
Concept explainers
Successive substitution of F atoms for H atoms in the molecule CH4 produces the molecules CH3F, CH2F2, CHF3, and CF4.
- a. Draw Lewis structures for each of the five molecules.
- b. Using VSEPR theory, predict the geometry of each of the five molecules.
- c. Specify the polarity (polar or nonpolar) for each of the five molecules.
(a)
Interpretation:
Lewis structures for the five molecules that are formed by successive substitution of
Concept Introduction:
Lewis structure clearly depicts the bonding and nonbonding electrons in the atom. This is only partially useful for the molecule that contains one or more multiple bonds and when coordinate covalent bond is present in the molecule. For drawing Lewis structure a systematic procedure is followed. They are,
- The total number of valence electrons that is present in molecule is calculated by adding all the valence electrons of the atoms present in the molecule.
- The chemical symbols for the atoms that is present in the molecule is written in the order that they are bonded. After this a single covalent bond is placed between each atoms as two electrons.
- The nonbonding electrons are added to each atom that is bonded to the central atom so that it contains octet of electrons. For hydrogen alone the “octet” is only two electrons.
- The remaining electrons has to be placed on the central atom in the structure.
- If there is no octet of electrons present in the central atom, then use one or more pairs of nonbonding electrons that is bonded to the central atom to form double or triple bonds.
- The total number of electrons has to be counted and it has to be confirmed whether the count is same as that of the number of valence electrons that is available for bonding.
Explanation of Solution
Given molecules are
For
Given molecule is
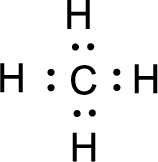
All the atoms present in the above structure contains octet of electrons. The total number of electron dots present in the above structure is 8 and it is same as the valence electrons of
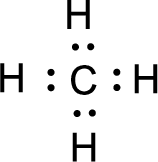
For
Given molecule is
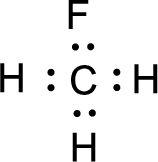
Nonbonding electrons are added to the fluorine atom. The resulting structure is,
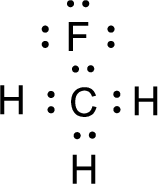
All the atoms present in the above structure contains octet of electrons. The total number of electron dots present in the above structure is 14 and it is same as the valence electrons of
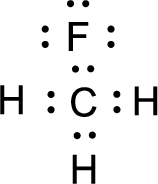
For
Given molecule is
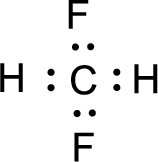
Nonbonding electrons are added to the fluorine atom. The resulting structure is,
All the atoms present in the above structure contains octet of electrons. The total number of electron dots present in the above structure is 20 and it is same as the valence electrons of
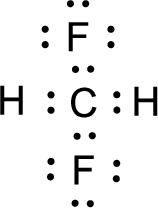
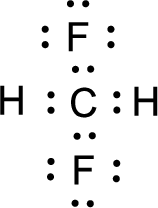
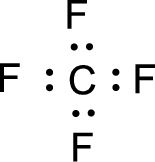
For
Given molecule is
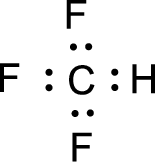
Nonbonding electrons are added to the fluorine atom. The resulting structure is,
All the atoms present in the above structure contains octet of electrons. The total number of electron dots present in the above structure is 26 and it is same as the valence electrons of
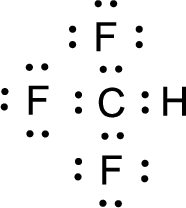
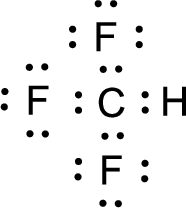
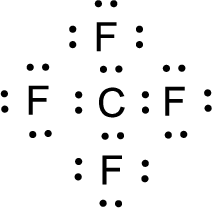
For
Given molecule is
Nonbonding electrons are added to the fluorine atom. The resulting structure is,
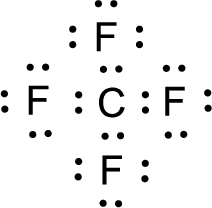
All the atoms present in the above structure contains octet of electrons. The total number of electron dots present in the above structure is 32 and it is same as the valence electrons of
(b)
Interpretation:
Molecule geometry has to be predicted for the five molecules using VSEPR theory.
Concept Introduction:
Information about the number of bonds and types of bonds can be obtained from Lewis structure but the molecular geometry cannot be obtained. Three dimensional arrangement of atoms in a molecule can be given by molecular geometry. Physical and chemical properties are determined by the molecular geometry of the molecule.
Using VSEPR theory and Lewis structure, the molecular geometry of the molecule that contain less number of atoms can be predicted. VSEPR theory uses the information from Lewis structure of the molecule to predict the molecular geometry of the molecule. Main concept of VSEPR theory is that electron pairs that are present in the valence shell adopt arrangement in a way that minimize the repulsion between like charges.
If the central atom contains two electron pairs, then it has to be far apart means, it has to be on opposite side of the nucleus. This means the angle has to be
If the central atom contains three electron pairs, then it has to be far apart means, it has to be on corner of a triangle. This means the angle has to be
If the central atom contains four electron pairs, then it has to be far apart means, it has to be in a tetrahedral arrangement. This means the angle has to be
The collection of valence electron that is present in localized region about central atom in a molecule is known as VSEPR electron group. This may contain two electrons, four electrons, or six electrons. The electron group that contain four and six electrons repel each other.
Tetrahedral VSEPR electron group:
The four electron pairs can be of three VSEPR electron groups. They are 4 bonding electron groups, 3 bonding and 1 nonbonding electron groups, and 2 bonding and 2 nonbonding electron groups. The molecular geometry that is associated with 4 bonding electron groups is tetrahedral. The molecular geometry that is associated with 3 bonding and 1 nonbonding electron groups is trigonal pyramidal. The molecular geometry that is associated with 2 bonding and 2 nonbonding electron groups is angular.
Trigonal planar VSEPR electron group:
The three electron pairs can be of two VSEPR electron groups. They are 3 bonding electron groups, and 2 bonding and 1 nonbonding electron groups. The molecular geometry that is associated with 3 bonding electron groups is trigonal planar. The molecular geometry that is associated with 2 bonding and 1 nonbonding electron groups is angular.
Linear VSEPR electron group:
The two electron pairs can be of only one VSEPR electron groups. It is only 2 bonding electron groups and the geometry associated with it is linear geometry.
Explanation of Solution
Given molecule is
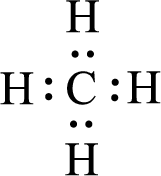
The central atom in the above molecule is found to be carbon. This has four bonding electron groups and zero nonbonding electron groups. The arrangement around the central atom is tetrahedral arrangement. Looking for molecular geometry, the central atom that contains four bonding electron groups and zero nonbonding electron groups and it has tetrahedral geometry as per VSEPR theory.
Given molecule is
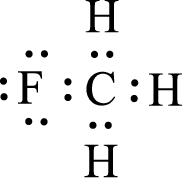
The central atom in the above molecule is found to be carbon. This has four bonding electron groups and zero nonbonding electron groups. The arrangement around the central atom is tetrahedral arrangement. Looking for molecular geometry, the central atom that contains four bonding electron groups and zero nonbonding electron groups and it has tetrahedral geometry as per VSEPR theory.
Given molecule is
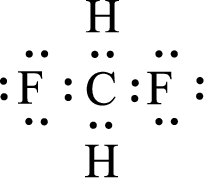
The central atom in the above molecule is found to be carbon. This has four bonding electron groups and zero nonbonding electron groups. The arrangement around the central atom is tetrahedral arrangement. Looking for molecular geometry, the central atom that contains four bonding electron groups and zero nonbonding electron groups and it has tetrahedral geometry as per VSEPR theory.
Given molecule is
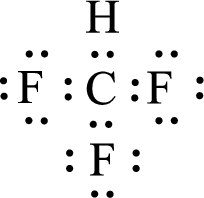
The central atom in the above molecule is found to be carbon. This has four bonding electron groups and zero nonbonding electron groups. The arrangement around the central atom is tetrahedral arrangement. Looking for molecular geometry, the central atom that contains four bonding electron groups and zero nonbonding electron groups and it has tetrahedral geometry as per VSEPR theory.
Given molecule is
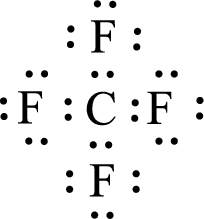
The central atom in the above molecule is found to be carbon. This has four bonding electron groups and zero nonbonding electron groups. The arrangement around the central atom is tetrahedral arrangement. Looking for molecular geometry, the central atom that contains four bonding electron groups and zero nonbonding electron groups and it has tetrahedral geometry as per VSEPR theory.
(c)
Interpretation:
The five molecules that are given has to be classified as polar and nonpolar.
Concept Introduction:
Measure of the degree of inequality in attraction of the bonding electrons to the various locations present within a molecule is known as molecular polarity. This can also be said in terms of electron attraction and that is in a molecule one part is favored than the other parts of the molecule.
If in a molecule there is an uneven distribution of electronic charges means it is known as polar molecule. If there is a symmetrical distribution of electron charge over the molecule means it is known as nonpolar molecule. Two factors that decide molecular polarity is bond polarity and geometry of molecule. If a molecule is symmetrical means then there won’t be any molecular polarity because the effect given by the polar bonds may cancel out each other.
The polarity of the bonds, arrangement of the bonds determines the degree of molecular polarity. If the electronegativity difference is more, then the molecule will be more polar.
Explanation of Solution
Given molecules are
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Bundle: General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry, 7th + OWLv2 Quick Prep for General Chemistry, 4 terms (24 months) Printed Access Card
- Part C IN H N. Br₂ (2 equiv.) AlBr3 Draw the molecule on the canvas by choosing buttons from the Tools (for bonds and + e (×) H± 12D T EXP. L CONT. דarrow_forward9. OA. Rank the expected boiling points of the compounds shown below from highest to lowest. Place your answer appropriately in the box. Only the answer in the box will be graded. (3) points) OH OH بر بد بدید 2 3arrow_forwardThere is an instrument in Johnson 334 that measures total-reflectance x-ray fluorescence (TXRF) to do elemental analysis (i.e., determine what elements are present in a sample). A researcher is preparing a to measure calcium content in a series of well water samples by TXRF with an internal standard of vanadium (atomic symbol: V). She has prepared a series of standard solutions to ensure a linear instrument response over the expected Ca concentration range of 40-80 ppm. The concentrations of Ca and V (ppm) and the instrument response (peak area, arbitrary units) are shown below. Also included is a sample spectrum. Equation 1 describes the response factor, K, relating the analyte signal (SA) and the standard signal (SIS) to their respective concentrations (CA and CIS). Ca, ppm V, ppm SCa, arb. units SV, arb. units 20.0 10.0 14375.11 14261.02 40.0 10.0 36182.15 17997.10 60.0 10.0 39275.74 12988.01 80.0 10.0 57530.75 14268.54 100.0…arrow_forward
- A mixture of 0.568 M H₂O, 0.438 M Cl₂O, and 0.710 M HClO are enclosed in a vessel at 25 °C. H₂O(g) + C₁₂O(g) = 2 HOCl(g) K = 0.0900 at 25°C с Calculate the equilibrium concentrations of each gas at 25 °C. [H₂O]= [C₁₂O]= [HOCI]= M Σ Marrow_forwardWhat units (if any) does the response factor (K) have? Does the response factor (K) depend upon how the concentration is expressed (e.g. molarity, ppm, ppb, etc.)?arrow_forwardProvide the structure, circle or draw, of the monomeric unit found in the biological polymeric materials given below. HO OH amylose OH OH 행 3 HO cellulose OH OH OH Ho HOarrow_forward
- OA. For the structure shown, rank the bond lengths (labeled a, b and c) from shortest to longest. Place your answer in the box. Only the answer in the box will be graded. (2 points) H -CH3 THe b Нarrow_forwardDon't used hand raitingarrow_forwardQuizzes - Gen Organic & Biological Che... ☆ myd21.lcc.edu + O G screenshot on mac - Google Search savings hulu youtube google disney+ HBO zlib Homework Hel...s | bartleby cell bio book Yuzu Reader: Chemistry G periodic table - Google Search b Home | bartleby 0:33:26 remaining CHEM 120 Chapter 5_Quiz 3 Page 1: 1 > 2 > 3 > 6 ¦ 5 > 4 > 7 ¦ 1 1 10 8 ¦ 9 a ¦ -- Quiz Information silicon-27 A doctor gives a patient 0.01 mC i of beta radiation. How many beta particles would the patient receive in I minute? (1 Ci = 3.7 x 10 10 d/s) Question 5 (1 point) Saved Listen 2.22 x 107 222 x 108 3.7 x 108 2.22 x 108 none of the above Question 6 (1 point) Listen The recommended dosage of 1-131 for a test is 4.2 μCi per kg of body mass. How many millicuries should be given to a 55 kg patient? (1 mCi = 1000 μСi)? 230 mCiarrow_forward

 Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHERChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHERChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning





