
Concept explainers
The following selected data were taken from the accounting records of Metcalf Manufacturing. The company uses direct-labor hours as its cost driver for
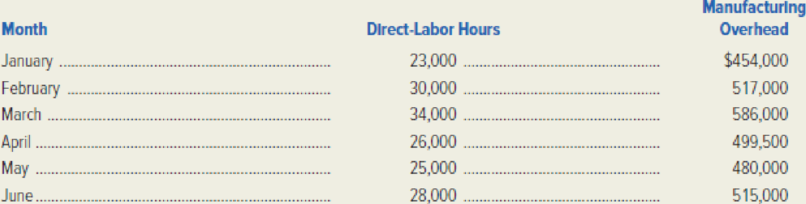
March’s costs consisted of machine supplies ($102,000),
The manufacturing overhead figures presented in the preceding table do not include Metcalf’s supervisory labor cost, which is step-fixed in nature. For volume levels of less than 15,000 hours, supervisory labor amounts to $45,000. The cost is $90,000 from 15,000–29,999 hours and $135,000 when activity reaches 30,000 hours or more.
Required:
- 1. Determine the machine supplies cost and depreciation for January.
- 2. Using the high-low method, analyze Metcalf’s plant maintenance cost and calculate the monthly fixed portion and the variable cost per direct-labor hour.
- 3. Assume that present cost behavior patterns continue into the latter half of the year. Estimate the total amount of manufacturing overhead the company can expect in November if 29,500 direct-labor hours are worked.
- 4. Briefly explain the difference between a fixed cost and a step-fixed cost.
- 5. Assume that a company has a step-fixed cost. Generally speaking, where on a step should the firm attempt to operate if it desires to achieve a maximum
return on its investment ?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 6 Solutions
Managerial Accounting: Creating Value in a Dynamic Business Environment
- Sales in Northway Inc. increased from $45,000 per year to $48,600 per year while net operating income increased from $12,000 to $15,600. Given this data, the company's degree of operating leverage must have been: a) 2.56 b) 3.08 c) 3.75 d) 5.05 help me with thisarrow_forwardFixed order quantity model?arrow_forwardProvide answer with calculationarrow_forward
- Sales in Northway Inc. increased from $45,000 per year to $48,600 per year while net operating income increased from $12,000 to $15,600. Given this data, the company's degree of operating leverage must have been: a) 2.56 b) 3.08 c) 3.75 d) 5.05arrow_forwardOffice Haven is an office supply store. Office Haven's revenue in the current year is $950 million, and its cost of goods sold is $720 million. Compute Office Haven's gross profit and its gross profit percentage.need answerarrow_forwardCalculate the debt to equity ratio general accountingarrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College

