
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Enatiomers for the given compound has to be drawn using perspective formula.
Concept Introduction:
Perspective formulas show the 3D array of atoms in which the solid wedges indicate bonds projecting above the plane of the drawing and wedge shaded with parallel line indicate bonds projecting below the plane of drawing.
Example:
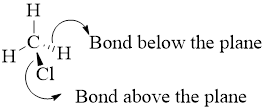
Enantiomers: These are stereoisomers that are not superimposable mirror images of each other and the configurations at all stereo genic centers are exactly opposite.
Enantiomer can be drawn by replacing the wedge with a dash from the perspective formula of a compound.
Chiral center: A chiral center is defined as the tetrahedral carbon atom in an organic molecule that is connected to four non-identical groups/substituents. It is sometimes known as a stereo genic center.
An achiral carbon is a carbon having two or more identical groups around it.
(b)
Interpretation:
Enatiomers for the given compound has to be drawn using perspective formula.
Concept Introduction:
Perspective formulas show the 3D array of atoms in which the solid wedges indicate bonds projecting above the plane of the drawing nad wedge shaded with parallel line indicate bonds projecting below the plane of drawing.
Example:
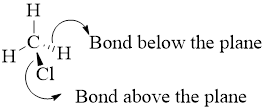
Enantiomers: These are stereoisomers that are not superimposable mirror images of each other and the configurations at all stereo genic centers are exactly opposite.
Enantiomer can be drawn by replacing the wedge with a dash from the perspective formula of a compound.
Chiral center: A chiral center is defined as the tetrahedral carbon atom in an organic molecule that is connected to four non-identical groups/substituents. It is sometimes known as a stereo genic center.
An achiral carbon is a carbon having two or more identical groups around it.
(c)
Interpretation:
Enatiomers for the given compound has to be drawn using perspective formula.
Concept Introduction:
Perspective formulas show the 3D array of atoms in which the solid wedges indicate bonds projecting above the plane of the drawing nad wedge shaded with parallel line indicate bonds projecting below the plane of drawing.
Example:
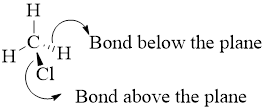
Enantiomers: These are stereoisomers that are not superimposable mirror images of each other and the configurations at all stereo genic centers are exactly opposite.
Enantiomer can be drawn by replacing the wedge with a dash from the perspective formula of a compound.
Chiral center: A chiral center is defined as the tetrahedral carbon atom in an organic molecule that is connected to four non-identical groups/substituents. It is sometimes known as a stereo genic center.
An achiral carbon is a carbon having two or more identical groups around it.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 4 Solutions
Essential Organic Chemistry, Global Edition
- The temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forwardQUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forwardpressure (atm) 3 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 0 0 200 temperature (K) 400 аarrow_forward
- er your payment details | bar xb Home | bartleby x + aleksogi/x/isl.exe/1o u-lgNskr7j8P3jH-1Qs_pBanHhviTCeeBZbufuBYT0Hz7m7D3ZcW81NC1d8Kzb4srFik1OUFhKMUXzhGpw7k1 O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 1 3- 0- 0 200 Explanation Check temperature (K) 400 X Q Search L G 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved Terms of Use Privacy Cearrow_forward5.arrow_forward6.arrow_forward

 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning


