
(a)
To graph:Graph of
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Calculation:
Graph of
Similarly,
| x | -2 | -1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| y | -2 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 0 |
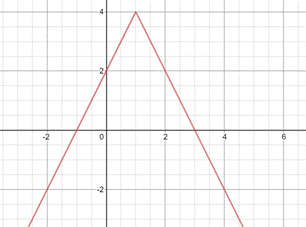
Conclusion:
It is a modulus function.
(b)
Vertex of the graph.
(b)
Answer to Problem 2CB
vertex of the graph is (1,4)
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Graph of the equation
Calculation:
The vertex of the graph is the point from where the line of graph changes its direction.
So the vertex of the graph is (1,4)
Conclusion:
vertex of the graph is (1,4)
(c)
Domain and range of the function.
(c)
Answer to Problem 2CB
The domain is
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Graph of the equation
Calculation:
By the graph it can be seen that the value of x for the equation is all real number
So the domain is
And the value of y axis is from 4 to -8
So the range is
Conclusion:
The domain is
(a)
x and y-intercept of the
(a)
Answer to Problem 2CB
The y-intercept is 2 and the x-intercept is 3.
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Calculation:
The y intercept of the
And the x-intercept of the
Conclusion:
The y-intercept is 2 and the x-intercept is 3.
(e)
The range of function by vertex and sign of a.
(e)
Answer to Problem 2CB
As the vertex is the point from where direction of line change so it will tell us about the highest or lowest value of range of function.and the sign of a will tell about the direction of line coming from so it will tell us the highest value of range.
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
As the vertex is the point from where direction of line change so it will tell us about the highest or lowest value of range of function.and the sign of a will tell about the direction of line coming from so it will tell us the highest value of range.
Conclusion:
As the vertex is the point from where direction of line change so it will tell us about the highest or lowest value of range of function.and the sign of a will tell about the direction of line coming from so it will tell us the highest value of range.
Chapter 5 Solutions
EP ALGEBRA 1-ETEXT ACCESS
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Thinking Mathematically (6th Edition)
Introductory Statistics
Elementary Statistics
College Algebra with Modeling & Visualization (5th Edition)
Elementary Statistics (13th Edition)
College Algebra (7th Edition)
- Solve the linear system of equations attached using Gaussian elimination (not Gauss-Jordan) and back subsitution. Remember that: A matrix is in row echelon form if Any row that consists only of zeros is at the bottom of the matrix. The first non-zero entry in each other row is 1. This entry is called aleading 1. The leading 1 of each row, after the first row, lies to the right of the leading 1 of the previous row.arrow_forwardPRIMERA EVALUACIÓN SUMATIVA 10. Determina la medida de los ángulos in- teriores coloreados en cada poligono. ⚫ Octágono regular A 11. Calcula es número de lados qu poligono regular, si la medida quiera de sus ángulos internos • a=156° A= (-2x+80 2 156 180- 360 0 = 24-360 360=24° • a = 162° 1620-180-360 6=18-360 360=19 2=360= 18 12. Calcula las medida ternos del cuadrilá B X+5 x+10 A X+X+ Sx+6 5x=3 x=30 0 лаб • Cuadrilátero 120° 110° • α = 166° 40' 200=180-360 0 = 26-360 360=20 ひ=360 20 18 J 60° ⚫a=169° 42' 51.43" 169.4143180-340 0 = 10.29 54-360 360 10.2857 2=360 10.2857 @Saarrow_forwardPlease help I'm a working mom trying to help my son last minute (6th grader)! Need help with the blank ones and check the ones he got with full calculation so we can use it to study! Especially the mixed number fractions cause I'm rusty. Thanks in advance!arrow_forward
- e Grade Breakdown x Dashboard | Big Spring HX Dashboard | Big Spring H x Home | Lesson | Assessm cds.caolacourses.edisonlearning.com/lessons/assessmentplayer Co bigspringsd.org bookmarks Prodigy New Tab my video Brielynn... Algebra 2 Part 1-Exam-EDCP.MA003.A D Question 6 D ? 10 17°F Mostly sunny BSMS Home Significant Events in... Classes 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 Solve using row operations: x-3y= -4; 2x - y = 7 Use the paperclip button below to attach files. Student can enter max 2000 characters BISU DAIAAA X2 X2 T ② Type here Q Search e I ✓ Paragra Oarrow_forward1+3+5+7+ …+300 using gauss’s problemarrow_forwardFactor the expression. 5x³ (x²+8x)² - 35x (x²+8x) 2arrow_forward
 Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning
Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press
Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





