
Concept explainers
Write the balanced net ionic equation for the reaction that takes place when aqueous solutions of the following solutes are mixed. If no reaction is likely, explain why no reaction would be expected for that combination of solutes.
l type='a'>
i>phosphoric acid 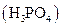 and calcium nitrate
and calcium nitrate
(a)
Interpretation:
The balanced net ionic equation for the reaction that takes place when aqueous solutions of the following solutes are mixed should be written. If no reaction is likely, why no reaction would be expected for that combination of solute should be explained.
Concept Introduction:
Deciding which products will form when two or more reactants added together is not an easy task without any experimental evidences. The best way to predict what products will form is to think of various possibilities and then decide which product is most likely to form. A solid compound must have a zero charge.
In a complete ionic equation, all strong electrolytes are represented as ions. But in net ionic equation, only the components which undergo a chemical change are shown. Ions which do not participate directly in the reaction which are called spectator ions are not shown in the net ionic equation.
Answer to Problem 24CR
A net ionic equation is not available.
Explanation of Solution
When potassium nitrate and sodium chloride are mixed, double displacement reaction happens where the two cations of the reactants simply exchange their anions. But no change is visible as all the reactants and products are strong electrolytes, they are completely dissociated in the solution. All ions behave as spectator ions. When we write the complete ionic equation,
All the ions in both sides are cancelled off each other. So there is no net ionic equation.
(b)
Interpretation:
The balanced net ionic equation for the reaction that takes place when aqueous solutions of the following solutes are mixed should be written. If no reaction is likely, why no reaction would be expected for that combination of solute should be explained.
Concept Introduction:
Deciding which products will form when two or more reactants added together is not an easy task without any experimental evidences. The best way to predict what products will form is to think of various possibilities and then decide which product is most likely to form. A solid compound must have a zero charge.
In a complete ionic equation, all strong electrolytes are represented as ions. But in net ionic equation, only the components which undergo a chemical change are shown. Ions which do not participate directly in the reaction which are called spectator ions are not shown in the net ionic equation.
Answer to Problem 24CR
A net ionic equation is not available.
Explanation of Solution
When calcium nitrate and sulfuric acid are mixed, double displacement reaction happens where the two cations of the reactants simply exchange their anions. But no change is visible as all the reactants and products are strong electrolytes, they are completely dissociated in the solution. All ions behave as spectator ions. When we write the complete ionic equation,
All the ions in both sides are cancelled off each other. So there is no net ionic equation.
(c)
Interpretation:
The balanced net ionic equation for the reaction that takes place when aqueous solutions of the following solutes are mixed should be written. If no reaction is likely, why no reaction would be expected for that combination of solute should be explained.
Concept Introduction:
Deciding which products will form when two or more reactants added together is not an easy task without any experimental evidences. The best way to predict what products will form is to think of various possibilities and then decide which product is most likely to form. A solid compound must have a zero charge.
In a complete ionic equation, all strong electrolytes are represented as ions. But in net ionic equation, only the components which undergo a chemical change are shown. Ions which do not participate directly in the reaction which are called spectator ions are not shown in the net ionic equation.
Answer to Problem 24CR
Explanation of Solution
When ammonium sulfide and lead (II) nitrate are mixed, double displacement reaction happens where the two cations of the reactants simply exchange their anions. Here a precipitation reaction takes place and PbS precipitate is formed. So this reaction is likely to happen. When the complete ionic equation is written,
All the similar cations and anions in both sides are cancelled off and therefore the net ionic equation is
(d)
Interpretation:
The balanced net ionic equation for the reaction that takes place when aqueous solutions of the following solutes are mixed should be written. If no reaction is likely, why no reaction would be expected for that combination of solute should be explained.
Concept Introduction:
Deciding which products will form when two or more reactants added together is not an easy task without any experimental evidences. The best way to predict what products will form is to think of various possibilities and then decide which product is most likely to form. A solid compound must have a zero charge.
In a complete ionic equation, all strong electrolytes are represented as ions. But in net ionic equation, only the components which undergo a chemical change are shown. Ions which do not participate directly in the reaction which are called spectator ions are not shown in the net ionic equation.
Answer to Problem 24CR
Explanation of Solution
When sodium carbonate and iron (III) chloride are mixed, double displacement reaction happens where the two cations of the reactants simply exchange their anions. Here a precipitation reaction takes place and Fe2 (CO3 )3 precipitate is formed. So this reaction is likely to happen. When the complete ionic equation is written,
All the similar cations and anions in both sides are cancelled off and therefore the net ionic equation is
(e)
Interpretation:
The balanced net ionic equation for the reaction that takes place when aqueous solutions of the following solutes are mixed should be written. If no reaction is likely, why no reaction would be expected for that combination of solute should be explained.
Concept Introduction:
Deciding which products will form when two or more reactants added together is not an easy task without any experimental evidences. The best way to predict what products will form is to think of various possibilities and then decide which product is most likely to form. A solid compound must have a zero charge.
In a complete ionic equation, all strong electrolytes are represented as ions. But in net ionic equation, only the components which undergo a chemical change are shown. Ions which do not participate directly in the reaction which are called spectator ions are not shown in the net ionic equation.
Answer to Problem 24CR
Explanation of Solution
When mercurous nitrate and calcium chloride are mixed, double displacement reaction happens where the two cations of the reactants simply exchange their anions. Here a precipitation reaction takes place and Hg2 Cl2 precipitate is formed. So this reaction is likely to happen. When the complete ionic equation is written,
All the similar cations and anions in both sides are cancelled off and therefore the net ionic equation is
(f)
Interpretation:
The balanced net ionic equation for the reaction that takes place when aqueous solutions of the following solutes are mixed should be written. If no reaction is likely, why no reaction would be expected for that combination of solute should be explained.
Concept Introduction:
Deciding which products will form when two or more reactants added together is not an easy task without any experimental evidences. The best way to predict what products will form is to think of various possibilities and then decide which product is most likely to form. A solid compound must have a zero charge.
In a complete ionic equation, all strong electrolytes are represented as ions. But in net ionic equation, only the components which undergo a chemical change are shown. Ions which do not participate directly in the reaction which are called spectator ions are not shown in the net ionic equation.
Answer to Problem 24CR
Explanation of Solution
When silver acetate and potassium chloride are mixed, double displacement reaction happens where the two cations of the reactants simply exchange their anions. Here a precipitation reaction takes place and AgCl precipitate is formed. So this reaction is likely to happen. When the complete ionic equation is written,
All the similar cations and anions in both sides are cancelled off and therefore the net ionic equation is
(g)
Interpretation:
The balanced net ionic equation for the reaction that takes place when aqueous solutions of the following solutes are mixed should be written. If no reaction is likely, why no reaction would be expected for that combination of solute should be explained.
Concept Introduction:
Deciding which products will form when two or more reactants added together is not an easy task without any experimental evidences. The best way to predict what products will form is to think of various possibilities and then decide which product is most likely to form. A solid compound must have a zero charge.
In a complete ionic equation, all strong electrolytes are represented as ions. But in net ionic equation, only the components which undergo a chemical change are shown. Ions which do not participate directly in the reaction which are called spectator ions are not shown in the net ionic equation.
Answer to Problem 24CR
Explanation of Solution
When phosphoric acid and calcium nitrate are mixed, double displacement reaction happens where the two cations of the reactants simply exchange their anions. Here a precipitation reaction takes place and Ca3 (PO4 )2 precipitate is formed. So this reaction is likely to happen. When the complete ionic equation is written,
All the similar cations and anions in both sides are cancelled off and therefore the net ionic equation is
(h)
Interpretation:
The balanced net ionic equation for the reaction that takes place when aqueous solutions of the following solutes are mixed should be written. If no reaction is likely, why no reaction would be expected for that combination of solute should be explained.
Concept Introduction:
Deciding which products will form when two or more reactants added together is not an easy task without any experimental evidences. The best way to predict what products will form is to think of various possibilities and then decide which product is most likely to form. A solid compound must have a zero charge.
In a complete ionic equation, all strong electrolytes are represented as ions. But in net ionic equation, only the components which undergo a chemical change are shown. Ions which do not participate directly in the reaction which are called spectator ions are not shown in the net ionic equation.
Answer to Problem 24CR
A net ionic equation is not available.
Explanation of Solution
Both sulfuric acid and nickel (II) sulfate has similar anion SO4 2-. Therefore, even though they exchange their anions, a chemical change will not happen. So this reaction is not likely to happen. The complete ionic equation is,
All the cations and anions cancel off each other so no net ionic equation is available.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
- The decimolar calomel electrode has a potential of 0.3335 V at 25°C compared to the standard hydrogen electrode. If the standard reduction potential of Hg22+ is 0.7973 V and the solubility product of Hg2Cl2 is 1.2x 10-18, find the activity of the chlorine ion at this electrode.Data: R = 8.314 J K-1 mol-1, F = 96485 C mol-1, T = 298.15 K.arrow_forward2. Add the following group of numbers using the correct number of significant figures for the answer. Show work to earn full credit such as rounding off the answer to the correct number of significant figures. Replace the question marks with the calculated answers or write the calculated answers near the question marks. 10916.345 37.40832 5.4043 3.94 + 0.0426 ? (7 significant figures)arrow_forwardThe emf at 25°C of the cell: Pt l H2(g) l dis X:KCl (sat) l Hg2Cl2(s) l Hg l Pt was 612 mV. When solution X was replaced by normal phosphate buffer solution with a pH of 6.86, the emf was 741 mV. Calculate the pH of solution X.arrow_forward
- Indicate how to calculate the potential E of the reaction Hg2Cl2(s) + 2e ⇄ 2Hg + 2Cl- as a function of the concentration of Cl- ions. Data: the solubility product of Hg2Cl2.arrow_forwardHow can Beer’s Law be used to determine the concentration in a selected food sample. Provide an in-depth discussion and examples of this.arrow_forwardb) H3C- H3C Me CH 3 I HN Me H+arrow_forward
- Using Luther's rule, determine the reference potentials of the electrodes corresponding to the low stability systems Co³+/Co and Cr²+/Cr from the data in the table. Electrodo ΕΝ Co²+/Co Co3+/Co²+ -0,28 +1,808 Cr³+ / Cr -0,508 Cr3+ / Cr²+ -0,41arrow_forwardThe molecule PYRIDINE, 6tt electrons and is there pore aromuntre and is Assigned the Following structure contenus Since aromatk moleculey undergo electrophilic allomatic substitution, Pyridine should undergo The Following reaction + HNO3 12504 a. write all of the possible Mononitration Products that could Result From this roaction Based upon the reaction the reaction mechanism determine which of these producty would be the major Product of the hegetionarrow_forwardUsing Benzene as starting materia Show how each of the Following molecules could Ve synthesked 9. CHI d. 10450 b 0 -50311 ८ City -5034 1-0-650 e NO2arrow_forward
- BA HBr of the fol 1)=MgCI 2) H₂O major NaOEt Ts Cl Py (pyridine) 1) 03 2) Me2S 1arrow_forward4. Provide a clear arrow-pushing mechanism for the following reactions. Do not skip proton transfers, do not combine steps, and make sure your arrows are clear enough to be interpreted without ambiguity. a) NHBoc ⚫OBn HO. H3C CO2CH3 -OBn H3C H3C. H3C. NHBOC CI CO2CH3arrow_forwardDraw structures of the following compounds and identify their role: mCPBA (MCPBA) DMS Py 9-BBN LAH Sia₂BH TsCI PCC t-BuOK LDA MeLi n-BuLi DMSO DMF Sodium Borohydride Lithium DiisopropylAmide 2arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax





