2-bromo-3-methylpentane reacting with the given nucleophile. Clearly drawn the stereochemistry, including a wedged bond, a dashed bond and two in-plane bonds at each stereogenic center. Omit any byproducts. Bri CH3CH2O- (conc.) Draw the major organic product or products.arrow_forwardTartaric acid (C4H6O6) is a diprotic weak acid. A sample of 875 mg tartaric acid are dissolved in 100 mL water and titrated with 0.994 M NaOH. How many mL of NaOH are needed to reach the first equivalence point? How many mL of NaOH are needed to reach the second equivalence point?arrow_forwardIncluding activity, calculate the solubility of Pb(IO3)2 in a matrix of 0.020 M Mg(NO3)2.arrow_forward
- Order the following series of compounds from highest to lowest reactivity to electrophilic aromatic substitution, explaining your answer: 2-nitrophenol, p-Toluidine, N-(4-methylphenyl)acetamide, 4-methylbenzonitrile, 4-(trifluoromethyl)benzonitrile.arrow_forwardOrdene la siguiente serie de compuestos de mayor a menor reactividad a la sustitución aromática electrofílica, explicando su respuesta: ácido bencenosulfónico, fluorobenceno, etilbenceno, clorobenceno, terc-butilbenceno, acetofenona.arrow_forwardCan I please get all final concentrations please!arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

