
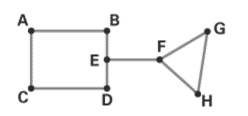
Use the preceding graph to answer the following questions:
a. How many edges does the graph have?
b. Which vertices are odd? Which are even?
c. Is the graph connected?
d. Does the graph have any bridges?
To find:
a. Find the number of edges in the graph.
b. Find the odd vertices and even vertices.
c. Check whether the graph is connected or not.
d. Check whether the graph has any bridge or not.
Answer to Problem 1CT
Solution:
a. The number of edges in the graph is 9.
b. The odd vertices are E, F and the even vertices are A, B, C, D, G, H.
c. The given graph is a connected graph.
d. The graph has one bridge namely EF.
Explanation of Solution
Graph:
A graph is a set of points, called vertices, and lines, called edges, that join pairs of vertices.
Vertex:
1. The points in the graph are called as vertex.
2. The point of intersection of a pair of edges is not a vertex.
3. A vertex of a graph is odd if it is the endpoint of an odd number of edges.
4. A vertex is even if it is the endpoint of an even number of edges.
Degree:
1. Degree of a vertex is the number of edges joined to that vertex.
2. If the degree is an odd number, then it is called as odd vertex.
3. If the degree of a vertex is even, then the vertex is called as even vertex.
Edge:
The line joining a pair of vertices is called as edge.
For example, we can refer a line joining the vertices A and B as edge AB or edge BA.
Connected graph:
A graph is connected if it is possible to travel from any vertex to any other vertex of the graph by moving along successive edges.
Bridge:
A bridge in a connected graph is an edge such that if it were removed, the graph would no longer be connected.
Calculation:
The graph in the problem is given below.
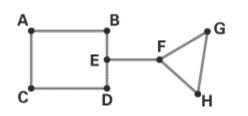
a. Find the number of edges:
The vertices in the graph are A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H.
The line joining the vertices is AB, AC, CD, BE, ED, EF, FG, FH and GH.
The number of edges in the graph is 9.
b. Find the odd vertices and even vertices:
Vertex A is the endpoint of two edges, so its degree is two.
Vertex B is the endpoint of two edges, so its degree is two.
Vertex C is the endpoint of two edges, so its degree is two.
Vertex D is the endpoint of two edges, so its degree is two.
Vertex E is the endpoint of two edges, so its degree is three
Vertex F is the endpoint of two edges, so its degree is three.
Vertex G is the endpoint of two edges, so its degree is two.
Vertex H is the endpoint of two edges, so its degree is two.
The odd vertices are E, F and the even vertices are A, B, C, D, G, H.
c. Check whether the graph is connected or not:
In a connected graph, there are no unreachable vertices.
In the given graph, we can travel from one vertex to another through successive edges.
For example, we can travel from vertex A to F through edges AB, BE, EF.
The given graph is a connected graph.
d. Check whether the graph has any bridge or not:
In the graph, if we remove the edge EF, then the graph becomes non connected graph. We cannot travel from vertex A to vertex G.
The edge EF is a bridge in the graph.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Mathematics All Around (6th Edition)
- 9:41 … 93 Applying an Exponential Function to Newton's Law of Cooling 60. Water in a water heater is originally Aa ← 122°F. The water heater is shut off and the water cools to the temperature of the surrounding air, which is 60°F. The water cools slowly because of the insulation inside the heater, and the value of k is measured as 0.00351. a. Write a function that models the temperature T (t) (in °F) of the water t hours after the water heater is shut off. b. What is the temperature of the water 12 hr after the heater is shut off? Round to the nearest degree. c. Dominic does not like to shower with water less than 115°F. If Dominic waits 24 hr. will the water still be warm enough for a shower? Mixed Exercises ger-ui.prod.mheducation.comarrow_forwardExplain the key points of 11.5.1arrow_forwardExplain the key points of 11.3.5arrow_forward
 College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell
Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage,
Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage, Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL




