
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The six-carbon backbones to be highlighted that will need a double bond such that it’s a constitutional isomer of molecules in column 2 of Model 7.
Concept Introduction:
The isomer which has the same molecular formula, but different bonding patterns or different connectivity is said to be constitutional isomer.
(b)
Interpretation:
The reason for the 2 structures given below to not form constitutional isomer needs to be determined.
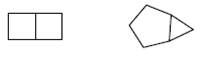
Concept Introduction:
The type of isomers that have the same molecular formula, but their bonding patterns are different, or their connectivity is not the same is said to be constitutional isomer.
(c)
Interpretation:
Whether the given statement is true or false needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
An isomer which has the same molecular formula, but the pattern of bonding or connectivity is different is said to be a constitutional isomer.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 6 Solutions
Custom eBook for Organic Chemistry
- What are the missing reagents for the spots labeled 1 and 3? Please give a detailed explanation and include the drawings and show how the synthesis proceeds with the reagents.arrow_forwardhelp with the rf values i am so confusedarrow_forwardPredict the organic reactant of X and Y that are involved in the reaction below, and draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic reactant. Please include all steps & drawings & explanations.arrow_forward
- What are the missing reagents for the spots labeled 1 and 3? Please give a detailed explanation and include the drawings and show how the synthesis proceeds with the reagents.arrow_forwardPlease provide the complete mechanism for the reaction below and include all appropriate arrows, formal charges, and intermediates. Please draw out the answerarrow_forwardPredict the major organic product for this reaction.arrow_forward
- help me with the rf value i am so confusedarrow_forwardPredict the major organic product for this reaction.arrow_forward3) The following molecule, chloral is a common precursor to chloral hydrate, an acetal type molecule that was a first-generation anesthetic. Draw a mechanism that accounts for tis formation and speculate why it does not require the use of an acid catalyst, like most hemiacetal and acetal reaction: (10 pts) H H₂Oarrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
