
Engineering Mechanics: Statics
13th Edition
ISBN: 9780132915540
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: Prentice Hall
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 5.4, Problem 3FP
The truss is supported by a pin at A and a roller at B. Determine the support reactions.
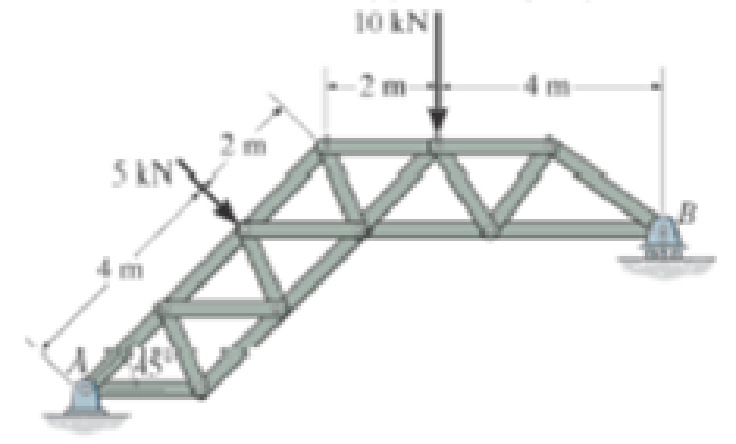
Prob. F5-3
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

schedule04:09
Students have asked these similar questions
handwritten solutions, please!!
> Homework 4 - Spring 2025.pdf
Spring 2025.pdf
k 4 - Spring 2025.pdf (447 KB)
Due: Thursday, February 27
Page
1
> of 2
ZOOM
1. A simply supported shaft is shown in Figure 1 with wo = 25 N/cm and M = 20 N cm. Use
singularity functions to determine the reactions at the supports. Assume EI = 1000 kN cm².
M
Wo
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70
80 90
100 110 cm
Figure 1 - Problem 1
2. A support hook was formed from a rectangular bar. Find the stresses at the inner and outer
surfaces at sections just above and just below O-B.
210 mm
A distillation column with a total condenser and a partial reboiler is separating ethanol andwater at 1.0 atm. Feed is 0.32 mol fraction ethanol and it enters as a saturated liquid at 100mol/s on the optimum plate. The distillate product is a saturated liquid with 80 mol% ethanol.The condenser removes 5615 kW. The bottoms product is 0.05 mol fraction ethanol. AssumeCMO is valid.(a) Find the number of equilibrium stages for this separation. [6 + PR](b) Find how much larger the actual reflux ratio, R, used is than Rmin, i.e. R/Rmin. [3]Note: the heats of vaporization of ethanol and water are λe = 38.58 and λw = 40.645
Chapter 5 Solutions
Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Ch. 5.2 - Prob. 1PCh. 5.2 - Prob. 2PCh. 5.2 - Prob. 3PCh. 5.2 - Prob. 4PCh. 5.2 - Prob. 5PCh. 5.2 - Prob. 6PCh. 5.2 - Prob. 7PCh. 5.2 - Prob. 8PCh. 5.2 - Prob. 9PCh. 5.4 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...
Ch. 5.4 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 5.4 - The truss is supported by a pin at A and a roller...Ch. 5.4 - Determine the components of reaction at the fixed...Ch. 5.4 - The 25 kg bar has a center of mass at G. If it is...Ch. 5.4 - Determine the reactions at the smooth contact...Ch. 5.4 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 5.4 - Prob. 11PCh. 5.4 - Determine the components of the support reactions...Ch. 5.4 - Prob. 13PCh. 5.4 - Prob. 14PCh. 5.4 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 5.4 - Determine the components of reaction at the...Ch. 5.4 - Prob. 17PCh. 5.4 - Determine the tension in the cable and the...Ch. 5.4 - Prob. 19PCh. 5.4 - Prob. 20PCh. 5.4 - Prob. 21PCh. 5.4 - Prob. 22PCh. 5.4 - Prob. 23PCh. 5.4 - Prob. 24PCh. 5.4 - Determine the magnitude of force at the pin A and...Ch. 5.4 - Prob. 26PCh. 5.4 - Prob. 27PCh. 5.4 - Prob. 28PCh. 5.4 - Prob. 29PCh. 5.4 - Prob. 30PCh. 5.4 - Prob. 31PCh. 5.4 - Prob. 32PCh. 5.4 - Prob. 33PCh. 5.4 - Prob. 34PCh. 5.4 - Prob. 35PCh. 5.4 - Prob. 36PCh. 5.4 - The boom supports the two vertical loads. Neglect...Ch. 5.4 - The boom is intended to support two vertical loads...Ch. 5.4 - Prob. 39PCh. 5.4 - Prob. 40PCh. 5.4 - Prob. 41PCh. 5.4 - The cantilevered jib crane is used to support the...Ch. 5.4 - The cantilevered jib crane is used to support the...Ch. 5.4 - Prob. 44PCh. 5.4 - Prob. 45PCh. 5.4 - Three uniform books each having a weight W and...Ch. 5.4 - Prob. 47PCh. 5.4 - Prob. 48PCh. 5.4 - Prob. 49PCh. 5.4 - Prob. 50PCh. 5.4 - Prob. 51PCh. 5.4 - A boy stands out at the end of the diving board,...Ch. 5.4 - The uniform beam has a weight Wand length l and is...Ch. 5.4 - Determine the distance d for placement of the load...Ch. 5.4 - If d = 1 m, and = 30, determine me normal...Ch. 5.4 - Prob. 56PCh. 5.4 - Assuming that the foundation exerts a linearly...Ch. 5.4 - Assuming that the foundation exerts a linearly...Ch. 5.4 - Prob. 59PCh. 5.4 - The 30-N uniform rod has a length of l = 1 m. If s...Ch. 5.4 - The uniform rod has a length I and weight W. It is...Ch. 5.7 - The uniform plate has a weight of 500 lb....Ch. 5.7 - Determine the reactions at the roller support A,...Ch. 5.7 - The rod is supported by smooth journal bearings at...Ch. 5.7 - Determine the support reactions at the smooth...Ch. 5.7 - Determine the force developed in the short link...Ch. 5.7 - Determine the components of reaction that the...Ch. 5.7 - Determine the tension each rope and the force that...Ch. 5.7 - Determine the vertical reactions at the wheels C...Ch. 5.7 - Prob. 64PCh. 5.7 - If these components have weights WA = 45000 Wa =...Ch. 5.7 - Prob. 66PCh. 5.7 - Prob. 67PCh. 5.7 - Prob. 68PCh. 5.7 - Prob. 69PCh. 5.7 - Determine the components of reaction at hinges A...Ch. 5.7 - Prob. 71PCh. 5.7 - Prob. 72PCh. 5.7 - Prob. 73PCh. 5.7 - Prob. 74PCh. 5.7 - Prob. 75PCh. 5.7 - Prob. 76PCh. 5.7 - Determine the horizontal equilibrium force P that...Ch. 5.7 - Determine the components of reaction at A and the...Ch. 5.7 - Compute the x, y, z components of reaction at the...Ch. 5.7 - Determine the magnitude of F2 which will cause the...Ch. 5.7 - Determine the x, y, z components of reaction at...Ch. 5.7 - Prob. 82PCh. 5.7 - Determine the horizontal tension T in the belt on...Ch. 5.7 - Determine the horizontal tension T in the belt on...Ch. 5.7 - If the roller at 8 can sustain a maximum load of 3...Ch. 5.7 - Determine the normal reaction at the roller A and...Ch. 5.7 - Prob. 87RPCh. 5.7 - Prob. 88RPCh. 5.7 - I he uniform rod of length L and weight W is...Ch. 5.7 - Determine the x, y, z components of reaction at...Ch. 5.7 - Determine the x, y, z components of reaction at...Ch. 5.7 - Determine the reactions at the supports A and B...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
The switch shown in Fig. P 7.4 has been open for a long time before closing at t = 0.
Figure P7.4
Find io(0−),...
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
When a class variable is said to reference an object, what is actually stored in the class variable?
Starting Out with Programming Logic and Design (5th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
What is an object?
Starting Out With Visual Basic (8th Edition)
Write some code that asks the user to enter either of the words append or new. According to the user response, ...
Java: An Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming (8th Edition)
When the compiler encounters a class, interface, or method with a bound type parameter, such as T extends Numbe...
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Data Structures (4th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Find the error in the following class: public class MyClass { private int x; private double y; public void MyCl...
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects (7th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- We have a feed that is a binary mixture of methanol and water (60.0 mol% methanol) that issent to a system of two flash drums hooked together. The vapor from the first drum is cooled,which partially condenses the vapor, and then is fed to the second flash drum. Both drumsoperate at 1.0 atm and are adiabatic. The feed to the first drum is 1000 kmol/hr. We desire aliquid product from the first drum that is 35.0 mol% methanol. The second drum operates at afraction vaporized of (V/F)2 = 0.25.(a) Find the liquid flow rate leaving the first flash drum, L1 (kmol/hr). [286 kmol/hr](b) Find the vapor composition leaving the second flash drum, y2. [0.85]arrow_forward= The steel curved bar shown has rectangular cross-section with a radial height h = 6 mm and thickness b = 4mm. The radius of the centroidal axis is R = 80 mm. A force P = 10 N is applied as shown. Assume the steel modulus of 207,000 MPa and G = 79.3(103) MPa, repectively. elasticity and shear modulus E = Find the vertical deflection at point B. Use Castigliano's method for a curved flexural member and since R/h > 10, neglect the effect of shear and axial load, thereby assuming that deflection is due to merely the bending moment. Note the inner and outer radii of the curves bar are: r = 80 + ½ (6) = 83 mm, r₁ = 80 − ½ (6) = 77 mm 2 2 Sπ/2 sin² 0 d = √π/² cos² 0 d0 = Π 0 4 大 C R B Parrow_forwardThe steel eyebolt shown in the figure is loaded with a force F = 75 lb. The eyebolt is formed from round wire of diameter d = 0.25 in to a radius R₁ = 0.50 in in the eye and at the shank. Estimate the stresses at the inner and outer surfaces at section A-A. Notice at the section A-A: r₁ = 0.5 in, ro = 0.75 in rc = 0.5 + 0.125 = 0.625 in Ri 200 F FAarrow_forward
- I have the fallowing question and solution from a reeds naval arc book. Im just confused as to where this answer came from and the formulas used. Wondering if i could have this answer/ solution broken down and explained in detail. A ship of 7000 tonne displacement has a waterplane areaof 1500 m2. In passing from sea water into river water of1005 kg/m3 there is an increase in draught of 10 cm. Find the Idensity of the sea water. picture of the "answer" is attachedarrow_forwardProblem A2 long steel tube has a rectangular cross-section with outer dimensions of 20 x 20 mm and a uniform wall thickness of 2. The tube is twisted along its length with torque, T. The tube material is 1045 CD steel with shear yield strength of S,, =315 MPa. Assume shear modulus, G = 79.3GPa. (a) Estimate the maximum torque that can be applied without yielding (b) Estimate the torque required to produce 5 degrees total angle of twist over the length of the tube. (c) What is the maximum torque that can be applied without yielding, if a solid rectangular shaft with dimensions of 20 x 20 is used? You may use the exact solution.arrow_forwardA simply supported beam is loaded as shown. Considering symmetry, the reactions at supports A and B are R₁ = R₂ = wa 2 Using the singularity method, determine the shear force V along the length of the beam as a function of distance x from the support A. A B Ir. 2a За W C R₁₂ x 2. Using the singularity method, determine the bending M along the length of the beam as a function of distance x, from the support A. 3. Using the singularity method, determine the beam slope and deflection along the length of the beam as a function of the distance x, from the support A. Assume the material modulus of elasticity, E and the moment of inertia of the beam cross-section, I are given.arrow_forward
- A steel tube, 2 m long, has a rectangular cross-section with outer dimensions of 20 × 30 mm and a uniform wall thickness of 1 mm. The tube is twisted along its length with torque, T. The tube material is 1018 CD steel with shear yield strength of Ssy =185 MPa. Assume shear modulus, G = 79.3GPa. (a) Estimate the maximum torque that can be applied without yielding.- (b) Estimate the torque required to produce 3 degrees total angle of twist over the length of the tube. (c) What is the maximum torque that can be applied without yielding, if a solid rectangular shaft with dimensions of 20 x 30 mm is used? You may use the exact solution:arrow_forward|The typical cruising altitude of a commercial jet airliner is 10,700 m above sea level where the local atmospheric temperature is 219 K, and the pressure is 0.25 bar. The aircraft utilizes a cold air-standard Brayton cycle as shown with a volume flow rate of 1450 m³/s. The compressor pressure ratio is 50, and the maximum cycle temperature is 1700 K. The compressor and turbine isentropic efficiencies are 90%. Neglect kinetic and potential energy effects in this problem. Assume constant specific heats with k=1.4, Ra=0.287 kJ/kg- K, Cp=1.0045 kJ/kg-K, and cv = 0.7175 kJ/kg-K. a) Draw a T-s diagram for this cycle on the diagram provided. b) Fill in the table below with the missing information. T[K] Heat exchanger Heat exchanger State P [bar] 1 0.25 2s 2 3 4s 4 Turbine c) (5pts) Determine the inlet air density in [kg/m³] (at state 1), and the system mass flowrate in [kg/s]. d) (10pts) Determine the net power developed in [MW]. Be sure to draw each component you are analyzing, define the…arrow_forwardOn the axis provide, draw a corresponding T-s diagram for the Brayton cycle shown given the following information: iv. V. vi. Compressor 1 is reversible, but Compressor 2 and the turbine are irreversible. The pressure drops through the regenerator are combustors are negligible. The pressures at state (1) and state (10) are equal to the atmospheric pressure. T 8 Regenerator fmm mmm Qin Combustor Compressor Compressor Turbine W cycle Intercooler mm Courarrow_forward
- For parts a) through e), consider the two power cycles shown in the diagram at the right, Cycle A: 1-2-3-4-1, and Cycle B: 1-2-3-4-1. a) What type of power cycles are shown? b) Which of cycles has a higher efficiency? c) Which of the cycles has a higher work output? d) For either cycle, would increasing the maximum cycle temperature (3) increase or decrease the efficiency? Cycle A: 1-2-3-4-1 3 3 Cycle B: 1-2-3-4-1 1 e) For either cycle, would decreasing the minimum cycle temperature (1) increase or decrease the efficiency? f) On the axis provide, draw a corresponding T-s diagram for the Rankine cycle shown given the following information: i. All turbines and pumps in the system are irreversible. ii. 111. The turbine inlet conditions (states 1 and 2) are superheated, while the 2nd stage turbine outlet is a saturated mixture. The condenser outlet state (4) and the CFWH outlet state (7) are saturated liquid. 2 Steam generator Condenser www Closed feedwater heater (1-y) T Pump Trap 8 (y) Sarrow_forwardProblem 4 A glass sphere with a 30 mm diameter is pressed against a flat carbon steel plate with a force of 5 N. Assume. For glass: E = 46.2 GPa, -0.245 and for steel E, 207 GPa, (a) Determine the radius of the contact surface. -0.292 (4 (b) Determine the maximum pressure at the contact surface. (4 (c) Calculate the principal stresses d., and a, in the glass sphere at the depth=0.037 mm. (d) Maximum shear stress in the glass sphere at the depth: 0.037 mm. (t (4 (e) Draw the Mohr circles for the stresses and show the point corresponding to the maximum shear stress. (3arrow_forwardSteam is the working fluid in the vapor power cycle with reheat shown in the figure. The mass flow rate is 0.5 kg/s, and the turbines and pump operate isentropically. The temperature at the inlet of both turbine stages (i.e. states 1 and 3) is 400 °C The condenser outlet is saturated liquid. 1. Fill in the table below with the missing information. Reheat section High- pressure turbine State P [bar] h [kJ/kg] s [kJ/kg-K] x [-] Steam generator 1 140 Condenser Pump 2 40 5 3 4 4 5 6 2.Draw a T-s diagram for this cycle on the diagram provided 3. Determine the net power output of this cycle in [kW]. Be sure to draw the component(s) you are analyzing, define the system, and apply conservation of energy in the space below. 4.Determine the total heat transferred into the system in [kW]. Be sure to draw the component you are analyzing, define the system, and apply conservation of energy in the space bel 5.Determine the cycle efficiency. Low-pressure turbinearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Mechanical SPRING DESIGN Strategy and Restrictions in Under 15 Minutes!; Author: Less Boring Lectures;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dsWQrzfQt3s;License: Standard Youtube License