
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The pKa value for a protonated
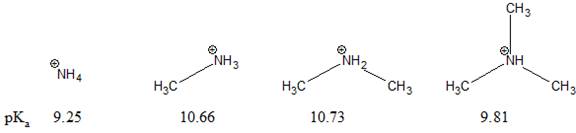
Concept introduction:
The stability of a charged species depends on the groups attached to the positively charged atom. The electron withdrawing group increases the concentration of positive charge on the nearby atom. While, the electron donating group decreases the concentration of positive charge on the nearby atom. This increases the stability of nearby positively charged atom. In general, cations are stabilized by electron-donating groups near the positive charge.
(b)
Interpretation:
The pKa value for a protonated amine (R3NH+) depends on the number of alkyl groups attached to N, as shown below. This order disagrees with what we would predict using charge stability. The reason for the discrepancy is to be explained.
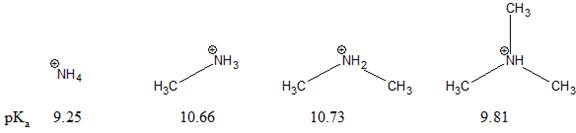
Concept introduction:
The stability of a charged species decreases as the effective electronegativity of an atom bearing a positive charge increases. The electron donating group decreases the concentration of positive charge on the nearby atom. This increases the stability of nearby positively charged atom. In general, cations are stabilized by electron-donating groups near the positive charge. Bulky group around the cation, reduces the solvation process. This decreases the stability of the ion and increases acidity.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 6 Solutions
EBK GET READY FOR ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- Would the following organic synthesis occur in one step? Add any missing products, required catalysts, inorganic reagents, and other important conditions. Please include a detailed explanation and drawings showing how the reaction may occur in one step.arrow_forward(a) Sketch the 'H NMR of the following chemical including the approximate chemical shifts, the multiplicity (splitting) of all signals and the integration (b) How many signals would you expect in the 13C NMR? CH3arrow_forwardDraw the Show the major and minor product(s) for the following reaction mechanisms for both reactions and show all resonance structures for any Explain why the major product is favoured? intermediates H-Brarrow_forward
- 3. Draw ALL THE POSSBILE PRODUCTS AND THE MECHANISMS WITH ALL RESONANCE STRUCTURES. Explain using the resonance structures why the major product(s) are formed over the minor product(s). H₂SO4, HONO CHarrow_forward7. Provide the product(s), starting material(s) and/or condition(s) required for the No mechanisms required. below reaction HO + H-I CI FO Br2, FeBr3 O I-Oarrow_forward6. Design the most efficient synthesis of the following product starting from phenot Provide the reaction conditions for each step (more than one step is required) and explain the selectivity of each reaction. NO MECHANISMS ARE REQUIRED. OH step(s) CIarrow_forward
- What is the skeletal structure of the product of the following organic reaction?arrow_forwardIf a reaction occurs, what would be the major products? Please include a detailed explanation as well as a drawing showing how the reaction occurs and what the final product is.arrow_forwardWhat is the major organic product of the following nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction of an acid chloride below?arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

