
Concept explainers
Trapezoidal approximation of the integral.
Answer to Problem 4QQ
Trapezoidal approximation:
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Function f is continuous on the closed interval [1, 7].
Function values:
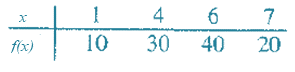
The widths of subinterval:
[1, 4], [4, 6], and [6, 7].
Since the widths of the subintervals are not same, the Trap Rule formula cannot be used directly.
Instead, find the area of each trapezoid and then sum them up.
For [1, 4]:
Width,
Heights,
And
Then
The area for this trapezoid,
For [4, 6]:
Width,
Heights,
And
Then
The area for this trapezoid,
For [6, 7]:
Width,
Heights,
And
Then
The area for this trapezoid,
Thus,
The approximation of integral:
Chapter 6 Solutions
Calculus: Graphical, Numerical, Algebraic
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
Calculus for Business, Economics, Life Sciences, and Social Sciences (14th Edition)
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
Precalculus
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
Elementary Statistics (13th Edition)
- K Find all values x = a where the function is discontinuous. For each value of x, give the limit of the function as x approaches a. Be sure to note when the limit doesn't exist. x-7 p(x) = X-7 Select the correct choice below and, if necessary, fill in the answer box(es) within your choice. (Use a comma to separate answers as needed.) OA. f is discontinuous at the single value x = OB. f is discontinuous at the single value x= OC. f is discontinuous at the two values x = OD. f is discontinuous at the two values x = The limit is The limit does not exist and is not co or - ∞. The limit for the smaller value is The limit for the larger value is The limit for the smaller value is The limit for the larger value does not exist and is not c∞ or -arrow_forwardK x3 +216 complete the table and use the results to find lim k(x). If k(x) = X+6 X-6 X -6.1 -6.01 - 6.001 - 5.999 - 5.99 -5.9 k(x) Complete the table. X -6.1 -6.01 - 6.001 - 5.999 - 5.99 - 5.9 k(x) (Round to three decimal places as needed.) Find the limit. Select the correct choice below and, if necessary, fill in the answer box within your choice.arrow_forwardSketch the slope field that represents the differential equation. × Clear Undo Redo y ४|० || 33 dy dxarrow_forward
- Sketch the slope field that represents the differential equation. × Clear Undo Redo dy 33 dx = -y "arrow_forwardMath Test 3 3 x³+y³ = Ꭹ = 9 2 2 x²+y² = 5 x+y=?arrow_forwardFor each of the following series, determine whether the absolute convergence series test determines absolute convergence or fails. For the ¿th series, if the test is inconclusive then let Mi = 4, while if the test determines absolute convergence let Mi 1 : 2: ∞ Σ(−1)"+¹ sin(2n); n=1 Σ n=1 Σ ((−1)”. COS n² 3+2n4 3: (+ 4: 5 : n=1 ∞ n 2+5n3 ПП n² 2 5+2n3 пп n² Σ(+)+ n=1 ∞ n=1 COS 4 2 3+8n3 П ηπ n- (−1)+1 sin (+727) 5 + 2m³ 4 = 8. Then the value of cos(M₁) + cos(2M2) + cos(3M3) + sin(2M) + sin(M5) is -0.027 -0.621 -1.794 -1.132 -1.498 -4.355 -2.000 2.716arrow_forward
- i need help with this question i tried by myself and so i am uploadding the question to be quided with step by step solution and please do not use chat gpt i am trying to learn thank you.arrow_forwardi need help with this question i tried by myself and so i am uploadding the question to be quided with step by step solution and please do not use chat gpt i am trying to learn thank you.arrow_forward1. 3 2 fx=14x²-15x²-9x- 2arrow_forward
- No it is not a graded assignment, its a review question but i only have the final answer not the working or explanationarrow_forwardClass, the class silues, and the class notes, whether the series does alternate and the absolute values of the terms decrease), and if the test does apply, determine whether the series converges or diverges. For the ith series, if the test does not apply the let Mi = 2, while if the test determines divergence then M¿ = 4, and if it determines convergence then M¿ = 8. 1: 2: 3 : 4: 5 : ∞ n=1 ∞ (−1)n+1. Σ(-1) +1 n=1 ∞ п 3m² +2 Σ(-1)+1 sin(2n). n=1 ∞ 2n² + 2n +3 4n2 +6 1 e-n + n² 3n23n+1 9n² +3 In(n + 1) 2n+1 Σ(-1) +1 n=1 ∞ Σ(-1)". n=1 Then the value of cos(M₁) + cos(2M2) + cos(3M3) + sin(2M4) + sin(M5) is 1.715 0.902 0.930 -1.647 -0.057 ● 2.013 1.141 4.274arrow_forward3. FCX14) = x²+3xx-y3 +.arrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





