
A timber beam AB of Length L and rectangular cross section carries a uniformly distributed load w and is supported as shown. (a) Show that the ratio τm/σm of the maximum values of the shearing and normal stresses in the beam is equal to 2h/L, where h and L are, respectively, the depth and the length of the beam. (b) Determine the depth h and the width b of the beam, knowing that L = 5 m, w = 8 kN/m, τm = 1.08 MPa, and σm = 12 MPa.
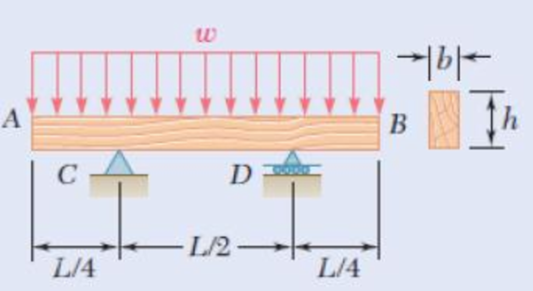
Fig. P6.20
(a)
To show that: The ratio
Answer to Problem 20P
The ratio
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The length of the beam AB is L.
The depth of the beam is h.
Calculation:
Calculate the area of the cross section as shown below.
Here, b is the width of the beam and h is the depth of the beam.
Calculate the section modulus of the cross section as shown below.
Due to the symmetry of the beam reaction at supports C and D are Equal.
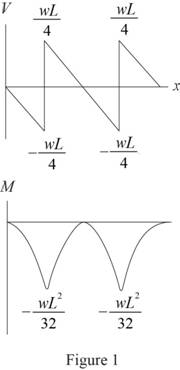
Calculate the shear force as shown below.
Shear force at A,
Shear force at A right,
Shear force at C,
Shear force at D,
Shear force at B,
Calculate the bending moment as shown below.
BM at A,
BM at C,
BM at D,
BM at B,
Sketch the shear force and bending moment diagram as shown in Figure 1.
Calculate the maximum shear stress as shown below.
Substitute
Calculate the maximum normal stress as shown below.
Substitute
Calculate the ratio
Therefore, the ratio
(b)
The depth and width of the beam.
Answer to Problem 20P
The depth of the beam is
The width of the beam is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The length (L) of the beam is
The load is
The maximum shear stress is
The maximum normal stress is
Calculation:
Refer to part (a).
Calculate the depth of the beam as shown below.
Substitute
Hence, the depth of the beam is
Calculate the width of the beam as shown below.
Substitute
Therefore, the width of the beam is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials, 7th Edition
- Copyright 2013 Pearson Education, publishing as Prentice Hall 2. Determine the force that the jaws J of the metal cutters exert on the smooth cable C if 100-N forces are applied to the handles. The jaws are pinned at E and A, and D and B. There is also a pin at F. E 400 mm 15° D B 30 mm² 80 mm/ 20 mm 15° $15° 20 mm 400 mm 15° 100 N 100 N 15°arrow_forwardDraw for it make a match which directionarrow_forwardQ.1) Block A is connected to block B by a pulley system as shown. The weights of blocks A and B are 100 lbs and 70 lbs, respectively. Assume negligible friction between the rope and all pulleys as well as between block B and the incline and neglect the mass of all pulleys and cables. Determine the angle 0 required to keep the system in equilibrium. (At least two FBDs must be drawn for full credit) B Ꮎ 000arrow_forward
- pls solvearrow_forward+1. 0,63 fin r= 0.051 P The stepped rod in sketch is subjected to a tensile force that varies between 4000 and 7000 lb. The rod has a machined surface finish everywhere except the shoulder area, where a grinding operation has been performed to improve the fatigue resistance of the rod. Using a 99% probability of survival, determine the safety factor for infinite life if the rod is made of AISI 1080 steel, quenched and tempered at 800°c Use the Goodman line. Does the part fail at the fillet? Explainarrow_forwardSolve this problem and show all of the workarrow_forward
- I need drawing solution,draw each one by one no Aiarrow_forwardQu. 17 Compute linear density values for [100] for silver (Ag). Express your answer in nm''. . Round off the answer to three significant figures. Qu. 18 Compute linear density value for [111] direction for silver (Ag). Express your answer in nm'. Round off the answer to three significant figures. Qu. 19 Compute planar density value for (100) plane for chromium (Cr). Express your answer in nm?. Round off the answer to two significant figures. Qu. 20 Compute planar density value for (110) plane for chromium (Cr). Express your answer in nm ≥ to four significant figures. show all work please in material engineeringarrow_forward3-142arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





