
In Problems 39-47, construct a mathematical model in the form of a linear programming problem. Do not solve.
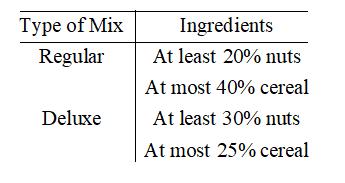
Trail mix. A company makes two brands of trail mix, regular and deluxe, by mixing dried fruits, nuts, and cereal. The recipes for the mixes are given in the table. The company has
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 6 Solutions
FINITE MATHMATICS F/ BUSI...-ACCESS
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Thinking Mathematically (6th Edition)
College Algebra (7th Edition)
Introductory Statistics
College Algebra with Modeling & Visualization (5th Edition)
- by (2) Gauss saidel - - method find (2) و X2 for the sestem X1 + 2x2=-4 2x1 + 2x2 = 1 Such thef (0) x2=-2arrow_forwardCan you please explain how to find the bounds of the integrals for X and Y and also explain how to find the inequalites that satisfy X and Y. I've looked at the solutions but its not clear to me on how the inequalities and bounds of the integral were obtained. If possible could you explain how to find the bounds of the integrals by sketching a graph with the region of integration. Thanksarrow_forwardax+b proof that se = - è (e" -1)" ë naxarrow_forward
- 20.11 ← UAS Sisa waktu 01:20:01 51%- Soal 2 Perhatikan gambar di bawah (Sembunyikan ) Belum dijawab Ditandai dari 1,00 5 A B E D 10 20 Jika ruas garis AB, PE, dan DC sejajar dan ketiganya tegak lurus dengan ruas garis BC, maka panjang ruas garis PE adalah ... (cukup tulis bilangannya tanpa spasi dalam bentuk desimal tiga angka di belakang koma, seperti a,bcd atau pecahan m/n untuk m n Jawaban: Jawaban ||| <arrow_forwarda Question 7. If det d e f ghi V3 = 2. Find det -1 2 Question 8. Let A = 1 4 5 0 3 2. 1 Find adj (A) 2 Find det (A) 3 Find A-1 2g 2h 2i -e-f -d 273 2a 2b 2carrow_forwardQuestion 1. Solve the system - x1 x2 + 3x3 + 2x4 -x1 + x22x3 + x4 2x12x2+7x3+7x4 Question 2. Consider the system = 1 =-2 = 1 3x1 - x2 + ax3 = 1 x1 + 3x2 + 2x3 x12x2+2x3 = -b = 4 1 For what values of a, b will the system be inconsistent? 2 For what values of a, b will the system have only one solution? For what values of a, b will the saystem have infinitely many solutions?arrow_forward
- Question 5. Let A, B, C ben x n-matrices, S is nonsigular. If A = S-1 BS, show that det (A) = det (B) Question 6. For what values of k is the matrix A = (2- k -1 -1 2) singular? karrow_forward20.07 52% X https://www.chegg.com/hc <: C Chegg Learn on the go = Chegg (X) Open in app EN-US ✔ What's your next question? √x #16 A surveyor sees a building across the river. Standing at point A he measures the angle of elevation from the ground to the top of the building to be 30 degrees. He steps back 100 feet and again measures the angle of elevation and finds it to be 15. (See Figure 12.26.) Assuming that it makes a 90-degree angle with the floor, approximately how tall is the building? 15 30° 100 A river Figure 12.26 Show image transcript Here's the best way to solve it. Solution ||| о building < Sharearrow_forward1 4 5 Question 3. Find A-1 (if exists), where A = -3 -1 -2 2 3 4 Question 4. State 4 equivalent conditions for a matrix A to be nonsingulararrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardModule Code: MATH380202 3. (a) Let {} be a white noise process with variance σ2. Define an ARMA(p,q) process {X} in terms of {+} and state (without proof) conditions for {X} to be (i) weakly stationary and (ii) invertible. Define what is meant by an ARIMA (p, d, q) process. Let {Y} be such an ARIMA(p, d, q) process and show how it can also be represented as an ARMA process, giving the AR and MA orders of this representation. (b) The following tables show the first nine sample autocorrelations and partial auto- correlations of X and Y₁ = VX+ for a series of n = 1095 observations. (Notice that the notation in this part has no relationship with the notation in part (a) of this question.) Identify a model for this time series and obtain preliminary estimates for the pa- rameters of your model. X₁ = 15.51, s² = 317.43. k 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Pk 0.981 0.974 0.968 akk 0.981 0.327 8 9 0.927 0.963 0.957 0.951 0.943 0.935 0.121 0.104 0.000 0.014 -0.067 -0.068 -0.012 Y₁ = VX : y = 0.03, s² = 11.48. k 1…arrow_forwardLet G be a graph with n ≥ 2 vertices x1, x2, . . . , xn, and let A be the adjacency matrixof G. Prove that if G is connected, then every entry in the matrix A^n−1 + A^nis positive.arrow_forward
 College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill Elementary AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9780998625713Author:Lynn Marecek, MaryAnne Anthony-SmithPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
Elementary AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9780998625713Author:Lynn Marecek, MaryAnne Anthony-SmithPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University



