
Concept explainers
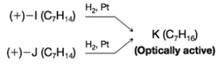
Compounds I and J both have the molecular formula
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 7 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Fundamentals of Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
Chemistry (7th Edition)
Laboratory Experiments in Microbiology (12th Edition) (What's New in Microbiology)
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
- true or false, given that a 20.00 mL sample of NaOH took 24.15 mL of 0.141 M HCI to reach the endpoint in a titration, the concentration of the NaOH is 1.17 M.arrow_forwardin the bromothymol blue experiment, pKa was measured. A closely related compound has a Ka of 2.10 x 10-5. What is the pKa?a) 7.1b) 4.7c) 2.0arrow_forwardcalculate the equilibrium concentration of H2 given that K= 0.017 at a constant temperature for this reaction. The inital concentration of HBr is 0.050 M.2HBr(g) ↔ H2(g) + Br2(g)a) 4.48 x 10-2 M b) 5.17 x 10-3 Mc) 1.03 x 10-2 Md) 1.70 x 10-2 Marrow_forward
- true or falsegiven these two equilibria with their equilibrium constants:H2(g) + CI2(l) ↔ 2HCI(g) K= 0.006 CI2(l) ↔ CI2(g) K= 0.30The equilibrium contstant for the following reaction is 1.8H2(g) + CI2 ↔ 2HCI(g)arrow_forwardI2(g) + CI2(g) ↔ 2ICIK for this reaction is 81.9. Find the equilibrium concentration of I2 if the inital concentration of I2 and CI2 are 0.010 Marrow_forwardtrue or false,the equilibrium constant for this reaction is 0.50.PCI5(g) ↔ PCI3(g) + CI2(g)Based on the above, the equilibrium constant for the following reaction is 0.25.2PCI5(g) ↔. 2PCI3(g) + 2CI2(g)arrow_forward
- true or false, using the following equilibrium, if carbon dioxide is added the equilibrium will shift toward the productsC(s) + CO2(g) ↔ 2CO(g)arrow_forward2S2O2/3- (aq) + I2 (aq) ---> S4O2/6- (aq) +2I- (aq) Experiment I2 (M) S2O3- (M) Initital Rate (M/s) 1 0.01 0.01 0.0004 2 0.01 0.02 0.0004 3 0.02 0.01 0.0008 Calculate the overall order for this reaction using the table data a) 3b) 0c) 2d) 1arrow_forwardthe decomposition of N2O5 is the first order with a half-life of 1.98 minutes. If the inital concentration of N2O5 is 0.200 M, what is the concentration after 6 minutes?a) 0.612 Mb) 0.035 Mc) 0.024 Md) 0.100 Marrow_forward
- 20.00 mL of 0.150 M HCI is titrated with 0.075 M NaOH. What volume of NaOH is needed?a) 50 mLb) 20 mLc) 40 mLd) 26.66 mLarrow_forward20.00 mL of 0.150 M NaOH is titrated with 37.75 mL of HCI. What is the molarity of the HCI?a) 0.150 Mb) 0.079 Mc) 0.025 Md) 0.050 Marrow_forwardin the following reaction, the OH- acts as which of these?NO2- (aq) + H2O (l) ⇌ OH- (aq) + HNO2 (aq)a) not a weak acidb) basec) acidarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





