
(a)
Interpretation:
It is to be determined whether the given solvent is suitable for a reaction involving
Concept introduction:
Leveling effects refers to the effect of a solvent on the behavior of acids and bases. If the reactant is a very strong acid or base, it can react with the solvent in an undesired proton transfer reaction. At equilibrium, the strongest acid that can occur in solution is the protonated solvent, and the strongest base that can occur in solution is the deprotonated solvent. For the leveling effect, a solvent is unsuitable for a particular reactant if the reactant (lower
Answer to Problem 6.9P
With respect to the leveling effect, water is not a suitable solvent for a reaction involving
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of
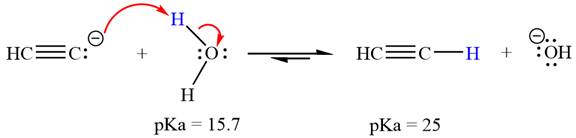
Water,
The solvent effect on the reactant is determined with respect to the leveling effect.
(b)
Interpretation:
It is to be determined whether the given solvent is suitable for a reaction involving
Concept introduction:
Leveling effects refers to the effect of a solvent on the behavior of acids and bases. If the reactant is a very strong acid or base, it can react with the solvent in an undesired proton transfer reaction. At equilibrium, the strongest acid that can occur in solution is the protonated solvent, and the strongest base that can occur in solution is the deprotonated solvent. For the leveling effect, a solvent is unsuitable for a particular reactant if the reactant (lower
Answer to Problem 6.9P
With respect to the leveling effect, ethanol is not a suitable solvent for a reaction involving
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of

Ethanol,
The solvent effect on the reactant is determined with respect to the leveling effect.
(c)
Interpretation:
It is to be determined whether the given solvent is suitable for a reaction involving
Concept introduction:
Leveling effects refers to the effect of a solvent on the behavior of acids and bases. If the reactant is a very strong acid or base, it can react with the solvent in an undesired proton transfer reaction. At equilibrium, the strongest acid that can occur in solution is the protonated solvent, and the strongest base that can occur in solution is the deprotonated solvent. For the leveling effect, a solvent is unsuitable for a particular reactant if the reactant (lower
Answer to Problem 6.9P
With respect to the leveling effect, ethanamide is not a suitable solvent for a reaction involving
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of
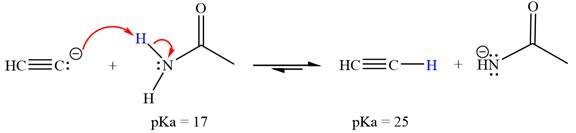
Ethanamide,
The solvent effect on the reactant is determined with respect to the leveling effect.
(d)
Interpretation:
It is to be determined whether the given solvent is suitable for a reaction involving
Concept introduction:
Leveling effects refers to the effect of a solvent on the behavior of acids and bases. If the reactant is a very strong acid or base, it can react with the solvent in an undesired proton transfer reaction. At equilibrium, the strongest acid that can occur in solution is the protonated solvent, and the strongest base that can occur in solution is the deprotonated solvent. For the leveling effect, a solvent is unsuitable for a particular reactant if the reactant (lower
Answer to Problem 6.9P
With respect to the leveling effect,
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of
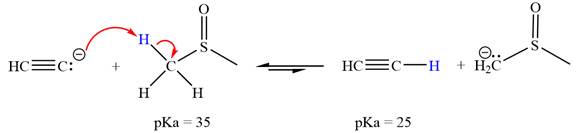
Acetylene,
The solvent effect on the reactant is determined with respect to the leveling effect.
