
(a)
Find the residual stress at
(a)
Answer to Problem 90P
The residual stress is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The yield stress for the beam is
The Young’s modulus of steel is
Calculation:
Show the cross-section of the beam as shown in Figure 1.
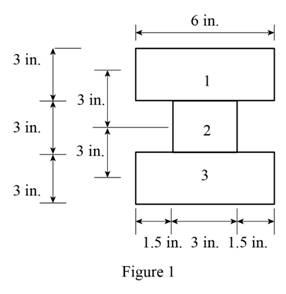
Refer Figure 1.
Calculate the area of the cross section
Here, b is the width of the cross section and d is the depth of the cross section.
Calculate the area of the portion (1)
Substitute
Calculate the area of the portion (2)
Substitute
Calculate the moment of inertia
Calculate the moment of inertia of portion (1)
Substitute
Calculate the moment of inertia of portion (2)
Substitute
Calculate the total moment of inertia
Substitute
Calculate the centroid (c) as shown below.
Substitute
Sketch the stress acting on the cross-section of the beam as shown in Figure 2.
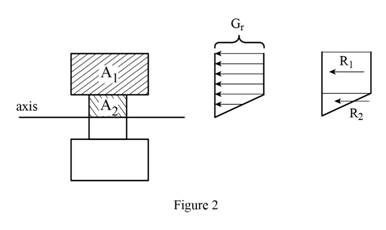
Refer Figure 2.
Calculate the area of the portion (2)
Substitute
Calculate the reaction applied to portion (1)
Substitute
Calculate the reaction applied to portion (2)
Substitute
Calculate the moment
Substitute
Calculate the stress
Substitute
Calculate the stress
Substitute
Calculate the residual stress at
Substitute
Calculate the residual stress at
Substitute
Sketch the stress distribution as shown in Figure 3.
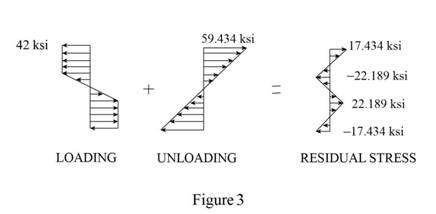
Hence, the residual stress is
(b)
Find the point where the residual stress is zero.
(b)
Answer to Problem 90P
The point where the residual stress is zero is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The yield stress for the beam is
The Young’s modulus of steel is
Calculation:
Consider that the residual stress
Calculate the yield stress
Calculate the point where the residual stress is zero as shown below.
Substitute
Substitute
Therefore, the point where the residual stress is zero is
(c)
Find the radius of curvature corresponding to the permanent deformation of the bar.
(c)
Answer to Problem 90P
The radius of curvature is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The yield stress for the beam is
The Young’s modulus of steel is
Calculation:
Refer to part (a).
The residual stress
Calculate the radius of curvature
Calculate the point where the residual stress is zero as shown below.
Substitute
Therefore, the radius of curvature is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials, 7th Edition
- 2. Figure below shows a U-tube manometer open at both ends and containing a column of liquid mercury of length l and specific weight y. Considering a small displacement x of the manometer meniscus from its equilibrium position (or datum), determine the equivalent spring constant associated with the restoring force. Datum Area, Aarrow_forward1. The consequences of a head-on collision of two automobiles can be studied by considering the impact of the automobile on a barrier, as shown in figure below. Construct a mathematical model (i.e., draw the diagram) by considering the masses of the automobile body, engine, transmission, and suspension and the elasticity of the bumpers, radiator, sheet metal body, driveline, and engine mounts.arrow_forward3.) 15.40 – Collar B moves up at constant velocity vB = 1.5 m/s. Rod AB has length = 1.2 m. The incline is at angle = 25°. Compute an expression for the angular velocity of rod AB, ė and the velocity of end A of the rod (✓✓) as a function of v₂,1,0,0. Then compute numerical answers for ȧ & y_ with 0 = 50°.arrow_forward
- 2.) 15.12 The assembly shown consists of the straight rod ABC which passes through and is welded to the grectangular plate DEFH. The assembly rotates about the axis AC with a constant angular velocity of 9 rad/s. Knowing that the motion when viewed from C is counterclockwise, determine the velocity and acceleration of corner F.arrow_forward500 Q3: The attachment shown in Fig.3 is made of 1040 HR. The static force is 30 kN. Specify the weldment (give the pattern, electrode number, type of weld, length of weld, and leg size). Fig. 3 All dimension in mm 30 kN 100 (10 Marks)arrow_forward(read image) (answer given)arrow_forward
- A cylinder and a disk are used as pulleys, as shown in the figure. Using the data given in the figure, if a body of mass m = 3 kg is released from rest after falling a height h 1.5 m, find: a) The velocity of the body. b) The angular velocity of the disk. c) The number of revolutions the cylinder has made. T₁ F Rd = 0.2 m md = 2 kg T T₂1 Rc = 0.4 m mc = 5 kg ☐ m = 3 kgarrow_forward(read image) (answer given)arrow_forward11-5. Compute all the dimensional changes for the steel bar when subjected to the loads shown. The proportional limit of the steel is 230 MPa. 265 kN 100 mm 600 kN 25 mm thickness X Z 600 kN 450 mm E=207×103 MPa; μ= 0.25 265 kNarrow_forward
- T₁ F Rd = 0.2 m md = 2 kg T₂ Tz1 Rc = 0.4 m mc = 5 kg m = 3 kgarrow_forward2. Find a basis of solutions by the Frobenius method. Try to identify the series as expansions of known functions. (x + 2)²y" + (x + 2)y' - y = 0 ; Hint: Let: z = x+2arrow_forward1. Find a power series solution in powers of x. y" - y' + x²y = 0arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





