
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics
12th Edition
ISBN: 9781259977268
Author: Ferdinand P. Beer, E. Russell Johnston Jr., David Mazurek
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 6.2, Problem 6.73P
6.70 through 6.74 classify as determinate or indeterminate. (All members act both in tension and in compression.)
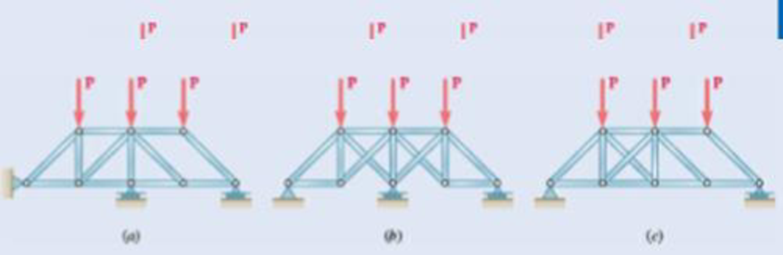
Fig. P6.73
Structure (a):
Rigid truss with r = 3, m = 14, n = 8,
so r + m = 17 > 2n = 16
so completely constrained but indeterminate
Structure (b): Simple truss (start with ABC and add joints alphabetically), with
r = 3, m = 13, n = 8, so r + m = 16 = 2n
so completely constrained and determinate
Structure (c):
Simple truss with r = 3, m = 13, n = 8, so r + m = 16 = 2n, hut horizontal reactions (Ax and Dx) are collinear, so cannot he resolved by any equilibrium equation.
Structure is improperly constrained.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Problem4.
The thin uniform disk of mass m = 1-kg and radius R = 0.1m spins about the bent shaft OG with
the angular speed w2 = 20 rad/s. At the same time, the shaft rotates about the z-axis with the angular
speed 001 = 10 rad/s. The angle between the bent portion of the shaft and the z-axis is ẞ = 35°. The
mass of the shaft is negligible compared to the mass of the disk.
a. Find the angular momentum of the disk with respect to point G, based on the axis
orientation as shown. Include an MVD in your solution.
b. Find the angular momentum of the disk with respect to point O, based on the axis
orientation as shown. (Note: O is NOT the center of fixed-point rotation.)
c. Find the kinetic energy of the assembly.
z
R
R
002
2R
x
Answer: H = -0.046ĵ-0.040 kg-m²/sec
Ho=-0.146-0.015 kg-m²/sec
T 0.518 N-m
=
Problem 3.
The assembly shown consists of a solid sphere of mass m and the uniform slender rod of the same
mass, both of which are welded to the shaft. The assembly is rotating with angular velocity w at a
particular moment. Find the angular momentum with respect to point O, in terms of the axes
shown.
Answer: Ñ。 = ½mc²wcosßsinßĵ + (}{mr²w + 2mb²w + ½ mc²wcos²ß) k
3
m
r
b
2
C
لا
m
Only question 2
Chapter 6 Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics
Ch. 6.1 - Using the method of joints, determine the force in...Ch. 6.1 - Using the method of joints, determine the force in...Ch. 6.1 - Using the method of joints, determine the force in...Ch. 6.1 - Using the method of joints, determine the force in...Ch. 6.1 - Using the method of joints, determine the force in...Ch. 6.1 - Using the method of joints, determine the force in...Ch. 6.1 - Using the method of joints, determine the force in...Ch. 6.1 - Using the method of joints, determine the force in...Ch. 6.1 - Using the method of joints, determine the force in...Ch. 6.1 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...
Ch. 6.1 - Determine the force in each member of the Gambrel...Ch. 6.1 - Determine the force in each member of the Howe...Ch. 6.1 - Using the method of joints, determine the force in...Ch. 6.1 - Prob. 6.14PCh. 6.1 - Determine the force in each member of the Warren...Ch. 6.1 - Solve Problem 6.15 assuming that the load applied...Ch. 6.1 - Determine the force in each member of the Pratt...Ch. 6.1 - The truss shown is one of several supporting an...Ch. 6.1 - Determine the force in each member of the Pratt...Ch. 6.1 - Solve Problem 6.19 assuming that the load applied...Ch. 6.1 - Determine the force in each of the members located...Ch. 6.1 - Determine the force in member DE and in each of...Ch. 6.1 - Determine the force in each of the members located...Ch. 6.1 - The portion of truss shown represents the upper...Ch. 6.1 - For the tower and loading of Prob. 6.24 and...Ch. 6.1 - Solve Problem 6.24 assuming that the cables...Ch. 6.1 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 6.1 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 6.1 - Determine whether the trusses of Problems 6.31a,...Ch. 6.1 - Determine whether the trusses of Problems 6.31b,...Ch. 6.1 - For the given loading, determine the zero-force...Ch. 6.1 - For the given loading, determine the zero-force...Ch. 6.1 - For the given loading, determine the zero-force...Ch. 6.1 - Determine the zero-force members in the truss of...Ch. 6.1 - The truss shown consists of six members and is...Ch. 6.1 - The truss shown consists of six members and is...Ch. 6.1 - The truss shown consists of six members and is...Ch. 6.1 - Prob. 6.38PCh. 6.1 - The truss shown consists of nine members and is...Ch. 6.1 - Solve Prob. 6.39 for P = 0 and Q = (900 N)k. 6.39...Ch. 6.1 - The truss shown consists of 18 members and is...Ch. 6.1 - The truss shown consists of 18 members and is...Ch. 6.2 - Determine the force in members BD and DE of the...Ch. 6.2 - Determine the force in members DG and EG of the...Ch. 6.2 - Determine the force in members BD and CD of the...Ch. 6.2 - Determine the force in members DF and DG of the...Ch. 6.2 - A floor truss is loaded as shown. Determine the...Ch. 6.2 - A floor truss is loaded as shown. Determine the...Ch. 6.2 - Determine the force in members CD and DF of the...Ch. 6.2 - Determine the force in members CE and EF of the...Ch. 6.2 - Determine the force in members DE and DF of the...Ch. 6.2 - Determine the force in members EG and EF of the...Ch. 6.2 - Determine the force in members DF and DE of the...Ch. 6.2 - Determine the force in members CD and CE of the...Ch. 6.2 - A Pratt roof truss is loaded as shown. Determine...Ch. 6.2 - A Pratt roof truss is loaded as shown. Determine...Ch. 6.2 - A Howe scissors roof truss is loaded as shown....Ch. 6.2 - A Howe scissors roof truss is loaded as shown....Ch. 6.2 - Determine the force in members AD, CD, and CE of...Ch. 6.2 - Determine the force in members DG, FG, and FH of...Ch. 6.2 - Determine the force in member GJ of the truss...Ch. 6.2 - Determine the force in members DG and FH of the...Ch. 6.2 - Prob. 6.63PCh. 6.2 - Prob. 6.64PCh. 6.2 - The diagonal members in the center panels of the...Ch. 6.2 - The diagonal members in the center panels of the...Ch. 6.2 - The diagonal members in the center panels of the...Ch. 6.2 - Solve Prob. 6.67 assuming that the 9-kip load has...Ch. 6.2 - Classify each of the structures shown as...Ch. 6.2 - Classify each of the structures shown as...Ch. 6.2 - 6.70 through 6.74 classify as determinate or...Ch. 6.2 - 6.70 through 6.74 classify as determinate or...Ch. 6.2 - 6.70 through 6.74 classify as determinate or...Ch. 6.2 - 6.70 through 6.74 classify as determinate or...Ch. 6.3 - For the frame and loading shown, draw the...Ch. 6.3 - For the frame and loading shown, draw the...Ch. 6.3 - Draw the free-body diagram(s) needed to determine...Ch. 6.3 - Knowing that the pulley has a radius of 0.5 m,...Ch. 6.3 - and 6.76 Determine the force in member BD and the...Ch. 6.3 - Prob. 6.76PCh. 6.3 - For the frame and loading shown, determine the...