
Concept explainers
Classify each of the structures shown as completely, partially, or improperly constrained; if completely constrained, further classify as determinate or indeterminate. (All members can act both in tension and in compression.)
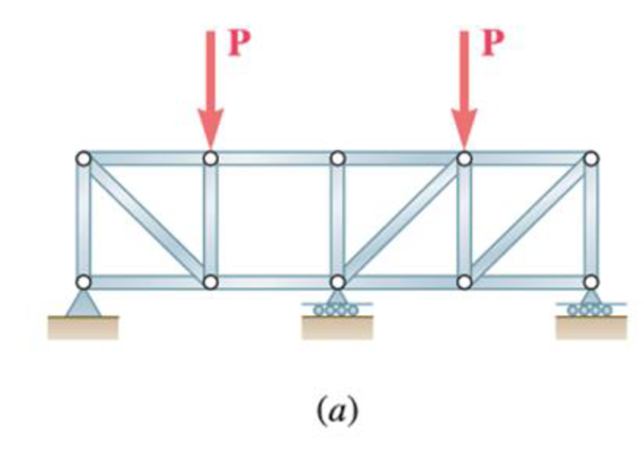
(a)
Classify the given structure as completely, partially, or improperly constrained and if completely constrained, further classify as determinate or indeterminate.
Answer to Problem 6.70P
The given structure is completely constrained and determinate.
Explanation of Solution
The structure is shown in Fig. P6.70 (a). The free-body diagram of the truss is given in Figure 1.
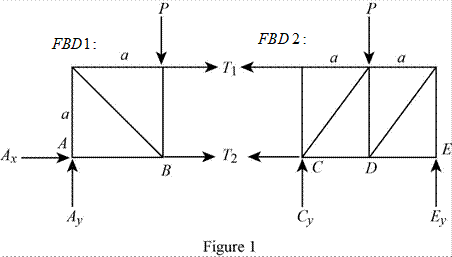 |
Write the condition for a truss to be completely constrained.
Here,
Write the condition for a truss to be partially constrained.
Write the expression for a truss to be indeterminate.
Write the expression for the condition for equilibrium.
Here,
Conclusion:
For the given truss,
Compute
Compute
So, for the given system,
Apply the condition for equilibrium in equation (IV) about various points of the structure in the free-body diagrams
Apply the condition for equilibrium in equation (V) about various points of the structure in the free-body diagrams
Since each section is a simple truss with reactions determined, the given structure is completely constrained and determinate.
Therefore, the given structure is completely constrained and determinate.
(b)
Classify the given structure as completely, partially, or improperly constrained and if completely constrained, further classify as determinate or indeterminate.
Answer to Problem 6.70P
The given structure is partially constrained.
Explanation of Solution
The structure is shown in Fig. P6.70 (b). It is a non-simple truss.
From equations (I), and (II), the conditions for the state of constrain of the structure is as follows,
Conclusion:
For the given truss,
Compute
Compute
So, for the given system,
Therefore, the given structure is partially constrained.
(c)
Classify the given structure as completely, partially, or improperly constrained and if completely constrained, further classify as determinate or indeterminate.
Answer to Problem 6.70P
The given structure is improperly constrained and indeterminate.
Explanation of Solution
The structure is shown in Fig. P6.70 (c). The free-body diagram of the truss is given in Figure 2.
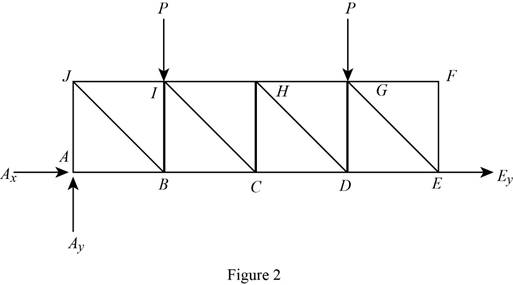
From equations (I), and (II), the conditions for the state of constrain of the structure is as follows,
Conclusion:
For the given truss,
Compute
Compute
It is clear that for the given system, the condition in equation (I) is satisfied, but the horizontal reaction forces
Therefore, the given structure is improperly constrained and indeterminate.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics
- this is an old practice exam, the answer is Fmin = 290.5lb but howarrow_forwardThis is an exam review question. The answer is Pmin = 622.9 lb but whyarrow_forwardPlease do not use any AI tools to solve this question. I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor. No AI-generated responses, please.arrow_forward
- Please do not use any AI tools to solve this question. I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor. No AI-generated responses, please.arrow_forwardPlease do not use any AI tools to solve this question. I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor. No AI-generated responses, please.arrow_forwardThis is an old practice exam. Fce = 110lb and FBCD = 62 lb but whyarrow_forward
- Quiz/An eccentrically loaded bracket is welded to the support as shown in Figure below. The load is static. The weld size for weld w1 is h1 = 4mm, for w2 h2 = 6mm, and for w3 is h3 =6.5 mm. Determine the safety factor (S.f) for the welds. F=29 kN. Use an AWS Electrode type (E100xx). 163 mm S 133 mm 140 mm Please solve the question above I solved the question but I'm sure the answer is wrong the link : https://drive.google.com/file/d/1w5UD2EPDiaKSx3W33aj Rv0olChuXtrQx/view?usp=sharingarrow_forwardQ2: (15 Marks) A water-LiBr vapor absorption system incorporates a heat exchanger as shown in the figure. The temperatures of the evaporator, the absorber, the condenser, and the generator are 10°C, 25°C, 40°C, and 100°C respectively. The strong liquid leaving the pump is heated to 50°C in the heat exchanger. The refrigerant flow rate through the condenser is 0.12 kg/s. Calculate (i) the heat rejected in the absorber, and (ii) the COP of the cycle. Yo 8 XE-V lo 9 Pc 7 condenser 5 Qgen PG 100 Qabs Pe evaporator PRV 6 PA 10 3 generator heat exchanger 2 pump 185 absorberarrow_forwardQ5:(? Design the duct system of the figure below by using the balanced pressure method. The velocity in the duct attached to the AHU must not exceed 5m/s. The pressure loss for each diffuser is equal to 10Pa. 100CFM 100CFM 100CFM ☑ ☑ 40m AHU -16m- 8m- -12m- 57m 250CFM 40m -14m- 26m 36m ☑ 250CFMarrow_forward
- A mass of ideal gas in a closed piston-cylinder system expands from 427 °C and 16 bar following the process law, pv1.36 = Constant (p times v to the power of 1.36 equals to a constant). For the gas, initial : final pressure ratio is 4:1 and the initial gas volume is 0.14 m³. The specific heat of the gas at constant pressure, Cp = 0.987 kJ/kg-K and the specific gas constant, R = 0.267 kJ/kg.K. Determine the change in total internal energy in the gas during the expansion. Enter your numerical answer in the answer box below in KILO JOULES (not in Joules) but do not enter the units. (There is no expected number of decimal points or significant figures).arrow_forwardmy ID# 016948724. Please solve this problem step by steparrow_forwardMy ID# 016948724 please find the forces for Fx=0: fy=0: fz=0: please help me to solve this problem step by steparrow_forward
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
