
Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781118539293
Author: J. David Irwin, R. Mark Nelms
Publisher: WILEY
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 5, Problem 49P
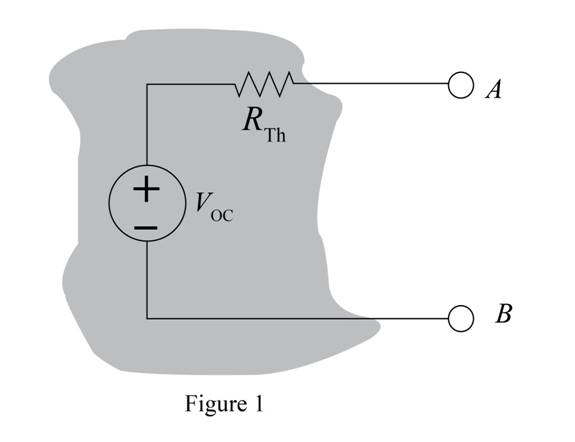
Given the linear circuit in Fig. P5.49, it is known that when a
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Find V show all steps
A wave radiated by an antenna is traveling in the outward radial direction
along the +z axis. Its radiated field in the far zone region is described by its
spherical components, and its polarization is right-hand (clockwise) circularly
polarized. This radiated field impinging upon a receiving antenna whose
polarization is also right-hand (clockwise) circularly polarized and whose
polarization unit vector is represented by
(ao-jas)
E₁ = E(7,0,0) (0-100)
Determine the polarization loss factor (PLF)
Find V0, it's an ideal Op-amp
Chapter 5 Solutions
Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis
Ch. 5 - Find Io in the network in Fig. P5.1 using...Ch. 5 - Find Io in the network in Fig. P5.2 using...Ch. 5 - Find Io in the network in Fig. P5.3 using...Ch. 5 - Find Vo in the network in Fig. P5.4 using...Ch. 5 - Find Io in the circuit in Fig. P5.5 using...Ch. 5 - Find Io in the network in Fig. P5.6 using...Ch. 5 - Find Io in the circuit in Fig. P5.7 using...Ch. 5 - Find Vo in the network in Fig. P5.8 using...Ch. 5 - Find Vo in the network in Fig. P5.9 using...Ch. 5 - In the network in Fig. P5.l0, find using...
Ch. 5 - Find Io in the network in Fig. P5.11 using...Ch. 5 - Find Io in the network in Fig. P5.12 using...Ch. 5 - Find IA in the network in Fig. P5.13 using...Ch. 5 - Using superposition, find IA in the circuit in...Ch. 5 - Find IA in the network in Fig. P5.15 using...Ch. 5 - Using superposition, find Vo in the network in...Ch. 5 - Use superposition to find Io in the circuit in...Ch. 5 - Use superposition to find Io in the network in...Ch. 5 - Use superposition to find Vo in the circuit in...Ch. 5 - Find Vo in the circuit in Fig. P5.20 using...Ch. 5 - Find Io in the circuit in Fig. P5.21 using...Ch. 5 - Use superposition to find Io in the circuit in...Ch. 5 - Use superposition to find Io in the network in...Ch. 5 - Use superposition to find Io in the circuit in...Ch. 5 - Use Thévenins theorem to find Vo in the network...Ch. 5 - Use Thévenins theorem to find in the network in...Ch. 5 - Use Thévenins theorem to find Vo in the network...Ch. 5 - Find Io in the network in Fig. P5.28 using...Ch. 5 - Find Vo in the network in Fig. P5.28 using...Ch. 5 - Use Thévenins theorem to find 10 in the network...Ch. 5 - Find Vo in the network in Fig. P5.31 using...Ch. 5 - Find Io in the circuit in Fig. P5.32 using...Ch. 5 - Find Io in the network in Fig. P5.33 using...Ch. 5 - Find Io in the network in Fig. P5.34 using...Ch. 5 - Find Io in the circuit in Fig. P5.35 using...Ch. 5 - Find Io in the network in Fig. P5.36 using...Ch. 5 - Using Thévenins theorem, find IA in the circuit...Ch. 5 - Find Vo in the network in Fig. P5.38 using...Ch. 5 - Find Vo in the circuit in Fig. P5.39 using...Ch. 5 - Find Io in the circuit in Fig. P5.40 using...Ch. 5 - Find Vo in the network in Fig. P5.41 using...Ch. 5 - Find Io in the network in Fig. P5.42 using...Ch. 5 - Find Vo in Fig. P5.43 using Thévenins theorem.Ch. 5 - Use Thévenins theorem to find Vo in the circuit...Ch. 5 - Use Thévenins theorem to find Io in Fig. P5.45.Ch. 5 - Find Vo in the network in Fig. P5.46 using...Ch. 5 - Use Thévenins theorem to find Io in the network...Ch. 5 - Use Thévenins theorem to find Io in the circuit...Ch. 5 - Given the linear circuit in Fig. P5.49, it is...Ch. 5 - If an 8-k load is connected to the terminals of...Ch. 5 - Use Nortons theorem to find Io in the circuit in...Ch. 5 - Find Io in the network in Fig. P5.52 using Nortons...Ch. 5 - Use Nortons theorem to find Io in the circuit in...Ch. 5 - Use Nortons theorem to find Vo in the network in...Ch. 5 - Find Io in the network in Fig. P5.55 using Nortons...Ch. 5 - Use Nortons theorem to find Vo in the network in...Ch. 5 - Find Vo in the network in Fig. P5.57 using Nortons...Ch. 5 - Use Nortons theorem to find Io in the circuit in...Ch. 5 - Find Vo in the circuit in Fig. P5.59 using Nortons...Ch. 5 - Use Nortons theorem to find Io in the network in...Ch. 5 - Use Nortons theorem to find Io in the circuit in...Ch. 5 - In the network in Fig. P5.62, find Vo using...Ch. 5 - Use Thévenins theorem to find 10 in the circuit...Ch. 5 - Find Vo in the network in Fig. P5.64 using...Ch. 5 - Use Thévenins theorem to find Vo in the circuit...Ch. 5 - Find Io in the circuit in Fig. P5.66 using...Ch. 5 - Use Thévenins theorem to find Io in the circuit...Ch. 5 - Use Thévenins theorem to find Vo in the circuit...Ch. 5 - Find Vo in the network in Fig. P5.69 using...Ch. 5 - Use Nortons theorem to find Vo in the network in...Ch. 5 - Find Vo in the circuit in Fig. P5.71 using...Ch. 5 - Find Vo in the network in Fig. P5.72 using...Ch. 5 - Find Vo in the network in Fig. P5.73 using Nortons...Ch. 5 - Use Thévenins theorem to find the power supplied...Ch. 5 - Find Vo in the circuit in Fig. P5.75 using...Ch. 5 - Find Vo in the network in Fig. P5.76 using...Ch. 5 - Find Vo in the network in Fig. P5.77 using...Ch. 5 - Use Thévenins theorem to find I2 in the circuit...Ch. 5 - Use Thévenins theorem to find Vo in the circuit...Ch. 5 - Use Thévenins theorem to find Vo in the circuit...Ch. 5 - Use Thévenins theorem to find Io in the network...Ch. 5 - Use Thévenins theorem to find Vo in the network...Ch. 5 - Find the Thévenin equivalent of the network in...Ch. 5 - Find the Thévenin equivalent of the network in...Ch. 5 - Find the Thévenin equivalent of the circuit in...Ch. 5 - Find the Thévenin equivalent of the network in...Ch. 5 - Find the Thévenin equivalent circuit of the...Ch. 5 - Find Vo in the network in Fig. P5.88 using source...Ch. 5 - Find Io in the network in Fig. P5.89 using source...Ch. 5 - Use source transformation to find Vo in the...Ch. 5 - Find 10 in the network in Fig. P5.91 using source...Ch. 5 - Find Vo in the network in Fig. P5.92 using source...Ch. 5 - Use source transformation to find Io in the...Ch. 5 - Find the Thévenin equivalent circuit of the...Ch. 5 - Find Io in the circuit in Fig. P5.95 using source...Ch. 5 - Find Io in the network in Fig. P5.96 using source...Ch. 5 - Find Io in the network in Fig. P5.97 using source...Ch. 5 - Find Vo in the network in Fig. P5.98 using source...Ch. 5 - Find Io in the network in Fig. P5.99 using source...Ch. 5 - Find in the circuit in Fig. P5.100 using source...Ch. 5 - Use source transformation to find Io in the...Ch. 5 - Using source transformation, find Vo in the...Ch. 5 - Use source transformation to find Io in the...Ch. 5 - Use source transformation to find Io in the...Ch. 5 - Use source transformation to find 10 in the...Ch. 5 - Using source transformation, find 10 in the...Ch. 5 - Use source exchange to find Io in the network in...Ch. 5 - Use a combination of Y- transformation and source...Ch. 5 - Use source exchange to find Io in the circuit in...Ch. 5 - Use source exchange to find Io in the network in...Ch. 5 - Use source exchange to find Io in the network in...Ch. 5 - Find RL in the network in Fig. P5.112 in order to...Ch. 5 - In the network in Fig. P5.113, find RL for maximum...Ch. 5 - Find RL for maximum power transfer and the maximum...Ch. 5 - Find RL for maximum power transfer and the maximum...Ch. 5 - Find RL for maximum power transfer and the maximum...Ch. 5 - Find RL for maximum power transfer and the maximum...Ch. 5 - Determine the value of RL in the network in Fig....Ch. 5 - Find RL for maximum power transfer and the maximum...Ch. 5 - Find the value of RL in the network in Fig. P5.120...Ch. 5 - Find the value of RL for maximum power transfer...Ch. 5 - Find the maximum power that can be transferred to...Ch. 5 - In the network in Fig. P5.123, find the value of...Ch. 5 - In the network in Fig. P5.124, find the value of...Ch. 5 - Find the value of RL in Fig. P5.125 for maximum...Ch. 5 - Calculate the maximum power that can be...Ch. 5 - Find RL for maximum power transfer and the maximum...Ch. 5 - Find the value of RL in Fig. P5.128 for maximum...Ch. 5 - A cell phone antenna picks up a call. If the...Ch. 5 - Some young engineers at the local electrical...Ch. 5 - Determine the maximum power that can be delivered...Ch. 5 - Find the value of the load RL in the network in...Ch. 5 - Find the value of RL in the network in fig. 5PFE-3...Ch. 5 - What is the current I in Fig. 5PFE4? a. 8 Ac. 0 A...Ch. 5 - What is the open-circuit voltage Voc at terminals...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Create a GUI application that draws the following of a magic wand, using polygons and polylines: Graphics
Java: An Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming (8th Edition)
Why is it useful for a programmer to have some background in language design, even though he or she may never a...
Concepts Of Programming Languages
The code for a library function must appear in a program in order for the program to call the library function.
Starting Out with Programming Logic and Design (5th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
13. Consider the following strange, but true, units:
1 batman = 3 kilograms [kg] 1 hogshead = 63 gallons [gal]
...
Thinking Like an Engineer: An Active Learning Approach (4th Edition)
This statement is like a chain of If statements. They perform their tests, one after the other, until one of th...
Starting Out With Visual Basic (8th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Fjjrjarrow_forwardHW_#1 HW_01.pdf EE 213-01 Assignments P Pearson MyLab and Mastering uah.instructure.com P Course Home Watch out for units (i.e, kQ, mA, etc), show all units on answers and clearly mark all answers 1)(5 pts) Specify if the following elements are absorbing or delivering power, and determine the amount of power being absorbed or delivered. 10 V + a) 5A + 5 V - b) 2A + 10 V -2A 2)(5 pts) Two circuits, shown by boxes A and B are connected as shown below. Use the current reference direction provided and the voltage reference polarity shown to determine the power for the interconnection. Also state the direction of power flow for the connection: form A to B or B to A. A I + I a) I = -6 A V = -20 Volts b) 1 = 8 A V = 30 Volts c) = 4 A V = -80 Volts d) I = -5 A V = 40 Volts B 3) (5 pts) Use Ohm's Law, KCL and KVL to determine values for V1, V2, V₁, I₁, and I2. 200 Ohms A, + 12 + V1 75 Ohms 3 Amps + V2 300 Ohms 25 Ohms 4) (5 pts) For the circuit in Problem 2, determine the power (expressed as a…arrow_forwardFind the power delivered across the 10 ohm resistorarrow_forward
- For the Circuit Below Find: A) io in terms of Rb and the numerical resistor values provided in the schematic. Reduce your solution to a minimal Equations B)the power delivered across Rb in terms of Rb and the numerical resistor values provided in the schematic. Reduce your solution to a minimal equation. C) the power delivered across Rc if Rb is 5 Q Ra $50 15Ω M 120 90V +1 Rb 150 150 m Rcarrow_forwardProblems A.1 The square-law modulator is a device for the generation of DSB-PC-AM signals. In the square-law modulator, the sum of the modulating signal and the carrier wave forms the input signal to a nonlinear device. The output signal of the nonlinear device is a linear combination of the input signal and the square of the input signal. The output signal of the nonlinear device is then band-pass filtered. The BPF has a center frequency that is the same as the carrier frequency and a bandwidth that is twice the message bandwidth. Show the output of the BPF is a DSB-PC-AM signal, and determine a requirement between the carrier frequency and the message bandwidth that must be satisfied.arrow_forwardGive the current voltage relationship of the D-MOSFET and E-MOSFET.arrow_forward
- Answer A is wrong.arrow_forwardThe part of machine level instruction, which tells the central processor what was to be done is: A. Address B. None of the above C. Operation code D. Operandarrow_forwardWhich of the following statement is TRUE? 1. In RISC processors, each instruction requires only two clock cycles to complete, resulting in consistent execution time 2. RISC has more transistors and fewer registers 3. RISC has more registers and fewer transistorsarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Maximum Power Transfer Theorem Using Nodal Analysis & Thevenin Equivalent Circuits; Author: The Organic Chemistry Tutor;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8CA6ZNXgI-Y;License: Standard Youtube License