
Organic Chemistry
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781305580350
Author: William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 4.6, Problem 1Q
Acid-Base Equilibria
Many factors contribute to the acidity of organic compounds. Electronegativity, resonance, induction, hybridization,
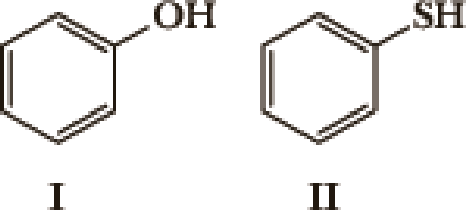
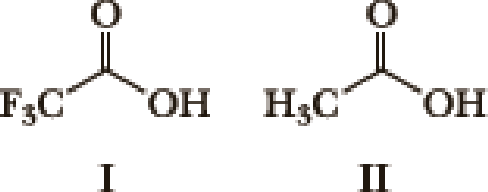
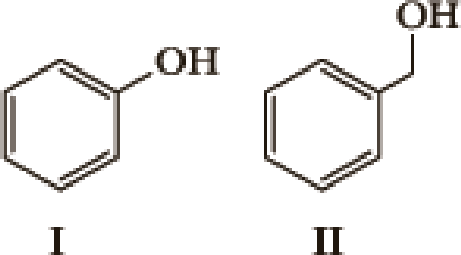
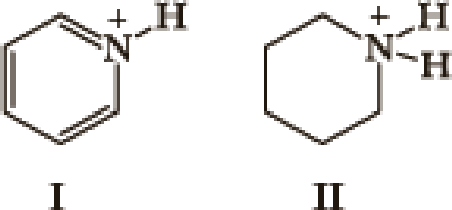
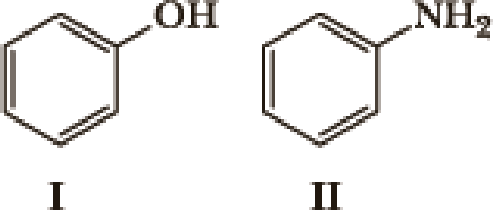
- 1. What factor(s) are the most important to consider when predicting the relative acidity of the two compounds?
- a. Electronegativity of the atom possessing the hydrogen.
- b. Resonance stabilization of the anionic conjugate base.
- c. Inductive stabilization of the anionic conjugate base.
- d. Hybridization of the atom possessing the hydrogen.
- e. The atomic size of the atom possessing the hydrogen.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
how many moles of H2O2 are required to react with 11g of N2H4 according to the following reaction? (atomic weights: N=14.01, H=1.008, O= 16.00) 7H2O2 + N2H4 -> 2HNO3 + 8H20
calculate the number of moles of H2 produced from 0.78 moles of Ga and 1.92 moles HCL? 2Ga+6HCL->2GaCl3+3H2
an adult human breathes 0.50L of air at 1 atm with each breath. If a 50L air tank at 200 atm is available, how man y breaths will the tank provide
Chapter 4 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
Ch. 4.2 - For each conjugate acid-base pair, identify the...Ch. 4.2 - Write these reactions as proton-transfer...Ch. 4.2 - Following is a structural formula for guanidine,...Ch. 4.2 - Write an equation to show the proton transfer...Ch. 4.3 - For each value of Ka, calculate the corresponding...Ch. 4.4 - Predict the position of equilibrium and calculate...Ch. 4.5 - Calculate Keq for a reaction with G0 = 17.1 kJ/mol...Ch. 4.6 - Acid-Base Equilibria Many factors contribute to...Ch. 4.6 - What is the relative trend in acidity and pKa of...Ch. 4.7 - Write an equation for the reaction between each...
Ch. 4 - For each conjugate acid-base pair, identify the...Ch. 4 - Complete a net ionic equation for each...Ch. 4 - Arrange the compounds in each set in order of...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.12PCh. 4 - In acetic acid, CH3COOH, the OH hydrogen is more...Ch. 4 - Which has the larger numerical value? (a) The pKa...Ch. 4 - In each pair, select the stronger acid. (a)...Ch. 4 - Arrange the compounds in each set in order of...Ch. 4 - Arrange the compounds in each set in order of...Ch. 4 - If the G for a reaction is 4.5 kcal/mol at 298 K,...Ch. 4 - Calculate the Keq for the following reactions from...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.20PCh. 4 - Answer true or false to the following statements...Ch. 4 - In each of the following three reaction coordinate...Ch. 4 - The acid-base chemistry reaction of barium...Ch. 4 - Unless under pressure, carbonic acid (H2CO3) in...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.25PCh. 4 - Acetic acid, CH3COOH, is a weak organic acid, pKa...Ch. 4 - Benzoic acid, C6H5COOH (pKa 4.19), is only...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.28PCh. 4 - One way to determine the predominant species at...Ch. 4 - Will acetylene react with sodium hydride according...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.31PCh. 4 - For each equation, label the Lewis acid and the...Ch. 4 - Complete the equation for the reaction between...Ch. 4 - Each of these reactions can be written as a Lewis...Ch. 4 - The sec-butyl cation can react as both a...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.36APCh. 4 - Prob. 4.37APCh. 4 - Prob. 4.38APCh. 4 - Explain why the hydronium ion, H3O+, is the...Ch. 4 - What is the strongest base that can exist in...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.42APCh. 4 - Prob. 4.43APCh. 4 - Methyl isocyanate, CH3N=C=O, is used in the...Ch. 4 - Offer an explanation for the following...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.46APCh. 4 - Alcohols (Chapter 10) are weak organic acids, pKa...Ch. 4 - As we shall see in Chapter 19, hydrogens on a...Ch. 4 - 2,4-Pentanedione is a considerably stronger acid...Ch. 4 - Write an equation for the acid-base reaction...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.51APCh. 4 - Prob. 4.52APCh. 4 - Prob. 4.53APCh. 4 - Following is a structural formula for imidazole, a...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Using reaction free energy to predict equilibrium composition Consider the following equilibrium: 2NO2 (g) = N2O4(g) AGº = -5.4 kJ Now suppose a reaction vessel is filled with 4.53 atm of dinitrogen tetroxide (N2O4) at 279. °C. Answer the following questions about this system: Under these conditions, will the pressure of N2O4 tend to rise or fall? Is it possible to reverse this tendency by adding NO2? In other words, if you said the pressure of N2O4 will tend to rise, can that be changed to a tendency to fall by adding NO2? Similarly, if you said the pressure of N2O4 will tend to fall, can that be changed to a tendency to '2' rise by adding NO2? If you said the tendency can be reversed in the second question, calculate the minimum pressure of NO 2 needed to reverse it. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. 00 rise ☐ x10 fall yes no ☐ atm G Ar 1arrow_forwardWhy do we analyse salt?arrow_forwardCurved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s). Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making steps. H H CH3OH, H+ H Select to Add Arrows H° 0:0 'H + Q HH ■ Select to Add Arrows CH3OH, H* H. H CH3OH, H+ HH ■ Select to Add Arrows i Please select a drawing or reagent from the question areaarrow_forward
- What are examples of analytical methods that can be used to analyse salt in tomato sauce?arrow_forwardA common alkene starting material is shown below. Predict the major product for each reaction. Use a dash or wedge bond to indicate the relative stereochemistry of substituents on asymmetric centers, where applicable. Ignore any inorganic byproducts H Šali OH H OH Select to Edit Select to Draw 1. BH3-THF 1. Hg(OAc)2, H2O =U= 2. H2O2, NaOH 2. NaBH4, NaOH + Please select a drawing or reagent from the question areaarrow_forwardWhat is the MOHR titration & AOAC method? What is it and how does it work? How can it be used to quantify salt in a sample?arrow_forward
- Predict the major products of this reaction. Cl₂ hv ? Draw only the major product or products in the drawing area below. If there's more than one major product, you can draw them in any arrangement you like. Be sure you use wedge and dash bonds if necessary, for example to distinguish between major products with different stereochemistry. If there will be no products because there will be no significant reaction, just check the box under the drawing area and leave it blank. Note for advanced students: you can ignore any products of repeated addition. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. 80 10 m 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibility DII A F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 F6 F7 F8 EO F11arrow_forwardGiven a system with an anodic overpotential, the variation of η as a function of current density- at low fields is linear.- at higher fields, it follows Tafel's law.Calculate the range of current densities for which the overpotential has the same value when calculated for both cases (the maximum relative difference will be 5%, compared to the behavior for higher fields).arrow_forwardUsing reaction free energy to predict equilibrium composition Consider the following equilibrium: N2 (g) + 3H2 (g) = 2NH3 (g) AGº = -34. KJ Now suppose a reaction vessel is filled with 8.06 atm of nitrogen (N2) and 2.58 atm of ammonia (NH3) at 106. °C. Answer the following questions about this system: rise Under these conditions, will the pressure of N2 tend to rise or fall? ☐ x10 fall Is it possible to reverse this tendency by adding H₂? In other words, if you said the pressure of N2 will tend to rise, can that be changed to a tendency to fall by adding H2? Similarly, if you said the pressure of N will tend to fall, can that be changed to a tendency to rise by adding H₂? If you said the tendency can be reversed in the second question, calculate the minimum pressure of H₂ needed to reverse it. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. yes no ☐ atm Х ด ? olo 18 Ararrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079113
Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305960060
Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. Hansen
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337399074
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:9781133949640
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:Cengage Learning
ENVIRONMENTAL POLLUTION; Author: 7activestudio;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oxtMFmDTv3Q;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY