
Concept explainers
Specify both the VSEPR electron group geometry about the central atom and the molecular geometry for each of the following molecules or polyatomic ions.
- a. CH4
- b. PH4+
- c. PH3
- d. NO3−
(a)
Interpretation:
Electron group geometry and Molecular geometry about the central atom for
Concept Introduction:
Information about the number of bonds and types of bonds can be obtained from Lewis structure but the molecular geometry cannot be obtained. Three dimensional arrangement of atoms in a molecule can be given by molecular geometry. Physical and chemical properties are determined by the molecular geometry of the molecule.
Using VSEPR theory and Lewis structure, the molecular geometry of the molecule that contain less number of atoms can be predicted. VSEPR theory uses the information from Lewis structure of the molecule to predict the molecular geometry of the molecule. Main concept of VSEPR theory is that electron pairs that are present in the valence shell adopt arrangement in a way that minimize the repulsion between like charges.
If the central atom contains two electron pairs, then it has to be far apart means, it has to be on opposite side of the nucleus. This means the angle has to be
If the central atom contains three electron pairs, then it has to be far apart means, it has to be on corner of a triangle. This means the angle has to be
If the central atom contains four electron pairs, then it has to be far apart means, it has to be in a tetrahedral arrangement. This means the angle has to be
The collection of valence electron that is present in localized region about central atom in a molecule is known as VSEPR electron group. This may contain two electrons, four electrons, or six electrons. The electron group that contain four and six electrons repel each other.
Tetrahedral VSEPR electron group:
The four electron pairs can be of three VSEPR electron groups. They are 4 bonding electron groups, 3 bonding and 1 nonbonding electron groups, and 2 bonding and 2 nonbonding electron groups. The molecular geometry that is associated with 4 bonding electron groups is tetrahedral. The molecular geometry that is associated with 3 bonding and 1 nonbonding electron groups is trigonal pyramidal. The molecular geometry that is associated with 2 bonding and 2 nonbonding electron groups is angular.
Trigonal planar VSEPR electron group:
The three electron pairs can be of two VSEPR electron groups. They are 3 bonding electron groups, and 2 bonding and 1 nonbonding electron groups. The molecular geometry that is associated with 3 bonding electron groups is trigonal planar. The molecular geometry that is associated with 2 bonding and 1 nonbonding electron groups is angular.
Linear VSEPR electron group:
The two electron pairs can be of only one VSEPR electron groups. It is only 2 bonding electron groups and the geometry associated with it is linear geometry.
Molecules with more than one central atom:
If a molecule contains more than one central atom then the molecular geometry for each central atom is given separately following the same rules applied for the molecules that contain one central atom.
Rules for predicting Geometry of molecules:
- Lewis structure for the given molecule has to be drawn.
- The number of VSEPR electron groups present about the central atom has to be counted in Lewis structure.
- Geometry has to be assigned considering minimum repulsion between the electron groups.
Answer to Problem 5.58EP
Electron group geometry is tetrahedral and molecular geometry about the central atom in
Explanation of Solution
Given molecule is
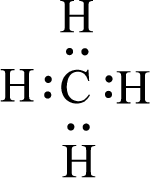
The above drawn structure for
The electron group geometry and molecular geometry about the central atom is tetrahedral.
Electron group geometry and molecular geometry is predicted for
(b)
Interpretation:
Electron group geometry and Molecular geometry about the central atom for
Concept Introduction:
Information about the number of bonds and types of bonds can be obtained from Lewis structure but the molecular geometry cannot be obtained. Three dimensional arrangement of atoms in a molecule can be given by molecular geometry. Physical and chemical properties are determined by the molecular geometry of the molecule.
Using VSEPR theory and Lewis structure, the molecular geometry of the molecule that contain less number of atoms can be predicted. VSEPR theory uses the information from Lewis structure of the molecule to predict the molecular geometry of the molecule. Main concept of VSEPR theory is that electron pairs that are present in the valence shell adopt arrangement in a way that minimize the repulsion between like charges.
If the central atom contains two electron pairs, then it has to be far apart means, it has to be on opposite side of the nucleus. This means the angle has to be
If the central atom contains three electron pairs, then it has to be far apart means, it has to be on corner of a triangle. This means the angle has to be
If the central atom contains four electron pairs, then it has to be far apart means, it has to be in a tetrahedral arrangement. This means the angle has to be
The collection of valence electron that is present in localized region about central atom in a molecule is known as VSEPR electron group. This may contain two electrons, four electrons, or six electrons. The electron group that contain four and six electrons repel each other.
Tetrahedral VSEPR electron group:
The four electron pairs can be of three VSEPR electron groups. They are 4 bonding electron groups, 3 bonding and 1 nonbonding electron groups, and 2 bonding and 2 nonbonding electron groups. The molecular geometry that is associated with 4 bonding electron groups is tetrahedral. The molecular geometry that is associated with 3 bonding and 1 nonbonding electron groups is trigonal pyramidal. The molecular geometry that is associated with 2 bonding and 2 nonbonding electron groups is angular.
Trigonal planar VSEPR electron group:
The three electron pairs can be of two VSEPR electron groups. They are 3 bonding electron groups, and 2 bonding and 1 nonbonding electron groups. The molecular geometry that is associated with 3 bonding electron groups is trigonal planar. The molecular geometry that is associated with 2 bonding and 1 nonbonding electron groups is angular.
Linear VSEPR electron group:
The two electron pairs can be of only one VSEPR electron groups. It is only 2 bonding electron groups and the geometry associated with it is linear geometry.
Molecules with more than one central atom:
If a molecule contains more than one central atom then the molecular geometry for each central atom is given separately following the same rules applied for the molecules that contain one central atom.
Rules for predicting Geometry of molecules:
- Lewis structure for the given molecule has to be drawn.
- The number of VSEPR electron groups present about the central atom has to be counted in Lewis structure.
- Geometry has to be assigned considering minimum repulsion between the electron groups.
Answer to Problem 5.58EP
Electron group geometry is tetrahedral and molecular geometry about the central atom in
Explanation of Solution
Given molecule is
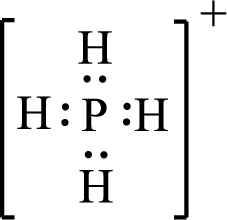
The above drawn structure for
The electron group geometry is tetrahedral and molecular geometry about the central atom is tetrahedral.
Electron group geometry and molecular geometry is predicted for
(c)
Interpretation:
Electron group geometry and Molecular geometry about the central atom for
Concept Introduction:
Information about the number of bonds and types of bonds can be obtained from Lewis structure but the molecular geometry cannot be obtained. Three dimensional arrangement of atoms in a molecule can be given by molecular geometry. Physical and chemical properties are determined by the molecular geometry of the molecule.
Using VSEPR theory and Lewis structure, the molecular geometry of the molecule that contain less number of atoms can be predicted. VSEPR theory uses the information from Lewis structure of the molecule to predict the molecular geometry of the molecule. Main concept of VSEPR theory is that electron pairs that are present in the valence shell adopt arrangement in a way that minimize the repulsion between like charges.
If the central atom contains two electron pairs, then it has to be far apart means, it has to be on opposite side of the nucleus. This means the angle has to be
If the central atom contains three electron pairs, then it has to be far apart means, it has to be on corner of a triangle. This means the angle has to be
If the central atom contains four electron pairs, then it has to be far apart means, it has to be in a tetrahedral arrangement. This means the angle has to be
The collection of valence electron that is present in localized region about central atom in a molecule is known as VSEPR electron group. This may contain two electrons, four electrons, or six electrons. The electron group that contain four and six electrons repel each other.
Tetrahedral VSEPR electron group:
The four electron pairs can be of three VSEPR electron groups. They are 4 bonding electron groups, 3 bonding and 1 nonbonding electron groups, and 2 bonding and 2 nonbonding electron groups. The molecular geometry that is associated with 4 bonding electron groups is tetrahedral. The molecular geometry that is associated with 3 bonding and 1 nonbonding electron groups is trigonal pyramidal. The molecular geometry that is associated with 2 bonding and 2 nonbonding electron groups is angular.
Trigonal planar VSEPR electron group:
The three electron pairs can be of two VSEPR electron groups. They are 3 bonding electron groups, and 2 bonding and 1 nonbonding electron groups. The molecular geometry that is associated with 3 bonding electron groups is trigonal planar. The molecular geometry that is associated with 2 bonding and 1 nonbonding electron groups is angular.
Linear VSEPR electron group:
The two electron pairs can be of only one VSEPR electron groups. It is only 2 bonding electron groups and the geometry associated with it is linear geometry.
Molecules with more than one central atom:
If a molecule contains more than one central atom then the molecular geometry for each central atom is given separately following the same rules applied for the molecules that contain one central atom.
Rules for predicting Geometry of molecules:
- Lewis structure for the given molecule has to be drawn.
- The number of VSEPR electron groups present about the central atom has to be counted in Lewis structure.
- Geometry has to be assigned considering minimum repulsion between the electron groups.
Answer to Problem 5.58EP
Electron group geometry is tetrahedral and molecular geometry about the central atom in
Explanation of Solution
Given molecule is
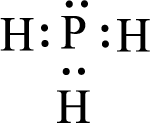
The above drawn structure for
The electron group geometry is tetrahedral and molecular geometry about the central atom is trigonal pyramidal.
Electron group geometry and molecular geometry is predicted for
(d)
Interpretation:
Electron group geometry and Molecular geometry about the central atom for
Concept Introduction:
Information about the number of bonds and types of bonds can be obtained from Lewis structure but the molecular geometry cannot be obtained. Three dimensional arrangement of atoms in a molecule can be given by molecular geometry. Physical and chemical properties are determined by the molecular geometry of the molecule.
Using VSEPR theory and Lewis structure, the molecular geometry of the molecule that contain less number of atoms can be predicted. VSEPR theory uses the information from Lewis structure of the molecule to predict the molecular geometry of the molecule. Main concept of VSEPR theory is that electron pairs that are present in the valence shell adopt arrangement in a way that minimize the repulsion between like charges.
If the central atom contains two electron pairs, then it has to be far apart means, it has to be on opposite side of the nucleus. This means the angle has to be
If the central atom contains three electron pairs, then it has to be far apart means, it has to be on corner of a triangle. This means the angle has to be
If the central atom contains four electron pairs, then it has to be far apart means, it has to be in a tetrahedral arrangement. This means the angle has to be
The collection of valence electron that is present in localized region about central atom in a molecule is known as VSEPR electron group. This may contain two electrons, four electrons, or six electrons. The electron group that contain four and six electrons repel each other.
Tetrahedral VSEPR electron group:
The four electron pairs can be of three VSEPR electron groups. They are 4 bonding electron groups, 3 bonding and 1 nonbonding electron groups, and 2 bonding and 2 nonbonding electron groups. The molecular geometry that is associated with 4 bonding electron groups is tetrahedral. The molecular geometry that is associated with 3 bonding and 1 nonbonding electron groups is trigonal pyramidal. The molecular geometry that is associated with 2 bonding and 2 nonbonding electron groups is angular.
Trigonal planar VSEPR electron group:
The three electron pairs can be of two VSEPR electron groups. They are 3 bonding electron groups, and 2 bonding and 1 nonbonding electron groups. The molecular geometry that is associated with 3 bonding electron groups is trigonal planar. The molecular geometry that is associated with 2 bonding and 1 nonbonding electron groups is angular.
Linear VSEPR electron group:
The two electron pairs can be of only one VSEPR electron groups. It is only 2 bonding electron groups and the geometry associated with it is linear geometry.
Molecules with more than one central atom:
If a molecule contains more than one central atom then the molecular geometry for each central atom is given separately following the same rules applied for the molecules that contain one central atom.
Rules for predicting Geometry of molecules:
- Lewis structure for the given molecule has to be drawn.
- The number of VSEPR electron groups present about the central atom has to be counted in Lewis structure.
- Geometry has to be assigned considering minimum repulsion between the electron groups.
Answer to Problem 5.58EP
Electron group geometry is trigonal planar and molecular geometry about the central atom in
Explanation of Solution
Given molecule is
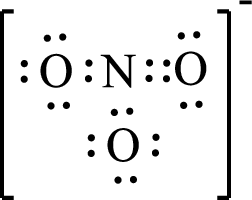
The above drawn structure for
The electron group geometry is trigonal planar and molecular geometry about the central atom is trigonal planar.
Electron group geometry and molecular geometry is predicted for
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Bundle: General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry, 7th + OWLv2 Quick Prep for General Chemistry, 4 terms (24 months) Printed Access Card
- Try: Draw possible resonance contributing structures for the following organic species: CH3CH2NO2 [CH2CHCH2] [CH2CHCHO] [CH2CHCH2] [CH2CHNH2]arrow_forwardComplete the following synthesis. (d). H+ ง сarrow_forwardCan the target compound be efficiently synthesized in good yield from the substituted benzene of the starting material? If yes, draw the synthesis. Include all steps and all reactants.arrow_forward
- This is a synthesis question. Why is this method wrong or worse than the "correct" method? You could do it thiss way, couldn't you?arrow_forwardTry: Draw the best Lewis structure showing all non-bonding electrons and all formal charges if any: (CH3)3CCNO NCO- HN3 [CH3OH2]*arrow_forwardWhat are the major products of the following reaction? Draw all the major products. If there are no major products, then there is no reaction that will take place. Use wedge and dash bonds when necessary.arrow_forward
- IX) By writing the appropriate electron configurations and orbital box diagrams briefly EXPLAIN in your own words each one of the following questions: a) The bond length of the Br2 molecule is 2.28 Å, while the bond length of the compound KBr is 3.34 Å. The radius of K✶ is 1.52 Å. Determine the atomic radius in Å of the bromine atom and of the bromide ion. Br = Br b) Explain why there is a large difference in the atomic sizes or radius of the two (Br and Br). Tarrow_forwardWhen 15.00 mL of 3.00 M NaOH was mixed in a calorimeter with 12.80 mL of 3.00 M HCl, both initially at room temperature (22.00 C), the temperature increased to 29.30 C. The resultant salt solution had a mass of 27.80 g and a specific heat capacity of 3.74 J/Kg. What is heat capacity of the calorimeter (in J/C)? Note: The molar enthalpy of neutralization per mole of HCl is -55.84 kJ/mol.arrow_forwardWhen 15.00 mL of 3.00 M NaOH was mixed in a calorimeter with 12.80 mL of 3.00 M HCl, both initially at room temperature (22.00 C), the temperature increased to 29.30 C. The resultant salt solution had a mass of 27.80 g and a specific heat capacity of 3.74 J/Kg. What is heat capacity of the calorimeter (in J/C)? Note: The molar enthalpy of neutralization per mole of HCl is -55.84 kJ/mol. Which experimental number must be initialled by the Lab TA for the first run of Part 1 of the experiment? a) the heat capacity of the calorimeter b) Mass of sample c) Ti d) The molarity of the HCl e) Tfarrow_forward
 World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning





