
Concept explainers
Design a class to represent a credit card. Think about the attributes of a credit card; that is, what data is on the card? What behaviors might be reasonable for a credit card? Use the answer to these questions to write a UML class diagram for a credit card class. Then give three examples or instances of this class.
Unified Modeling Language (UML)
Unified Modeling Language (UML) is a modeling language in software engineering, which is used to visualize the design of the proposing system.
- In software development life cycle, it comes under the “documenting the program” phase.
- UML is used to document the developing system; this documentation helps the end user to understand the whole project.
- It visualizes all the components used in the developed object-oriented software; it shows all the elements and its relation.
Class diagram:
Class diagram is a static model which represents the system’s static structure and its relationship using attributes, relationships, objects, and operations.
- The relationship between the classes in the class diagram is called association.
- It is represented by drawing a line called association path between classes and placing the labels in between the association path.
- The instance of one class can be associated with more than one instance of another class and it is referred as multiplicity.
Steps to create class diagram:
- Identify objects
- Identify the attributes and behaviors
- Draw association between the classes.
Representing the class diagram:
- Every class in the class diagram is represented using a rectangle.
- The rectangle is divided into three parts,
- The first part contains the name of the class
- The middle part contains the attributes and derived attributes
- The last part contains the methods.
| Class name |
|
-Attribute name |
| +Operation name() |
Explanation of Solution
Attributes:
- Initially, identify the reasonable attributes for “CreditCard” class.
- The “CreditCard” contains the card number, card name, expiry date for card, and so on.
- So, let us take the followings are the attributes for “CreditCard” class.
- “cardNo”
- “name”
- “cardExpiryDate”
Explanation of Solution
Behaviors:
- Initially, identify the reasonable behaviors for “CreditCard” class.
- The “CreditCard” contains the “getCredit”, “getPurchase” and so on.
- So, let us take the followings are the behaviors for “CreditCard” class.
- “getCredit()”
- “getPurchase()”
Explanation of Solution
The UML class diagram for credit card is shown below:
The “CreditCard” class is shown in the following class diagram:
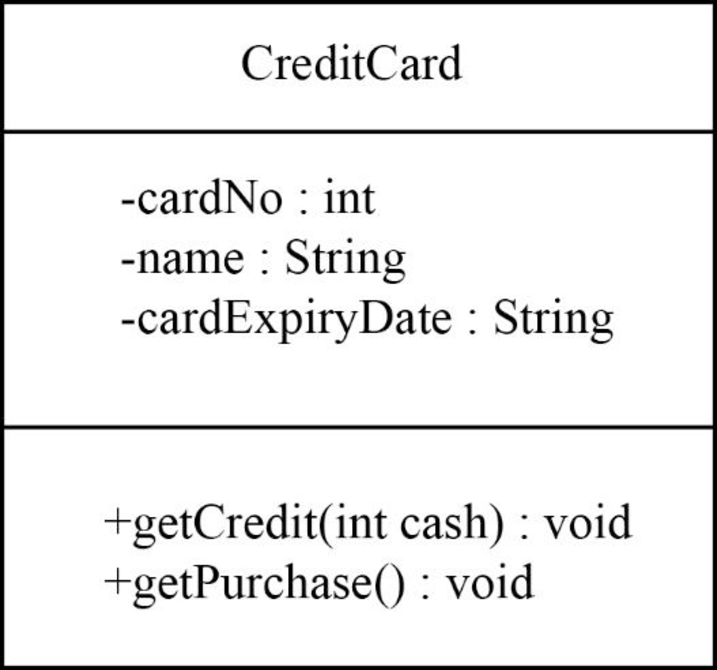
Explanation:
In the above diagram,
- The class name is “CreditCard”.
- The “cardNo”, “name”, and “cardExpiryDate” are attributes of “CreditCard” class.
- The “getCredit()” and “getPurchase()” are methods or operation name of “CreditCard” class.
- “getCredit()” method is used to gets the credit card amount from bank.
- “getPurchase()” is used to purchase the products by using the credit card.
Examples of objects of this “CreditCard”class:
First object:
The first object is “customer1” for this “CreditCard” class is shown below:

Explanation:
In the above diagram,
- The “customer1” object for “CreditCard” class.
- Assign the “cardNo” as “123456”, “name” as “XXXX” and “cardExpiryDate” as “03/02/2001” are the attributes of the “CreditCard” class.
Second object:
The second object is “customer2” for this “CreditCard” class is shown below:

Explanation:
In the above diagram,
- The “customer2” object for “CreditCard” class.
- Assign the “cardNo” as “234578”, “name” as “YYYY” and “cardExpiryDate” as “12/11/2022” are the attributes of the “CreditCard” class.
Third object:
The third object is “customer3” for this “CreditCard” class is shown below:
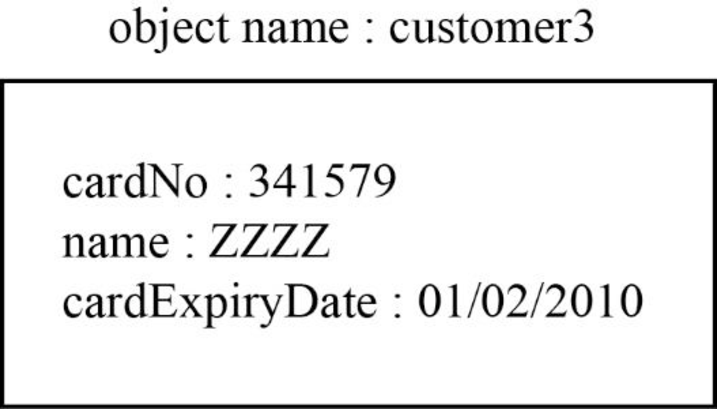
Explanation:
In the above diagram,
- The “customer3” object for “CreditCard” class.
- Assign the “cardNo” as “341579”, “name” as “ZZZZ” and “cardExpiryDate” as “01/02/2010” are the attributes of the “CreditCard” class.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Java: An Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming (8th Edition)
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Problem Solving with C++ (10th Edition)
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
SURVEY OF OPERATING SYSTEMS
Java How to Program, Early Objects (11th Edition) (Deitel: How to Program)
Starting Out with C++ from Control Structures to Objects (9th Edition)
Elementary Surveying: An Introduction To Geomatics (15th Edition)
- 2:21 m Ο 21% AlmaNet WE ARE HIRING Experienced Freshers Salesforce Platform Developer APPLY NOW SEND YOUR CV: Email: hr.almanet@gmail.com Contact: +91 6264643660 Visit: www.almanet.in Locations: India, USA, UK, Vietnam (Remote & Hybrid Options Available)arrow_forwardProvide a detailed explanation of the architecture on the diagramarrow_forwardhello please explain the architecture in the diagram below. thanks youarrow_forward
- Complete the JavaScript function addPixels () to calculate the sum of pixelAmount and the given element's cssProperty value, and return the new "px" value. Ex: If helloElem's width is 150px, then calling addPixels (hello Elem, "width", 50) should return 150px + 50px = "200px". SHOW EXPECTED HTML JavaScript 1 function addPixels (element, cssProperty, pixelAmount) { 2 3 /* Your solution goes here *1 4 } 5 6 const helloElem = document.querySelector("# helloMessage"); 7 const newVal = addPixels (helloElem, "width", 50); 8 helloElem.style.setProperty("width", newVal); [arrow_forwardSolve in MATLABarrow_forwardHello please look at the attached picture. I need an detailed explanation of the architecturearrow_forward
- Information Security Risk and Vulnerability Assessment 1- Which TCP/IP protocol is used to convert the IP address to the Mac address? Explain 2-What popular switch feature allows you to create communication boundaries between systems connected to the switch3- what types of vulnerability directly related to the programmer of the software?4- Who ensures the entity implements appropriate security controls to protect an asset? Please do not use AI and add refrencearrow_forwardFind the voltage V0 across the 4K resistor using the mesh method or nodal analysis. Note: I have already simulated it and the value it should give is -1.714Varrow_forwardResolver por superposicionarrow_forward
- Describe three (3) Multiplexing techniques common for fiber optic linksarrow_forwardCould you help me to know features of the following concepts: - commercial CA - memory integrity - WMI filterarrow_forwardBriefly describe the issues involved in using ATM technology in Local Area Networksarrow_forward
- Programming Logic & Design ComprehensiveComputer ScienceISBN:9781337669405Author:FARRELLPublisher:Cengage
 Microsoft Visual C#Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102100Author:Joyce, Farrell.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Microsoft Visual C#Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102100Author:Joyce, Farrell.Publisher:Cengage Learning, EBK JAVA PROGRAMMINGComputer ScienceISBN:9781337671385Author:FARRELLPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK JAVA PROGRAMMINGComputer ScienceISBN:9781337671385Author:FARRELLPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT  C++ for Engineers and ScientistsComputer ScienceISBN:9781133187844Author:Bronson, Gary J.Publisher:Course Technology Ptr
C++ for Engineers and ScientistsComputer ScienceISBN:9781133187844Author:Bronson, Gary J.Publisher:Course Technology Ptr C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102087Author:D. S. MalikPublisher:Cengage Learning
C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102087Author:D. S. MalikPublisher:Cengage Learning New Perspectives on HTML5, CSS3, and JavaScriptComputer ScienceISBN:9781305503922Author:Patrick M. CareyPublisher:Cengage Learning
New Perspectives on HTML5, CSS3, and JavaScriptComputer ScienceISBN:9781305503922Author:Patrick M. CareyPublisher:Cengage Learning





