
Concept explainers
(a)
To find : the maximum and minimum point of the function
(a)
Answer to Problem 84E
The maximum points of the function are (π, -π-1) _ radians.
The minimum point of the function are (0, 1) _ radians.
Explanation of Solution
Given information : Function f(x)=secx+tanx−x ; Trigonometric Equation secxtanx+sec2x=1 ; [0,2π)
Concept Involved:
A maximum is a high point and a minimum is a low point over the given interval.
Graph:
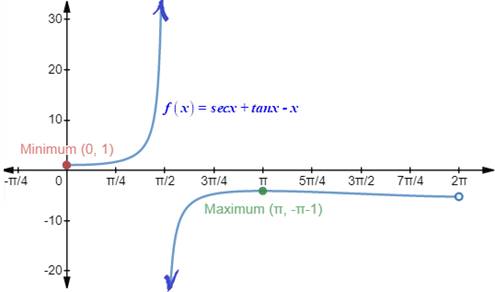
Interpretation:
The graph of the function f(x)=secx+tanx-x shows, at x=π radians the graph has the maximum value of −π−1 and at x=0 radians the graph has the minimum value of 1 .
(b)
To find : all the solutions of the trigonometric equations in the given interval
(b)
Answer to Problem 84E
The solution to the given trigonometric equation are x= 0, & π _ radians.
Explanation of Solution
Given information : Function f(x)=secx+tanx−x ; Trigonometric Equation secxtanx+sec2x=1 ; [0,2π)
Concept Involved:
Solution to a
To solve a trigonometric equation, use standard algebraic techniques (when possible) such as collecting like terms, extracting square roots, and factoring.
Our preliminary goal in solving a trigonometric equation is to isolate the trigonometric function on one side of the equation.
Calculation:
Subtracting 1 on both sides of the equation secxtanx+sec2x=1
secxtanx+sec2x−1=1 −1
Simplify on both sides of the equation
secxtanx+sec2x−1=0
Use the Pythagorean Identity sec2x−1=tan2x
secxtanx+tan2x=0
Factor the Greatest Common Factor in the left side of the equation
tanx(secx+tanx)=0
Using the zero factor property which states that if a⋅b=0 then a=0 (or) b=0 , we need to set each factor to zero.
tanx=0▶1st equation
secx+tanx=0▶2nd equation
Solving the 1st equation and finding x values that makes it true in the interval [0,2π)
- By taking inverse tangent on both sides tan−1(tanx)=0
x=0, π
Solving the 2nd equation and finding x values that makes it true in the interval [0,2π)
- By rewriting left side of the equation using reciprocal identity and quotient identity
1cosx+sinxcosx=0
1+sinxcosx=0
At x=π2 , the numerator is zero, but it makes the denominator also zero. So there is no solution to this equation.
Conclusion:
x=0 & π radians are the zero of the function and solution to the equation secxtanx+sec2x=1 in the interval [0,2π)
Chapter 5 Solutions
EBK PRECALCULUS W/LIMITS
- can you solve this question using partial fraction decomposition and explain the steps used along the wayarrow_forwardIntegral How 80*1037 IW 1012 S е ऍ dw answer=0 How 70+10 A 80*1037 Ln (Iwl+1) du answer=123.6K 70*1637arrow_forwardcan you solve this question and explain the steps used along the wayarrow_forward
- can you solve this question and explain the steps used along the wayarrow_forwardcan you solve this question and explain the steps used along the wayarrow_forwardCan the expert solve an Intestal In detall? 110x/0³ W. 1 SW = dw A 40x103π ⑤M-1 大 80*10³/ 12 10% 70*1037 80x103 || dw OP= # Sin (w/+1) dw A 70*10*Aarrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





