
Engineering Mechanics: Statics
13th Edition
ISBN: 9780132915540
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: Prentice Hall
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 5.7, Problem 9FP
The rod is supported by smooth journal bearings at A, B and C and is subjected to the two faces Determine the reactions at these supports.
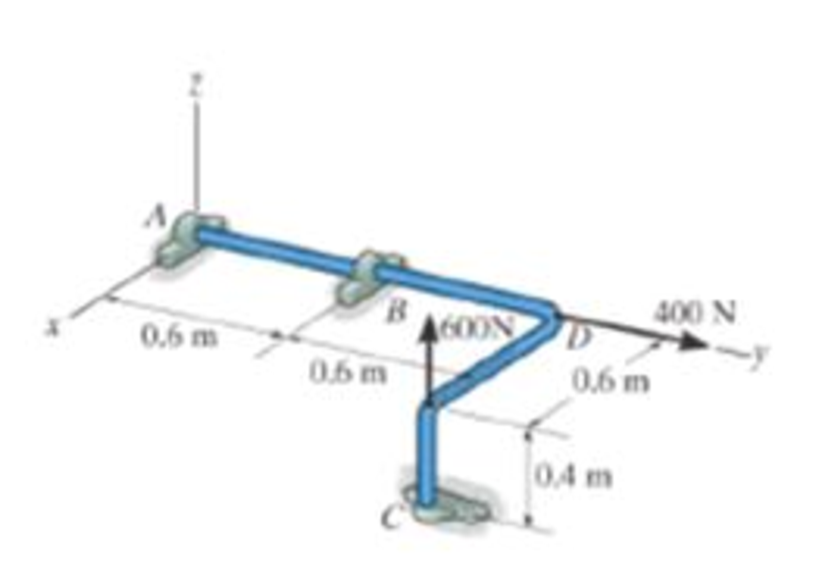
Prob. F5-9
Expert Solution & Answer
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

schedule09:05
Students have asked these similar questions
Only 100% sure experts solve it correct complete solutions okk don't use guidelines or ai answers okk will dislike okkk. Only human experts solved it
Airplanes A and B, flying at constant velocity and at the same altitude, are tracking the eye
of hurricane C. The relative velocity of C with respect to A is 300 kph 65.0° South of West,
and the relative velocity of C with respect to B is 375 kph 50.0° South of East.
A
120.0 km
B
1N
1. Determine the relative velocity of B with respect to A.
A ground-based radar indicates that hurricane C is moving
at a speed of 40.0 kph due north.
2. Determine the velocity of airplane A.
3. Determine the velocity of airplane B.
Consider that at the start of the tracking expedition, the
distance between the planes is 120.0 km and their initial
positions are horizontally collinear.
4. Given the velocities obtained in items 2 and 3, should
the pilots of planes A and B be concerned whether the
planes will collide at any given time? Prove using
pertinent calculations. (Hint: x = x + vt)
0
Only 100% sure experts solve it correct complete solutions okk don't use guidelines or ai answers okk will dislike okkk.
Chapter 5 Solutions
Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Ch. 5.2 - Prob. 1PCh. 5.2 - Prob. 2PCh. 5.2 - Prob. 3PCh. 5.2 - Prob. 4PCh. 5.2 - Prob. 5PCh. 5.2 - Prob. 6PCh. 5.2 - Prob. 7PCh. 5.2 - Prob. 8PCh. 5.2 - Prob. 9PCh. 5.4 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...
Ch. 5.4 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 5.4 - The truss is supported by a pin at A and a roller...Ch. 5.4 - Determine the components of reaction at the fixed...Ch. 5.4 - The 25 kg bar has a center of mass at G. If it is...Ch. 5.4 - Determine the reactions at the smooth contact...Ch. 5.4 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 5.4 - Prob. 11PCh. 5.4 - Determine the components of the support reactions...Ch. 5.4 - Prob. 13PCh. 5.4 - Prob. 14PCh. 5.4 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 5.4 - Determine the components of reaction at the...Ch. 5.4 - Prob. 17PCh. 5.4 - Determine the tension in the cable and the...Ch. 5.4 - Prob. 19PCh. 5.4 - Prob. 20PCh. 5.4 - Prob. 21PCh. 5.4 - Prob. 22PCh. 5.4 - Prob. 23PCh. 5.4 - Prob. 24PCh. 5.4 - Determine the magnitude of force at the pin A and...Ch. 5.4 - Prob. 26PCh. 5.4 - Prob. 27PCh. 5.4 - Prob. 28PCh. 5.4 - Prob. 29PCh. 5.4 - Prob. 30PCh. 5.4 - Prob. 31PCh. 5.4 - Prob. 32PCh. 5.4 - Prob. 33PCh. 5.4 - Prob. 34PCh. 5.4 - Prob. 35PCh. 5.4 - Prob. 36PCh. 5.4 - The boom supports the two vertical loads. Neglect...Ch. 5.4 - The boom is intended to support two vertical loads...Ch. 5.4 - Prob. 39PCh. 5.4 - Prob. 40PCh. 5.4 - Prob. 41PCh. 5.4 - The cantilevered jib crane is used to support the...Ch. 5.4 - The cantilevered jib crane is used to support the...Ch. 5.4 - Prob. 44PCh. 5.4 - Prob. 45PCh. 5.4 - Three uniform books each having a weight W and...Ch. 5.4 - Prob. 47PCh. 5.4 - Prob. 48PCh. 5.4 - Prob. 49PCh. 5.4 - Prob. 50PCh. 5.4 - Prob. 51PCh. 5.4 - A boy stands out at the end of the diving board,...Ch. 5.4 - The uniform beam has a weight Wand length l and is...Ch. 5.4 - Determine the distance d for placement of the load...Ch. 5.4 - If d = 1 m, and = 30, determine me normal...Ch. 5.4 - Prob. 56PCh. 5.4 - Assuming that the foundation exerts a linearly...Ch. 5.4 - Assuming that the foundation exerts a linearly...Ch. 5.4 - Prob. 59PCh. 5.4 - The 30-N uniform rod has a length of l = 1 m. If s...Ch. 5.4 - The uniform rod has a length I and weight W. It is...Ch. 5.7 - The uniform plate has a weight of 500 lb....Ch. 5.7 - Determine the reactions at the roller support A,...Ch. 5.7 - The rod is supported by smooth journal bearings at...Ch. 5.7 - Determine the support reactions at the smooth...Ch. 5.7 - Determine the force developed in the short link...Ch. 5.7 - Determine the components of reaction that the...Ch. 5.7 - Determine the tension each rope and the force that...Ch. 5.7 - Determine the vertical reactions at the wheels C...Ch. 5.7 - Prob. 64PCh. 5.7 - If these components have weights WA = 45000 Wa =...Ch. 5.7 - Prob. 66PCh. 5.7 - Prob. 67PCh. 5.7 - Prob. 68PCh. 5.7 - Prob. 69PCh. 5.7 - Determine the components of reaction at hinges A...Ch. 5.7 - Prob. 71PCh. 5.7 - Prob. 72PCh. 5.7 - Prob. 73PCh. 5.7 - Prob. 74PCh. 5.7 - Prob. 75PCh. 5.7 - Prob. 76PCh. 5.7 - Determine the horizontal equilibrium force P that...Ch. 5.7 - Determine the components of reaction at A and the...Ch. 5.7 - Compute the x, y, z components of reaction at the...Ch. 5.7 - Determine the magnitude of F2 which will cause the...Ch. 5.7 - Determine the x, y, z components of reaction at...Ch. 5.7 - Prob. 82PCh. 5.7 - Determine the horizontal tension T in the belt on...Ch. 5.7 - Determine the horizontal tension T in the belt on...Ch. 5.7 - If the roller at 8 can sustain a maximum load of 3...Ch. 5.7 - Determine the normal reaction at the roller A and...Ch. 5.7 - Prob. 87RPCh. 5.7 - Prob. 88RPCh. 5.7 - I he uniform rod of length L and weight W is...Ch. 5.7 - Determine the x, y, z components of reaction at...Ch. 5.7 - Determine the x, y, z components of reaction at...Ch. 5.7 - Determine the reactions at the supports A and B...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Show that for circular motion, force = mass * velocity squared/radius.
Thinking Like an Engineer: An Active Learning Approach (4th Edition)
Define a class called Counter. An object of this class is used to count things, so it records a count that is a...
Java: An Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming (8th Edition)
Describe the three types of anomalies that can arise in a table and the negative consequences of each.
Modern Database Management
(True or False) If is the length of str, then is the string consisting of the last character of str.
Introduction To Programming Using Visual Basic (11th Edition)
Which of the following statements will cause an error? a. x = 17 b. 17 = x c. x = 99999 d. x = '17'
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
For the circuit shown, find (a) the voltage υ, (b) the power delivered to the circuit by the current source, an...
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Solve this probem and show all of the workarrow_forwardThe differential equation of a cruise control system is provided by the following equation: WRITE OUT SOLUTION DO NOT USE A COPIED SOLUTION Find the closed loop transfer function with respect to the reference velocity (vr) . a. Find the poles of the closed loop transfer function for different values of K. How does the poles move as you change K? b. Find the step response for different values of K and plot in MATLAB. What can you observe?arrow_forwardSolve this problem and show all of the workarrow_forward
- Determine the minimum applied force P required to move wedge A to the right. The spring is compressed a distance of 175 mm. Neglect the weight of A and B. The coefficient of static friction for all contacting surface is μs = 0.35. Neglect friction at the rollers. k = = 15 kN/m P A B 10°arrow_forwardDO NOT COPY SOLUTION- will report The differential equation of a cruise control system is provided by the following equation: Find the closed loop transfer function with respect to the reference velocity (vr) . a. Find the poles of the closed loop transfer function for different values of K. How does the poles move as you change K? b. Find the step response for different values of K and plot in MATLAB. What can you observe?arrow_forwarda box shaped barge 37m long, 6.4 m beam, floats at an even keel draught of 2.5 m in water density 1.025 kg/m3. If a mass is added and the vessel moves into water density 1000 kg/m3, determine the magnitude of this mass if the fore end and aft end draughts are 2.4m and 3.8m respectively.arrow_forward
- a ship 125m long and 17.5m beam floats in seawater of 1.025 t/m3 at a draught of 8m. the waterplane coefficient is 0.83, block coefficient 0.759 and midship section area coefficient 0.98. calculate i) prismatic coefficient ii) TPC iii) change in mean draught if the vessel moves into water of 1.016 t/m3arrow_forwardc. For the given transfer function, find tp, ts, tr, Mp . Plot the resulting step response. G(s) = 40/(s^2 + 4s + 40) handplot only, and solve for eacharrow_forwardA ship of 9000 tonne displacement floats in fresh water of 1.000 t/m3 at a draught 50 mm below the sea water line. The waterplane area is 1650 m2. Calculate the mass of cargo which must be added so that when entering seawater of 1.025 t/m3 it floats at the seawater line.arrow_forward
- A ship of 15000 tonne displacement floats at a draught of 7 metres in water of 1.000t/cub. Metre.It is required to load the maximum amount of oil to give the ship a draught of 7.0 metre in seawater ofdensity 1.025 t/cub.metre. If the waterplane area is 2150 square metre, calculate the massof oil requiredarrow_forwardA ship of 8000 tonne displacement floats in seawater of 1.025 t/m3 and has a TPC of 14. The vessel moves into fresh water of 1.000 t/m3 and loads 300 tonne of oil fuel. Calculate the change in mean draught.arrow_forwardAuto Controls DONT COPY ANSWERS - will report Perform the partial fraction expansion of the following transfer function and find the impulse response: G(s) = (s/2 + 5/3) / (s^2 + 4s + 6) G(s) =( 6s^2 + 50) / (s+3)(s^2 +4)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Extent of Reaction; Author: LearnChemE;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=__stMf3OLP4;License: Standard Youtube License