
Concept explainers
A rigid circular plate of 125-mm radius is attached to a solid 150 × 200-mm rectangular post, with the center of the plate directly above the center of the post. If a 4-kN force P is applied at E with θ = 30°, determine (a) the stress at point A, (b) the stress at point B, (c) the point where the neutral axis intersects line ABD.
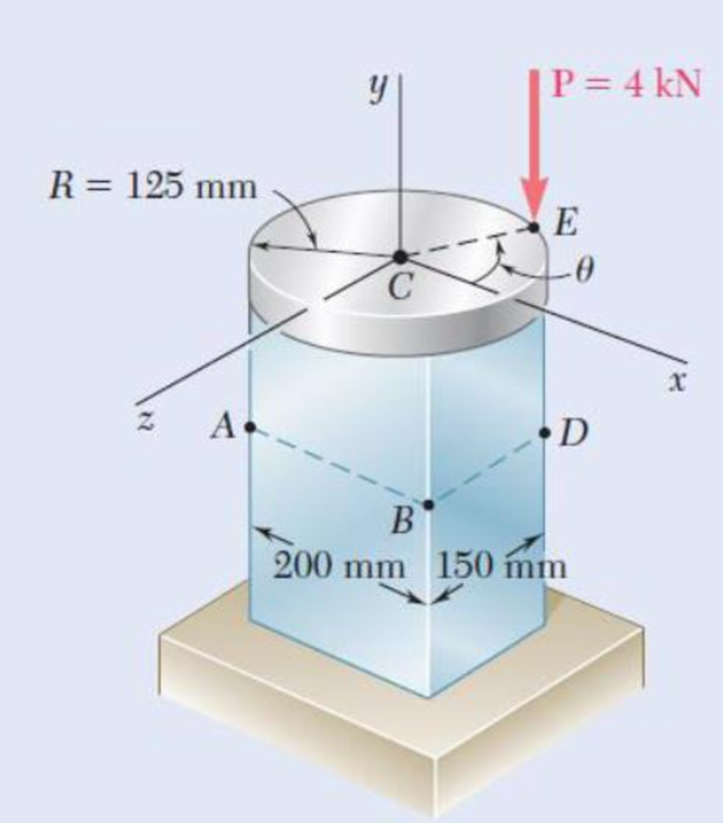
Fig. P4.148
(a)
Find the value of stress at point A.
Answer to Problem 148P
The stress at point A is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The radius of the circular plate is
The width of the rectangular post is
The applied force is
Calculation:
Sketch the cross section of disk as shown in Figure 1.
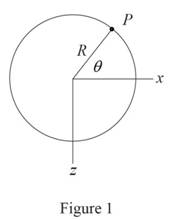
Refer to Figure 1.
Consider the value of angle
Calculate the moment along
Substitute
Calculate the moment along
Substitute
Sketch the cross section of the rectangular post as shown in Figure 2.
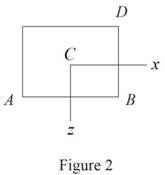
Refer to Figure 2.
Calculate the area
Substitute
Calculate the moment of inertia along
Substitute
Calculate the moment of inertia along
Substitute
Calculate the stress
Refer to Figure 2.
The location of point A along
The location of point A along
Calculate the stress at A
Substitute
Hence, the stress at A is
(b)
The values of stress at B.
Answer to Problem 148P
The stress at B is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Calculation:
Calculate the stress at B
Refer to Figure 2 in part (a).
The location of point B along
The location of point B along
Substitute
Hence, the stress at B is
(c)
The point where the neutral axis intersect ABD.
Answer to Problem 148P
The point where the neutral axis intersect ABD is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Calculation:
The stress at G
Refer to Figure 2 in part (a).
The location of point G along
The location of point G along
Substitute
Show the distance (d) between the point A and the point G as follows:
Thus, The point where the neutral axis intersect ABD is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials, 7th Edition
- 2.36 A 250-mm bar of 150 x 30-mm rectangular cross section consists of two aluminum layers, 5 mm thick, brazed to a center brass layer of the same thickness. If it is subjected to centric forces of magni- tude P = 30 kN, and knowing that E, = 70 GPa and E, = 105 GPa, determine the normal stress (a) in the aluminum layers, (b) in the brass layer. P' 250 mm 5 mm 5 mm 5 mm Aluminum Brass Aluminum P 30 mm Fig. P2.36arrow_forward2.13 A steel plate, which is 1.5 m by 1.5 m and 30 mm thick, is lifted by four cables attached to its corners that meet at a point that is 2 m above the plate. Determine the required cross-sectional area of the cables if the stress in them is not to exceed 20 MPa. Steel plate Prob. 2.13 Cablesarrow_forwardFig. 2 4. A steel shaft of diameter 50 mm and length 1.2 m (E = 210 GPa and v = 0.3) is loaded with multiple force system. At a point in the shaft, the state of stress relative to the x, y, z coordinate system was found to be: [600 0 T = 0 320 MPa -480 (a) Draw a cube element showing the stress components on each coordinate face (Hint: No vector lines for zero stresses; Warning: A stress element without reference axes will receive zero point). (b) From the given stress tensor, determine the values of (i) octahedral normal stress (Goct) and (ii) octahedral shear stress (toct). (c) From your answer in (b), determine (i) dilatational strain energy Udilat '); and (ii) deviatoric strain energy (Udist). (d) Find the total strain energy at the point.arrow_forward
- 5.86 The cast iron inverted T-section supports two concentrated loads of magni- tude P. The working stresses are 48 MPa in tension, 140 MPa in compression, and 30 MPa in shear. (a) Show that the neutral axis of the cross section is located at d = 48.75 mm and that the moment of inertia of the cross-sectional area about this axis is I = 11.918 x 106 mm“. (b) Find the maximum allowable value of P. 1.0 m 1.0 m 15 mm 3 m 150 mm NA- d 15 mm 150 mm FIG. P5.86arrow_forwardPROBLEM 1.3 3 in. 30 kips Two solid cylindrical rods AB and BC are welded together at B and loaded as shown. Determine the magnitude of the force P for which the tensile stress in rod AB is twice the magnitude of the compressive stress in rod BC. 30 kips 40 in PROBLEM 1.4 In Prob. 1.3, knowing that P = 40 kips, determine the average normal stress at the midsection of (a) rod AB, (b) rod BC.arrow_forward4.17. Determine the components of stress from the results obtained in (a) v=rsin 0, ve = 2r cos 0 (b) VT = cos 0, 1/4 = 0 (c) v = V₁ = 0 (d) v = (1 - 4) cos 0, Ve= - - (1 + 4/4) sin 0 - Barrow_forward
- Three forces, each of magnitude P = 3 kN, are applied to the structure shown. Determine the cross-sectional area of the uniform portion of rod BE for which the normal stress in that portion is +100 MPa. The cross-sectional area of the uniform portion of rod BE is mm2.arrow_forward+3 in- B in. A vertical force P of magnitude 20 kips is applied at point C located on the axis of symmetry of the cross section of a short column. Knowing that y = 5 in., determine (a) the stress at point A, (b) the stress at point B, (c) the location of the neutral axis. 2 in. 4 in. A 2 in. 2 in. 1 in. (a) (b)arrow_forwardThe member having a rectangular cross-section, Fig. a, is designed to resist a moment of 40 N # m. In order to increase its strength and rigidity, it is proposed that two small ribs be added at its bottom, Fig. b. Determine the maximum normal stress in the member for both cases.arrow_forward
- Knowing that the clamp shown has been tightened until P= 400 N, determine (a) the stress at point A, (b) the stress at point B, (c) the location of the neutral axis of section a-a.arrow_forwardPROBLEM 1.2 Two solid cylindrical rods AB and BC are welded together at B and loaded as shown. Knowing that d = 50 mm and dz = 30 mm, find the average normal stress at the midsection of (a) rod AB, (b) rod BC. 300 mm 40 kN 250 mm V30 KNarrow_forwardTwo gage marks are placed exactly 250 mm apart on a 12-mm-diameter aluminum rod with E = 73 GPa and an ultimate strength of 140 MPa. Knowing that the distance between the gage marks is 250.28 mm after a load is applied, determine the stress in the rodarrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