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the components of all forces acting on...Ch. 6.3 - The hydraulic cylinder CF, which partially...Ch. 6.3 - The hydraulic cylinder CF, which partially...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the components of all forces acting on...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the components of all forces acting on...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the components of the reactions at A and...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the components of the reactions at D and...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the components of the reactions at A and...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the components of the reactions at A and...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the components of the reactions at A and...Ch. 6.3 - The 48-lb load can be moved along the line of...Ch. 6.3 - The 48-lb load is removed and a 288-lb in....Ch. 6.3 - (a) Show that, when a frame supports a pulley at...Ch. 6.3 - Knowing that each pulley has a radius of 250 mm,...Ch. 6.3 - Knowing that the pulley has a radius of 75 mm,...Ch. 6.3 - Prob. 6.93PCh. 6.3 - Prob. 6.94PCh. 6.3 - A trailer weighing 2400 lb is attached to a...Ch. 6.3 - In order to obtain a better weight distribution...Ch. 6.3 - The cab and motor units of the front-end loader...Ch. 6.3 - Solve Problem 6.97 assuming that the 75-kN load...Ch. 6.3 - Knowing that P = 90 lb and Q = 60 lb, determine...Ch. 6.3 - Knowing that P = 90 lb and Q = 60 lb, determine...Ch. 6.3 - For the frame and loading shown, determine the...Ch. 6.3 - For the frame and loading shown, determine the...Ch. 6.3 - Prob. 6.103PCh. 6.3 - Prob. 6.104PCh. 6.3 - For the frame and loading shown, determine the...Ch. 6.3 - Solve Prob. 6.105 assuming that the 6-kN load has...Ch. 6.3 - The axis of the three-hinge arch ABC is a parabola...Ch. 6.3 - The axis of the three-hinge arch ABC is a parabola...Ch. 6.3 - 6.109 and 6.110 Neglecting the effect of friction...Ch. 6.3 - and 6.110 Neglecting the effect of friction at the...Ch. 6.3 - 6.111, 6.112, and 6.113 Members ABC and CDE are...Ch. 6.3 - 6.111, 6.112, and 6.113 Members ABC and CDE are...Ch. 6.3 - 6.111, 6.112, and 6.113 Members ABC and CDE are...Ch. 6.3 - Members ABC and CDE are pin-connected at C and...Ch. 6.3 - Solve Prob. 6.112 assuming that the force P is...Ch. 6.3 - Solve Prob. 6.114 assuming that the force P is...Ch. 6.3 - Four beams, each with a length of 2a, are nailed...Ch. 6.3 - Four beams, each with a length of 3a, are held...Ch. 6.3 - 6.119 through 6.121 Each of the frames shown...Ch. 6.3 - 6.119 through 6.121 Each of the frames shown...Ch. 6.3 - 6.119 through 6.121 Each of the frames shown...Ch. 6.4 - An 84-lb force is applied to the toggle vise at C....Ch. 6.4 - For the system and loading shown, draw the...Ch. 6.4 - A small barrel weighing 60 lb is lifted by a pair...Ch. 6.4 - The position of member ABC is controlled by the...Ch. 6.4 - The shear shown is used to cut and trim...Ch. 6.4 - A 100-lb force directed vertically downward is...Ch. 6.4 - Prob. 6.124PCh. 6.4 - The control rod CE passes through a horizontal...Ch. 6.4 - Solve Prob. 6.125 when (a) = 0, (b) = 6. Fig....Ch. 6.4 - The press shown is used to emboss a small seal at...Ch. 6.4 - The press shown is used to emboss a small seal at...Ch. 6.4 - The pin at B is attached to member ABC and can...Ch. 6.4 - The pin at B is attached to member ABC and can...Ch. 6.4 - Arm ABC is connected by pins to a collar at B and...Ch. 6.4 - Arm ABC is connected by pins to a collar at B and...Ch. 6.4 - The Whitworth mechanism shown is used to produce a...Ch. 6.4 - Solve Prob. 6.133 when (a) = 60, (b) = 90. Fig....Ch. 6.4 - and 6.136 Two rods are connected by a slider block...Ch. 6.4 - and 6.136 Two rods are connected by a slider block...Ch. 6.4 - 6.137 and 6.138 Rod CD is attached to the collar D...Ch. 6.4 - 6.137 and 6.138 Rod CD is attached to the collar D...Ch. 6.4 - Two hydraulic cylinders control the position of...Ch. 6.4 - Two hydraulic cylinders control the position of...Ch. 6.4 - A steel ingot weighing 8000 lb is lifted by a pair...Ch. 6.4 - If the toggle shown is added to the tongs of Prob....Ch. 6.4 - A 9-m length of railroad rail of mass 40 kg/m is...Ch. 6.4 - The gear-pulling assembly shown consists of a...Ch. 6.4 - The pliers shown are used to grip a...Ch. 6.4 - Prob. 6.146PCh. 6.4 - In using the bolt cutter shown, a worker applies...Ch. 6.4 - The upper blade and lower handle of the...Ch. 6.4 - and 6.150 Determine the force P that must be...Ch. 6.4 - and 6.150 Determine the force P that must be...Ch. 6.4 - Because the brace shown must remain in position...Ch. 6.4 - The specialized plumbing wrench shown is used in...Ch. 6.4 - Prob. 6.153PCh. 6.4 - For the frame and loading shown, determine the...Ch. 6.4 - The telescoping arm ABC is used to provide an...Ch. 6.4 - The telescoping arm ABC of Prob. 6.155 can be...Ch. 6.4 - The motion of the backhoe bucket shown is...Ch. 6.4 - Solve Prob. 6.157 assuming that the 2-kip force P...Ch. 6.4 - The gears A and D are rigidly attached to...Ch. 6.4 - In the planetary gear system shown, the radius of...Ch. 6.4 - Two shafts AC and CF, which lie in the vertical xy...Ch. 6.4 - Two shafts AC and CF, which lie in the vertical xy...Ch. 6.4 - The large mechanical tongs shown are used to grab...Ch. 6 - Using the method of joints, determine the force in...Ch. 6 - Using the method of joints, determine the force in...Ch. 6 - A stadium roof truss is loaded as shown. Determine...Ch. 6 - A stadium roof truss is loaded as shown. Determine...Ch. 6 - Determine the components of all forces acting on...Ch. 6 - Determine the components of the reactions at A and...Ch. 6 - Knowing that the pulley has a radius of 50 mm,...Ch. 6 - For the frame and loading shown, determine the...Ch. 6 - For the frame and loading shown, determine the...Ch. 6 - Water pressure in the supply system exerts a...Ch. 6 - A couple M with a magnitude of 1.5 kNm is applied...Ch. 6 - The compound-lever pruning shears shown can be...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Only question 1arrow_forwardOnly question 3arrow_forwardI have Euler parameters that describe the orientation of N relative to Q, e = -0.7071*n3, e4 = 0.7071. I have Euler parameters that describe the orientation of U relative to N, e = -1/sqrt(3)*n1, e4 = sqrt(2/3). After using euler parameter rule of successive rotations, I get euler parameters that describe the orientation of U relative to Q, e = -0.4082*n1 - 0.4082*n2 - 0.5774*n3. I need euler parameters that describe the orientation of U relative to Q in vector basis of q instead of n. How do I get that?arrow_forward
- Describe at least 4 processes in engineering where control charts are (or should be) appliedarrow_forwardDescribe at least two (2) processes where control charts are (or should be) applied.arrow_forwardProblem 3: A cube-shaped spacecraft is in a circular Earth orbit. Let N (n,) be inertial and the spacecraft is denoted S (ŝ₁). The spacecraft is described such that ¯½º = J ŝ₁ŝ₁ + J ŝ₂§₂ + J §¸Ŝ3 Location of the spacecraft in the orbit is determined by the orbit-fixed unit vectors ê, that are oriented by the angle (Qt), where is a constant angular rate. 52 €3 3> 2t 55 Λ Из At the instant when Qt = 90°, the spacecraft S is oriented relative to the orbit such that 8₁ = 0° Space-three 1-2-3 angles 0₂ = 60° and ES = $₂ rad/s 0₁ = 135° (a) At this instant, determine the direction cosine matrix that describes the orientation of the spacecraft with respect to the inertial frame N.arrow_forward
- This problem illustrates that the factor of safety for a machine element depends on the particular point selected for analysis. Here you are to compute factors of safety, based upon the distortion-energy theory, for stress elements at A and B of the member shown in the figure. This bar is made of AISI 1006 cold-drawn steel and is loaded by the forces F = 1.100 kN, P = 8.00 kN, and T = 50.00 N-m. Given: Sy = 280 MPa. B -100 mm- 15-mm D. a) Determine the value of the axial stress at point B. b) Determine the value of the shear stress at point B. c) Determine the value of the Von Mises stress at point B. P Farrow_forwardA piston-cylinder device initially contains 0.08 m^3 of nitrogen gas at 130 kPa and 170°C. The nitrogen is expanded to a pressure of 80 kPa via isentropic expansion. Determine the final temperature and the boundary work done by the system during this process.arrow_forwardA Carnot (ideal) heat pump is to be used to heat a house and maintain it at 22°C in winter. On a day when the average outdoor temperature remains at about 0°C, the house is estimated to lose heat at a rate of 65,000 kJ/h. If the heat pump consumes 6 kW of power while operating, determine: (a) how long the heat pump ran on that day (b) the total heating costs, assuming an average price of 11¢/kWh for electricity (c) the heating cost for the same day if an 85% efficient electric furnace is used instead of a heat pump.arrow_forward
- From the information in the image, I needed to find the orientation of U relative to Q in vector basis q_hat. I transformed the euler angle/axis representation to euler parameters. Then I got its conjugate in order to get the euler parameter in N frame relative to Q. The problem gave the euler angle/axis representation in Q frame relative to N, so I needed to find the conjugate. Then I used the euler parameter rule of successive rotation to find the final euler parameters that describe the orientation of U relative to Q. However that orientation is in n_hat which is the intermediate frame. How do I get the final result in q_hat?arrow_forwardA proposed method of power generation involves collecting and storing solar energy in large artificial lakes a few meters deep, called solar ponds. Solar energy is absorbed by all parts of the pond, and the water temperature rises everywhere. The top part of the pond, however, loses much of the heat it absorbs to the atmosphere, and as a result, the cool surface water serves as insulation for the bottom part of the pond and helps trap the energy there. Usually, salt is planted at the bottom of the pond to prevent the rise of this hot water to the top. A heat engine that uses an organic fluid, such as alcohol, as the working fluid can be operated between the top and the bottom portions of the pond. If the water temperature is 27°C near the surface and 72°C near the bottom of the pond, determine the maximum thermal efficiency that this power plant can have. Treat the cycle as an ideal heat engine. Would a heat engine operating under these temperature conditions (27°C and 72°C) be…arrow_forwardA standard Carnot heat engine cycle is executed in a closed system between the temperature limits of 320 and 1350 K, with air as the working fluid. The pressures before and after the isothermal compression are 150 and 300 kPa, respectively. Sketch the TS diagram for this cycle. If the net work output per cycle is 0.75 kJ, determine the efficiency of the cycle and the heat transfer to the air (working fluid) per cycle.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Differences between Temporary Joining and Permanent Joining.; Author: Academic Gain Tutorials;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PTr8QZhgXyg;License: Standard Youtube License