(e)
Interpretation:
It is to be determined whether the given solvent is suitable for a reaction involving
Concept introduction:
Leveling effects refers to the effect of a solvent on the behavior of acids and bases. If the reactant is a very strong acid or base, it can react with the solvent in an undesired proton transfer reaction. At equilibrium, the strongest acid that can occur in solution is the protonated solvent, and the strongest base that can occur in solution is the deprotonated solvent. For the leveling effect, a solvent is unsuitable for a particular reactant if the reactant (lower
Answer to Problem 6.9P
With respect to the leveling effect,
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of
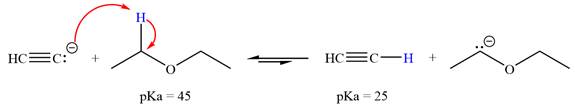
Acetylene,
The solvent effect on the reactant is determined with respect to the leveling effect.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
EBK GET READY FOR ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- (3 pts) Use the Kapustinskii equation to calculate the lattice enthalpy for MgBr2 anddiscuss any differences between this result and that from #4.arrow_forward(3 pts) Silver metal adopts a fcc unit cell structure and has an atomic radius of 144 pm. Fromthis information, calculate the density of silver. Show all work.arrow_forward4. (3 pts) From the information below, determine the lattice enthalpy for MgBr2. Show all work. AH/(kJ mol-¹) Sublimation of Mg(s) +148 lonization of Mg(g) +2187 to Mg2+(g) Vaporization of Br₂(1) +31 Dissociation of Br,(g) +193 Electron gain by Br(g) -331 Formation of MgBr₂(s) -524arrow_forward
- 1. (4 pts-2 pts each part) Consider the crystal structures of NaCl, ZnS, and CsCl (not necessarily shown in this order). a. For one of the three compounds, justify that the unit cell is consistent with stoichiometry of the compound. b. In each of the crystal structures, the cations reside in certain holes in the anions' packing structures. For each compound, what type of holes are occupied by the cations and explain why those particular types of holes are preferred.arrow_forward(2 pts) What do you expect to happen in a Na2O crystal if a Cl− ion replaces one of the O2−ions in the lattice?arrow_forward(2 pts) WSe2 is an ionic compound semiconductor that can be made to be p-type or n-type.What must happen to the chemical composition for it to be p-type? What must happen tothe chemical composition for it to be n-type?arrow_forward
- 8. (2 pts) Silicon semiconductors have a bandgap of 1.11 eV. What is the longest photon wavelength that can promote an electron from the valence band to the conduction band in a silicon-based photovoltaic solar cell? Show all work. E = hv = hc/λ h = 6.626 x 10-34 Js c = 3.00 x 108 m/s 1 eV 1.602 x 10-19 Jarrow_forwardA solution containing 100.0 mL of 0.155 M EDTA buffered to pH 10.00 was titrated with 100.0 mL of 0.0152 M Hg(ClO4)2 in a cell: calomel electrode (saturated)//titration solution/Hg(l) Given the formation constant of Hg(EDTA)2-, logKf= 21.5, and alphaY4-=0.30, find out the cell voltage E. Hg2+(aq) + 2e- = Hg(l) E0= 0.852 V E' (calomel electrode, saturated KCl) = 0.241 Varrow_forwardFrom the following reduction potentials I2 (s) + 2e- = 2I- (aq) E0= 0.535 V I2 (aq) + 2e- = 2I- (aq) E0= 0.620 V I3- (aq) + 2e- = 3I- (aq) E0= 0.535 V a) Calculate the equilibrium constant for I2 (aq) + I- (aq) = I3- (aq). b) Calculate the equilibrium constant for I2 (s) + I- (aq) = I3- (aq). c) Calculate the solubility of I2 (s) in water.arrow_forward
- 2. (3 pts) Consider the unit cell for the spinel compound, CrFe204. How many total particles are in the unit cell? Also, show how the number of particles and their positions are consistent with the CrFe204 stoichiometry - this may or may not be reflected by the particle colors in the diagram. (HINT: In the diagram, the blue particle is in an interior position while each red particle is either in a corner or face position.)arrow_forwardFrom the following potentials, calculate the activity of Cl- in saturated KCl. E0 (calomel electrode)= 0.268 V E (calomel electrode, saturated KCl)= 0.241 Varrow_forwardCalculate the voltage of each of the following cells. a) Fe(s)/Fe2+ (1.55 x 10-2 M)//Cu2+ (6.55 x 10-3 M)/Cu(s) b) Pt, H2 (0.255 bar)/HCl (4.55 x 10-4 M), AgCl (sat'd)/Ag Fe2+ +2e- = Fe E0= -0.44 V Cu2+ + 2e- = Cu E0= 0.337 V Ag+ + e- = Ag E0= 0.799 V AgCl(s) + e- = Ag(s) + Cl- E0= 0.222 V 2H+ + 2e- = H2 E0= 0.000 Varrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning


