
Concept explainers
(a)
To find : the maximum and minimum point of the function
(a)
Answer to Problem 79E
The maximum points of the function are (π/3, 1.25)&(5π/3, 1.25) _ radians.
The minimum point of the function are (0,1)&(π, -1) _ radians.
Explanation of Solution
Given information : Function f(x)=sin2x+cosx ; Trigonometric Equation 2sinxcosx−sinx=0 ; [0,2π)
Concept Involved:
A maximum is a high point and a minimum is a low point over the given interval.
Graph:
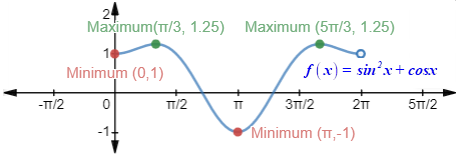
Interpretation:
The graph shows, at x=π/3 &5π/3 radians the graph has the maximum value of 1.25 and at x=0 &π radians the graph has the minimum value of 1&−1 respectively.
(b)
To find : all the solutions of the trigonometric equations in the given interval
(b)
Answer to Problem 79E
The solution to the given trigonometric equation are x=0, π/3, π, & 5π/3 _ radians.
Explanation of Solution
Given information : Function f(x)=sin2x+cosx ; Trigonometric Equation 2sinxcosx−sinx=0 ; [0,2π)
Concept Involved:
Solution to a
To solve a trigonometric equation, use standard algebraic techniques (when possible) such as collecting like terms, extracting square roots, and factoring.
Our preliminary goal in solving a trigonometric equation is to isolate the trigonometric function on one side of the equation.
Calculation:
Factor the Greatest Common Factor of left side of the equation 2sinxcosx−sinx=0
sinx(2cosx−1)=0
Using the zero factor property which states that if a⋅b=0 then a=0 (or) b=0 , we need to set each factor to zero.
sinx=0▶1st equation
2cosx−1=0▶2nd equation
Solving the 1st equation and finding x values that makes it true in the interval [0,2π)
x=sin−1(0)
x=0, π
Solving the 2nd equation and finding x values that makes it true in the interval [0,2π)
- By adding 1 on both sides of the equation
- By simplifying on both sides of the equation
- By dividing 2 on both sides of the equation
- By simplifying fraction on both sides of the equation
2cosx−1=02cosx=12cosx2=12cosx=12x=cos−1(12)x=π3, 5π3
Conclusion:
x=0, π3, π, &5π3 radians are the zero of the function and solution to the equation 2sinxcosx−sinx=0 in the interval [0,2π)
Chapter 5 Solutions
EBK PRECALCULUS W/LIMITS
- 4 In the integral dxf1dy (7)², make the change of variables x = ½(r− s), y = ½(r + s), and evaluate the integral. Hint: Find the limits on r and s by sketching the area of integration in the (x, y) plane along with the r and s axes, and then show that the same area can be covered by s from 0 to r and r from 0 to 1.arrow_forward7. What are all values of 0, for 0≤0<2л, where 2 sin² 0=-sin? - 5π 6 π (A) 0, л, and 6 7π (B) 0,л, 11π , and 6 6 π 3π π (C) 5π 2 2 3 , and π 3π 2π (D) 2' 2'3 , and 3 4元 3 1 די } I -2m 3 1 -3 บ 1 # 1 I 3# 3m 8. The graph of g is shown above. Which of the following is an expression for g(x)? (A) 1+ tan(x) (B) 1-tan (x) (C) 1-tan (2x) (D) 1-tan + X - 9. The function j is given by j(x)=2(sin x)(cos x)-cos x. Solve j(x) = 0 for values of x in the interval Quiz A: Topic 3.10 Trigonometric Equations and Inequalities Created by Bryan Passwaterarrow_forwardcan you solve this question using the right triangle method and explain the steps used along the wayarrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





