
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations and Connections
1st Edition
ISBN: 9781133939146
Author: Katz, Debora M.
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 5.3, Problem 5.3CE
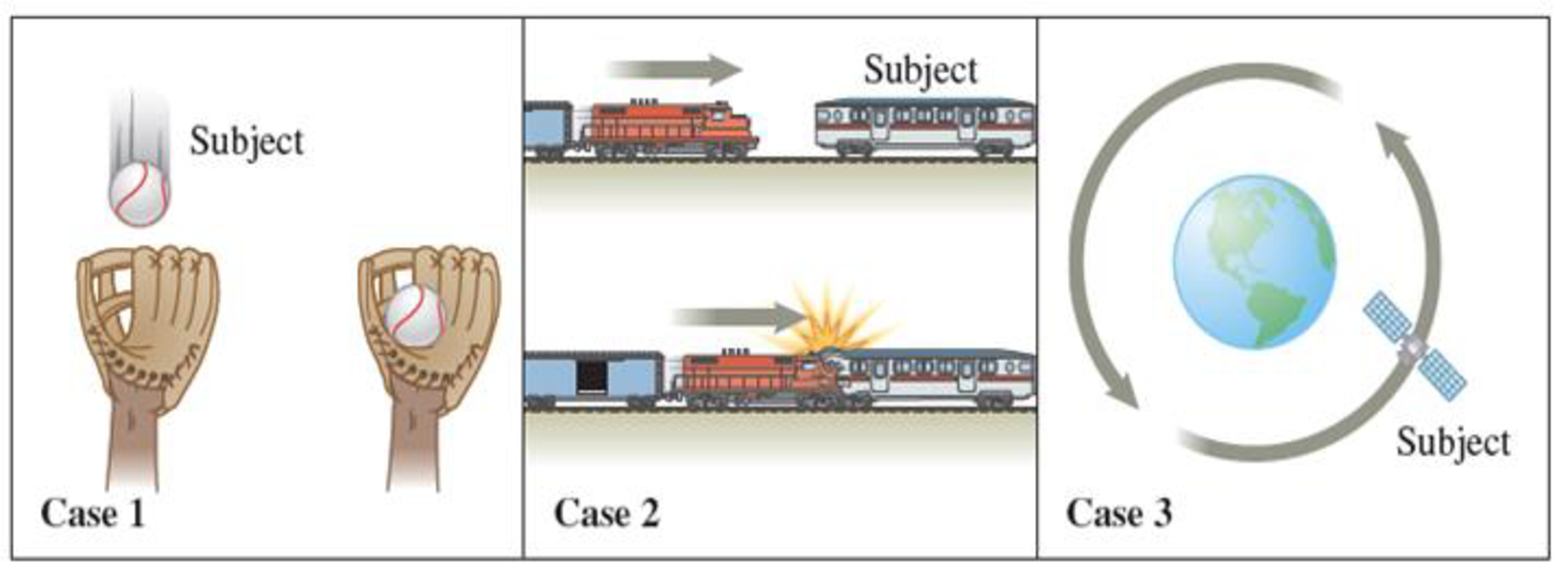
Shown in Figure 5.4 are four situations in which a force acts on a subject. The subject is labeled in each case.
Case 1. A baseball glove stops a vertically falling baseball.
Case 2. CASE STUDY A freight train collides with a slopped passenger train.
Case 3. A satellite orbits the Earth.
For each case, identify the source of the force and the direction of the force. Then state whether a contact force or a field force is involved.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Make sure to draw a Free Body Diagram as well
Make sure to draw a Free Body Diagram as well
Make sure to draw a Free Body Diagram please as well
Chapter 5 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations and Connections
Ch. 5.2 - Because Newtons first law is counterintuitive, it...Ch. 5.2 - Train Collision and Newtons First Law A group of...Ch. 5.3 - Shown in Figure 5.4 are four situations in which a...Ch. 5.3 - A person stands on a spring scale in an elevator...Ch. 5.4 - Prob. 5.5CECh. 5.5 - Prob. 5.6CECh. 5.6 - a. Take a moment to be sure that you understand...Ch. 5.7 - Imagine weighing the same bunch of bananas with...Ch. 5.7 - For all three situations, find the magnitude and...Ch. 5.9 - Prob. 5.10CE
Ch. 5.9 - A child jumping off the monkey bars at a...Ch. 5.9 - Prob. 5.12CECh. 5 - Why is it easier to lift a very large beach ball...Ch. 5 - Prob. 2PQCh. 5 - Imagine pushing two blocks on ice. The light block...Ch. 5 - When Julia Child would cook an omelet, she would...Ch. 5 - Prob. 5PQCh. 5 - Prob. 6PQCh. 5 - Prob. 7PQCh. 5 - Prob. 8PQCh. 5 - Prob. 9PQCh. 5 - Prob. 10PQCh. 5 - Prob. 11PQCh. 5 - You blow a small piece of paper through the air....Ch. 5 - Prob. 13PQCh. 5 - Prob. 14PQCh. 5 - Prob. 15PQCh. 5 - Prob. 16PQCh. 5 - Prob. 17PQCh. 5 - A ball hanging from a light string or rod can be...Ch. 5 - Prob. 19PQCh. 5 - You are riding a luxury bus. In front of you is a...Ch. 5 - Prob. 21PQCh. 5 - A particle with mass m = 4.00 kg accelerates...Ch. 5 - The x and y coordinates of a 4.00-kg particle...Ch. 5 - In the movie Garden State, one of the characters...Ch. 5 - The starship Enterprise has its tractor beam...Ch. 5 - A race car is moving around a circular track at a...Ch. 5 - A particle of mass m1 accelerates at 4.25 m/s2...Ch. 5 - Prob. 28PQCh. 5 - Two forces F1=(62.98i15.80j) N and...Ch. 5 - Three forces F1=(62.98i15.80j) N,...Ch. 5 - A hockey stick pushes a 0.160-kg puck with...Ch. 5 - If the vector components of the position of a...Ch. 5 - If the vector components of the position of a...Ch. 5 - A 15.0-kg object is in free fall near the surface...Ch. 5 - A black widow spider hangs motionless from a web...Ch. 5 - Determine whether each of the following statements...Ch. 5 - You place tomatoes in the pan of a hanging spring...Ch. 5 - Kinetic friction is proportional to the normal...Ch. 5 - A student takes the elevator up to the fourth...Ch. 5 - A sleigh is being pulled horizontally by a train...Ch. 5 - Two blocks are connected by a rope that passes...Ch. 5 - Find an expression for the carts acceleration in...Ch. 5 - A woman uses a rope to pull a block of mass m...Ch. 5 - A student working on a school project modeled a...Ch. 5 - One great form of athletic competition for...Ch. 5 - A heavy crate of mass 50.0 kg is pulled at...Ch. 5 - A block with mass m1 hangs from a rope that is...Ch. 5 - To get in shape, you head to the local gym to...Ch. 5 - A block with mass m1 hangs from a rope that is...Ch. 5 - FIGURE P5.49 Problems 49 and 50. Suppose the...Ch. 5 - Two objects, m1 = 3.00 kg and m2 = 8.50 kg, are...Ch. 5 - A runaway piano starts from rest and slides down a...Ch. 5 - Does the ground need to exert a force on you for...Ch. 5 - A boxer breaks his hand by punching another boxers...Ch. 5 - Prob. 55PQCh. 5 - A textbook rests on a movable wooden plank that is...Ch. 5 - Prob. 57PQCh. 5 - Prob. 58PQCh. 5 - Prob. 59PQCh. 5 - A worker is attempting to lift a 55.0-kg palette...Ch. 5 - Prob. 61PQCh. 5 - A concept map is a visual representation of...Ch. 5 - A 75.0-g arrow, fired at a speed of 110 m/s to the...Ch. 5 - Prob. 64PQCh. 5 - A box with mass m1 = 6.00 kg sliding on a rough...Ch. 5 - Prob. 66PQCh. 5 - A cosmic ray muon with mass m = 1.88 1028 kg...Ch. 5 - Prob. 68PQCh. 5 - Prob. 69PQCh. 5 - A 1.50-kg particle initially at rest and at the...Ch. 5 - A block of ice (m = 15.0 kg) with an attached rope...Ch. 5 - A block of ice (m = 15.0 kg) with an attached rope...Ch. 5 - Prob. 73PQCh. 5 - Starting from rest, a rectangular toy block with...Ch. 5 - When a 1.50-kg dress hangs midway from a taut...Ch. 5 - Jamal and Dayo are lifting a large chest, weighing...Ch. 5 - A heavy chandelier with mass 125 kg is hung by...Ch. 5 - Two children, Raffi and John, sitting on sleds...Ch. 5 - Two boxes with masses m1 = 4.00 kg and m2 = 10.0...Ch. 5 - Two blocks of mass m1 = 1.50 kg and m2 = 5.00 kg...Ch. 5 - An aerial demonstration aircraft dives at an angle...Ch. 5 - A painter sits on a scaffold that is connected to...Ch. 5 - Three crates with masses m1 = 5.45 kg, m2 = 7.88...Ch. 5 - A small block with mass m is set on the top of an...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- please answer this asap!!!!arrow_forwardRT = 4.7E-30 18V IT = 2.3E-3A+ 12 38Ω ли 56Ω ли r5 27Ω ли r3 28Ω r4 > 75Ω r6 600 0.343V 75.8A Now figure out how much current in going through the r4 resistor. |4 = unit And then use that current to find the voltage drop across the r resistor. V4 = unitarrow_forward7 Find the volume inside the cone z² = x²+y², above the (x, y) plane, and between the spheres x²+y²+z² = 1 and x² + y²+z² = 4. Hint: use spherical polar coordinates.arrow_forward
- ганм Two long, straight wires are oriented perpendicular to the page, as shown in the figure(Figure 1). The current in one wire is I₁ = 3.0 A, pointing into the page, and the current in the other wire is 12 4.0 A, pointing out of the page. = Find the magnitude and direction of the net magnetic field at point P. Express your answer using two significant figures. VO ΜΕ ΑΣΦ ? Figure P 5.0 cm 5.0 cm ₁ = 3.0 A 12 = 4.0 A B: μΤ You have already submitted this answer. Enter a new answer. No credit lost. Try again. Submit Previous Answers Request Answer 1 of 1 Part B X Express your answer using two significant figures. ΜΕ ΑΣΦ 0 = 0 ? below the dashed line to the right P You have already submitted this answer. Enter a new answer. No credit lost. Try again.arrow_forwardAn infinitely long conducting cylindrical rod with a positive charge λ per unit length is surrounded by a conducting cylindrical shell (which is also infinitely long) with a charge per unit length of −2λ and radius r1, as shown in the figure. What is σinner, the surface charge density (charge per unit area) on the inner surface of the conducting shell? What is σouter, the surface charge density on the outside of the conducting shell? (Recall from the problem statement that the conducting shell has a total charge per unit length given by −2λ.)arrow_forwardA small conducting spherical shell with inner radius aa and outer radius b is concentric with a larger conducting spherical shell with inner radius c and outer radius d (Figure 1). The inner shell has total charge +2q, and the outer shell has charge −2q. What's the total charge on the inner surface of the small shell? What's the total charge on the outer surface of the small shell? What's the total charge on the inner surface of the large shell? What's the total charge on the outer surface of the large shell?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University
Newton's Third Law of Motion: Action and Reaction; Author: Professor Dave explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=y61_VPKH2B4;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY