
(a)
Interpretation:
The engineering stress-strain curve should be plotted and the 0.2 % offset yield strength should be calculated for the given data of polyvinyl chloride.
Concept Introduction:
The maximum amount of elastic deformation which is bearable by any material is defined as yield strength.
Answer to Problem 6.39P
The yield strength for 0.2% offset is 11,600 psi for a given sample of polyvinyl chloride.
Explanation of Solution
The tabular data providing details about the load and length difference for a given sample.
Let us calculate the stress for the sample with the help of below formula:
| Load (lb.) | |
| 0 | 0.00000 |
| 300 | 0.00746 |
| 600 | 0.01496 |
| 900 | 0.02374 |
| 1200 | 0.032 |
| 1500 | 0.046 |
| 1660 | 0.07 (maximum load) |
| 1600 | 0.094 |
| 1420 | 0.12 (fracture) |
For determining the strain of the a given sample,
With the use of a givenspreadsheet and applied loads, one can tabulate the engineering stress and strain as follows:
| Load (F) | Length ( | Change in length ( | Gage length | Stress ( | Strain ( |
| 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| 300 | 2 | 0.00746 | 2.00746 | 2386.635 | 0.00373 |
| 600 | 2 | 0.01496 | 2.01496 | 4773.27 | 0.00748 |
| 900 | 2 | 0.02374 | 2.02374 | 7159.905 | 0.0.1187 |
| 1200 | 2 | 0.032 | 2.032 | 9546.539 | 0.016 |
| 1500 | 2 | 0.046 | 2.046 | 11933.17 | 0.023 |
| 1660 | 2 | 0.07 | 2.07 | 13206.05 | 0.035 |
| 1600 | 2 | 0.094 | 2.094 | 12728.72 | 0.047 |
| 1420 | 2 | 0.12 | 2.12 | 11296.74 | 0.06 |
Now, one can plot the stress-strain curve from the above gathered tabular data as below:
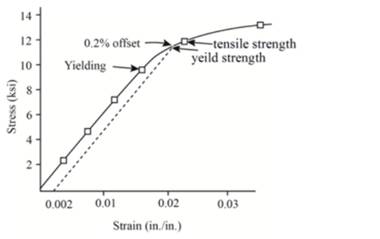
The above graph can provide the value of yield strength for 0.2% offset as 11,600 psi.
Therefore, polyvinyl chloride sample has the yield strength for 0.2% offset as 11,600 psi.
(b)
Interpretation:
With the help of plotted engineering stress-strain curve, the tensile strength should be calculated.
Concept Introduction:
Tensile strength can be defined as the measurement of maximum deformation which can be bearable by any material without undergoing necking condition.
Answer to Problem 6.39P
The tensile strength will be 12728.72 psi for a given sample of polyvinyl chloride.
Explanation of Solution
With the use of a givenspreadsheet and applied loads, one can tabulate the engineering stress and strain as below:
| Load (F) | Length ( | Change in length ( | Gage length | Stress ( | Strain ( |
| 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| 300 | 2 | 0.00746 | 2.00746 | 2386.635 | 0.00373 |
| 600 | 2 | 0.01496 | 2.01496 | 4773.27 | 0.00748 |
| 900 | 2 | 0.02374 | 2.02374 | 7159.905 | 0.0.1187 |
| 1200 | 2 | 0.032 | 2.032 | 9546.539 | 0.016 |
| 1500 | 2 | 0.046 | 2.046 | 11933.17 | 0.023 |
| 1660 | 2 | 0.07 | 2.07 | 13206.05 | 0.035 |
| 1600 | 2 | 0.094 | 2.094 | 12728.72 | 0.047 |
| 1420 | 2 | 0.12 | 2.12 | 11296.74 | 0.06 |
Now, one can plot the stress-strain curve from the above gathered tabular data as below:
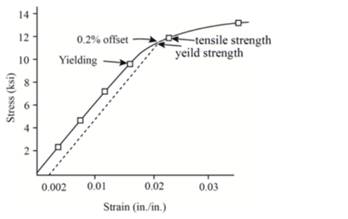
The above graph can provide the value of tensile strength as 12728.72 psi.
Therefore, the given sample of polyvinyl chloride has the tensile strength of12728.72 psi.
(c)
Interpretation:
With the help of plotted engineering stress-strain curve, the value of modulus of elasticity should be calculated.
Concept Introduction:
Modulus of elasticity is also known as coefficient of elasticity or elastic modulus and can be defined as the ratio of the stress in the a given object body to the corresponding strain.
Answer to Problem 6.39P
The value of modulus of elasticity is 603193 psi for give polyvinyl chloride.
Explanation of Solution
With the use of a givenspreadsheet and applied loads, one can tabulate the engineering stress and strain as below:
| Load (F) | Length ( | Change in length ( | Gage length | Stress ( | Strain ( |
| 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| 300 | 2 | 0.00746 | 2.00746 | 2386.635 | 0.00373 |
| 600 | 2 | 0.01496 | 2.01496 | 4773.27 | 0.00748 |
| 900 | 2 | 0.02374 | 2.02374 | 7159.905 | 0.0.1187 |
| 1200 | 2 | 0.032 | 2.032 | 9546.539 | 0.016 |
| 1500 | 2 | 0.046 | 2.046 | 11933.17 | 0.023 |
| 1660 | 2 | 0.07 | 2.07 | 13206.05 | 0.035 |
| 1600 | 2 | 0.094 | 2.094 | 12728.72 | 0.047 |
| 1420 | 2 | 0.12 | 2.12 | 11296.74 | 0.06 |
Now, one can plot the stress-strain curve from the above gathered tabular data as below:
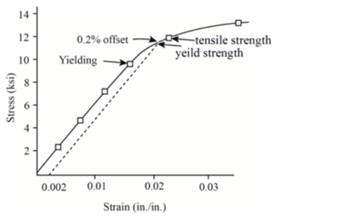
The formula of Hook's law can be used for calculating modulus of elasticity.
Therefore, the value of modulus of elasticity for given polyvinyl chloride is 603193 psi.
(d)
Interpretation:
With the help of plotted engineering stress-strain curve, the value of % elongation should be calculated.
Concept Introduction:
Elongation is defined as term used to determine the change in gauge length of any material when it is on static tension test.
Answer to Problem 6.39P
The value of % elongation is 4.5 % for a given polyvinyl chloride.
Explanation of Solution
With the use of a givenspreadsheet and applied loads, one can tabulate the engineering stress and strain as below:
| Load (F) | Length ( | Change in length ( | Gage length | Stress ( | Strain ( |
| 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| 300 | 2 | 0.00746 | 2.00746 | 2386.635 | 0.00373 |
| 600 | 2 | 0.01496 | 2.01496 | 4773.27 | 0.00748 |
| 900 | 2 | 0.02374 | 2.02374 | 7159.905 | 0.0.1187 |
| 1200 | 2 | 0.032 | 2.032 | 9546.539 | 0.016 |
| 1500 | 2 | 0.046 | 2.046 | 11933.17 | 0.023 |
| 1660 | 2 | 0.07 | 2.07 | 13206.05 | 0.035 |
| 1600 | 2 | 0.094 | 2.094 | 12728.72 | 0.047 |
| 1420 | 2 | 0.12 | 2.12 | 11296.74 | 0.06 |
Now, one can plot the stress-strain curve from the above gathered tabular data as below:
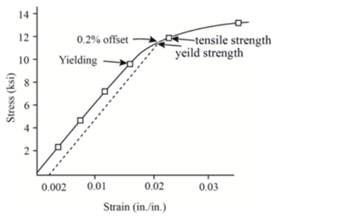
The following formula can be used to determine the value of % elongation.
Therefore, thevalue of % elongationis 4.5% for given polyvinyl chloride sample.
(e)
Interpretation:
With the help of plotted engineering stress-strain curve, the value of % reduction in area should be calculated.
Concept Introduction:
Reduction if area of any material is directly related to the reduction in cross-section area of the tensile test piece after fracture.
Answer to Problem 6.39P
The value of % reduction in area is 3.5 % for a given polyvinyl chloride.
Explanation of Solution
With the use of a givenspreadsheet and applied loads, one can tabulate the engineering stress and strain as below:
| Load (F) | Length ( | Change in length ( | Gage length | Stress ( | Strain ( |
| 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| 300 | 2 | 0.00746 | 2.00746 | 2386.635 | 0.00373 |
| 600 | 2 | 0.01496 | 2.01496 | 4773.27 | 0.00748 |
| 900 | 2 | 0.02374 | 2.02374 | 7159.905 | 0.0.1187 |
| 1200 | 2 | 0.032 | 2.032 | 9546.539 | 0.016 |
| 1500 | 2 | 0.046 | 2.046 | 11933.17 | 0.023 |
| 1660 | 2 | 0.07 | 2.07 | 13206.05 | 0.035 |
| 1600 | 2 | 0.094 | 2.094 | 12728.72 | 0.047 |
| 1420 | 2 | 0.12 | 2.12 | 11296.74 | 0.06 |
Now, one can plot the stress-strain curve from the above gathered tabular data as below:
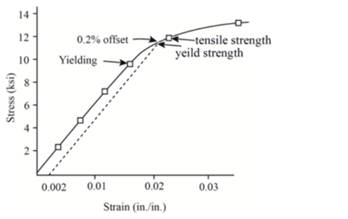
The following formula can be used to determine the value of % reduction in area.
Therefore, the given polyvinyl chloride sample carries 3.5% the value of % reduction in area.
(f)
Interpretation:
With the help of plotted engineering stress-strain curve, the engineering stress should be determined at fracture.
Concept Introduction:
Engineering stress is a term explained as a force or applied load on the a given object's cross-sectional area and it is also known as nominal stress.
Answer to Problem 6.39P
The engineering stress is 11,296.74 psi fora given polyvinyl chloride.
Explanation of Solution
With the use of a givenspreadsheet and applied loads, one can tabulate the engineering stress and strain as below:
| Load (F) | Length ( | Change in length ( | Gage length | Stress ( | Strain ( |
| 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| 300 | 2 | 0.00746 | 2.00746 | 2386.635 | 0.00373 |
| 600 | 2 | 0.01496 | 2.01496 | 4773.27 | 0.00748 |
| 900 | 2 | 0.02374 | 2.02374 | 7159.905 | 0.0.1187 |
| 1200 | 2 | 0.032 | 2.032 | 9546.539 | 0.016 |
| 1500 | 2 | 0.046 | 2.046 | 11933.17 | 0.023 |
| 1660 | 2 | 0.07 | 2.07 | 13206.05 | 0.035 |
| 1600 | 2 | 0.094 | 2.094 | 12728.72 | 0.047 |
| 1420 | 2 | 0.12 | 2.12 | 11296.74 | 0.06 |
Now, one can plot the stress-strain curve from the above gathered tabular data as below:
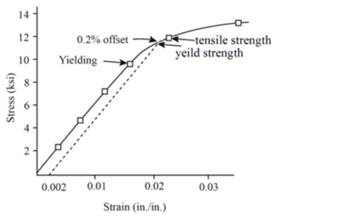
Above graph is extended upto fracture strength as follows:
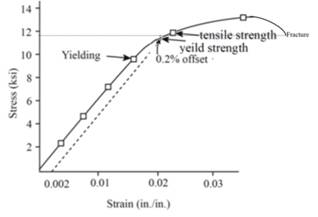
Therefore,the value of engineering stress will be 11,296.74 psi for a given polyvinyl chloride.
(g)
Interpretation:
With the help of plotted engineering stress-strain curve, the value of modulus of resilience should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
The amount of energy required to get absorbed by the material to return back to its original state is defined as resilience.
Modulus of resilience can be defined as the energy required by the material to return from its stress condition from zero to the yield stress limit.
Answer to Problem 6.39P
The value of modulus of resilience is 76.37 psi for a given polyvinyl chloride.
Explanation of Solution
With the use of a givenspreadsheet and applied loads, one can tabulate the engineering stress and strain as below:
| Load (F) | Length ( | Change in length ( | Gage length | Stress ( | Strain ( |
| 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| 300 | 2 | 0.00746 | 2.00746 | 2386.635 | 0.00373 |
| 600 | 2 | 0.01496 | 2.01496 | 4773.27 | 0.00748 |
| 900 | 2 | 0.02374 | 2.02374 | 7159.905 | 0.0.1187 |
| 1200 | 2 | 0.032 | 2.032 | 9546.539 | 0.016 |
| 1500 | 2 | 0.046 | 2.046 | 11933.17 | 0.023 |
| 1660 | 2 | 0.07 | 2.07 | 13206.05 | 0.035 |
| 1600 | 2 | 0.094 | 2.094 | 12728.72 | 0.047 |
| 1420 | 2 | 0.12 | 2.12 | 11296.74 | 0.06 |
Now, one can plot the stress-strain curve from the above gathered tabular data as below:
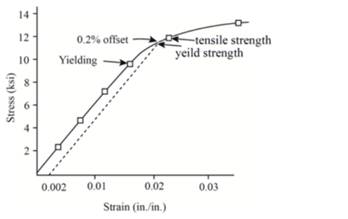
From the graph, the value of modulus of resilience is 9546.539 psi.
Now,
Therefore, the sample of polyvinyl chloride has 76.37 psi as the value of modulus of resilience.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Essentials Of Materials Science And Engineering
- Given the following addresses, which two addresses conflict in the cache: The numb of locations in the cache is 2048, the cahche is indexed by address bits 15 to 5 and the tag bits are from 31 to 16. (a) 0x0000 0100 (b) 0x0000 1400 (c) 0x0010 0100 (d) 0x0100 0140arrow_forwardWrite a love poem about someone longing for a sandwich. Make it sonnet,and give it a tone that straddles a serious love poem and whimsy appropriate for a poem about a sandwich.arrow_forwardpower systems engineeringarrow_forward
- power systemsarrow_forward2. Consider the following pseudocode for partition: function partition (A,L,R) pivotkey = A [R] t = L for i L to R-1 inclusive: if A[i] A[i] t = t + 1 end if end for A [t] A[R] return t end function Suppose we call partition (A,0,5) on A=[10,1,9,2,8,5]. Show the state of the list at the indicated instances. Initial A After i=0 ends After 1 ends After i 2 ends After i = 3 ends After i = 4 ends After final swap 10 19 285 [12 pts]arrow_forwardDraw as a 3D object/Isometricarrow_forward
- power systemsarrow_forward.NET Interactive Solving Sudoku using Grover's Algorithm We will now solve a simple problem using Grover's algorithm, for which we do not necessarily know the solution beforehand. Our problem is a 2x2 binary sudoku, which in our case has two simple rules: •No column may contain the same value twice •No row may contain the same value twice If we assign each square in our sudoku to a variable like so: 1 V V₁ V3 V2 we want our circuit to output a solution to this sudoku. Note that, while this approach of using Grover's algorithm to solve this problem is not practical (you can probably find the solution in your head!), the purpose of this example is to demonstrate the conversion of classical decision problems into oracles for Grover's algorithm. Turning the Problem into a Circuit We want to create an oracle that will help us solve this problem, and we will start by creating a circuit that identifies a correct solution, we simply need to create a classical function on a quantum circuit that…arrow_forwardpower systemsarrow_forward
- Post-tensioned AASHTO Type II girders are to be used to support a deck with unsupported span equal to 10 meters. Two levels of Grade 250, 10 x 15.2 mm Ø 7-wire strand are used to tension the girders with 5 tendons per level, where the tendons on top stressed before the ones on the bottom. The girder is simply supported at both ends. The anchors are located 100 mm above the neutral axis at the supports while the eccentricity is measured at 400 mm at the midspan. The tendon profile follows a parabolic shape using a rigid metal sheathing. A concrete topping (slab) 130 mm thick is placed above the beam with a total tributary width of 4 meters. Use maximum values for ranges (table values). Assume that the critical section of the beam is at 0.45LDetermine the losses (friction loss, anchorage, elastic shortening, creep, shrinkage, relaxation). Determine the stresses at the top fibers @ critical section before placing a concrete topping, right after stress transfer. Determine the stress at the…arrow_forwardpower systemsarrow_forwardpower system engineeringarrow_forward
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsEngineeringISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsEngineeringISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Essentials Of Materials Science And EngineeringEngineeringISBN:9781337385497Author:WRIGHT, Wendelin J.Publisher:Cengage,
Essentials Of Materials Science And EngineeringEngineeringISBN:9781337385497Author:WRIGHT, Wendelin J.Publisher:Cengage, Industrial Motor ControlEngineeringISBN:9781133691808Author:Stephen HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Industrial Motor ControlEngineeringISBN:9781133691808Author:Stephen HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Basics Of Engineering EconomyEngineeringISBN:9780073376356Author:Leland Blank, Anthony TarquinPublisher:MCGRAW-HILL HIGHER EDUCATION
Basics Of Engineering EconomyEngineeringISBN:9780073376356Author:Leland Blank, Anthony TarquinPublisher:MCGRAW-HILL HIGHER EDUCATION Structural Steel Design (6th Edition)EngineeringISBN:9780134589657Author:Jack C. McCormac, Stephen F. CsernakPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Steel Design (6th Edition)EngineeringISBN:9780134589657Author:Jack C. McCormac, Stephen F. CsernakPublisher:PEARSON Fundamentals of Materials Science and Engineering...EngineeringISBN:9781119175483Author:William D. Callister Jr., David G. RethwischPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Materials Science and Engineering...EngineeringISBN:9781119175483Author:William D. Callister Jr., David G. RethwischPublisher:WILEY





