
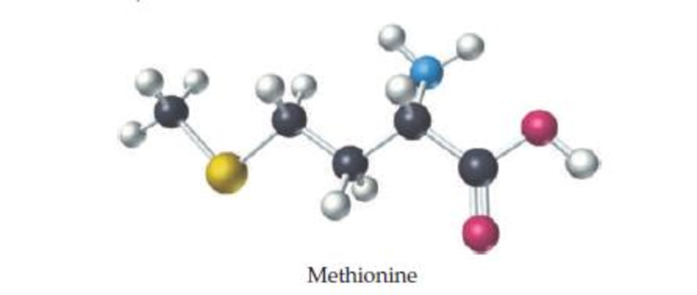
Methionine, an amino acid used by organisms to make proteins, can be represented by the following ball-and-stick molecular model. Write the formula for methionine, and give its molecular weight (red = O, black = C, blue = N, yellow = S, white = H).
Interpretation:
The formula and molecular weight for methionine and should be determined by using the given ball- and- stick molecular model.
Concept Introduction:
Molecular Formula: It is the simplest representation of composition of chemical substance where each and every type of atom is written with the total number of the atom present in the substance.
Molecular weight: The sum of mass of all atoms present in formula of chemical substance is referred as molecular or formula weight of that substance.
Answer to Problem 6.15UKC
The empirical formula for the given structure is
The molecular weight of
Explanation of Solution
Comparing the given details such as red color indicates
The molecular weight for
Finally, molecular weight is obtained by adding
The molecular formula for methionine and molecular weight is determined by using the given ball- and- stick molecular model with details.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (8th Edition)
- what are the different classes and some examples of neuroprotectants that can be used to treat, prevent, or combat neurotoxicity/a neurotoxicant...for example, antioxidants, nutraceuticals, etc.,..?arrow_forwardImagine that aldolase can react with the seven carbon molecule Sedoheptulose-1,7-bisphosphate (below). Use the mechanism to predict the two products generated. Please draw out the stereochemistry in a fischer projection.arrow_forwardSodium borohydride (NaBH4) is a potent inhibitor of aldolase. It is known to ONLY inhibit theenzyme when it is complexed with substrate. Treatment of the enzyme alone has no effect.What is the mechanism for this inhibition? Please draw out the mechanism and show how it inhibits this.arrow_forward
- Show the fate of the proton on the 4-Oxygen molecule of F-1,6-BP. Please include a drawing showing the electron flow that occurs.arrow_forward1. Which one is the major organic product obtained from the following aldol condensation? O NaOH, H₂O heat A B C D Earrow_forwardAn organic chemist ordered the wrong item. She wanted to obtain 1-hydroxy-2-butanone, butinstead ordered 2-hydroxybutyraldehyde. As a good biochemist, show how the organic chemistcould use biological catalysis to make her desired compound. Please show the mechanism by drawing.arrow_forward
- Show the fate of the hydrogen on carbon-2 of glucose. Please draw out the structure using curve arrows to show electron flow.arrow_forward3. Which one of the compounds below is the major product formed by the reaction sequence shown here? CH3 + CH3NO2 NaOH H2, Ni ? nitromethane acetophenone OH OH HO HN- u x x x x Ph A HO -NH2 HO H Ph Ph Ph N- H B Ph NH2 D Earrow_forward4. Only ONE of the five compounds below can be prepared by an aldol condensation in which a single carbonyl compound is treated with base. Which one is it? To solve this problem, reverse the aldol condensation that formed each of these molecules to find out what two molecules came together to make the products. The one in which the two molecules are identical is the answer. Ph Ph ཚིག གནས ག ནཱ ཀ ན ཀནཱ A Ph H B Ph Ph H D Ph. Ph Ph E Harrow_forward
- 5. Which one is the major organic product obtained from the following reaction sequence? First, equimolar amounts of cyclopentanone and LDA are mixed at -78°C. Then propionaldehyde (propanal) is added. Addition of aqueous acid completes the process. LDA, -78°C. 1. 2. H₂O* H A B H 0 D H H Earrow_forward2. Which one is the major organic product obtained from the following reaction? NaOH, H₂O heat A B C D Earrow_forwardCH3CH2CHO + propanal PhCH2CHO 2-phenylacetaldehyde mixture of four products NaOH 10. In the crossed aldol reaction of propanal and 2-phenylacetaldehyde shown above, a mixture of four products will be formed. Which ONE of the compounds below will NOT be formed in this crossed aldol reaction? OH Ph A H OH OH Ph H B OH OH H H H Ph Ph C Ph D Earrow_forward
 Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage Learning Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College





