
Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
6th Edition
ISBN: 9780078028229
Author: Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 4.6, Problem 11PP
Find the Norton equivalent circuit for the circuit in Fig. 4.42. at terminals a-b.
Answer: RN = 90 Ω, IN = 4.5 A.
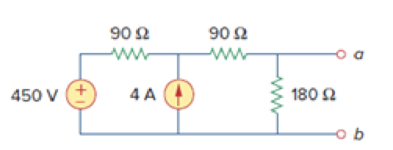
Figure 4.42
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Figure shows the block diagram of a feedback control system with a disturbance signal N(s). Obtain the output Y(s) due to both R(s) and N(s).
A 3-phase, 6-pole induction motor is con-
nected to a 60 Hz supply. The voltage in-
duced in the rotor bars is 4 V when the ro-
tor is locked. If the motor turns in the same
direction as the flux, calculate the approxi-
mate voltage induced and its frequency:
a. At 300 r/min
b. At 1000 r/min
c. At 1500 r/min
Make a drawing of the magnetic field cre-
ated by a 3-phase, 12-pole induction motor.
How can we change the direction of rota-
tion of a 3-phase induction motor?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Ch. 4.2 - Figure 4.3 For Practice Prob. 4.1. For the circuit...Ch. 4.2 - Figure 4.5 For Practice Prob. 4.2. Assume that Vo...Ch. 4.3 - Figure 4.8 Using the superposition theorem, find...Ch. 4.3 - Figure 4.11 Use superposition to find vx in the...Ch. 4.3 - Find I in the circuit of Fig. 4.14 using the...Ch. 4.4 - Find io in the circuit of Fig. 4.19 using source...Ch. 4.4 - Use source transformation to find ix in the...Ch. 4.5 - Using Thevenins theorem, find the equivalent...Ch. 4.5 - Find the Thevenin equivalent circuit of the...Ch. 4.5 - Obtain the Thevenin equivalent of the circuit in...
Ch. 4.6 - Find the Norton equivalent circuit for the circuit...Ch. 4.6 - Find the Norton equivalent circuit of the circuit...Ch. 4.8 - Determine the value of RL that will draw the...Ch. 4.9 - Rework Practice Prob. 4.9 using PSpice. Find the...Ch. 4.9 - Fin d the maximum power transferred to RL if the...Ch. 4.10 - The measured open-circuit voltage across a certain...Ch. 4.10 - Prob. 17PPCh. 4.10 - Obtain the current through the galvanometer,...Ch. 4 - The current through a branch in a linear network...Ch. 4 - For superposition, it is not required that only...Ch. 4 - The superposition principle applies to power...Ch. 4 - Refer to Fig. 4.67. The Thevenin resistance at...Ch. 4 - The Thevenin voltage across terminals a and b of...Ch. 4 - The Norton current at terminals a and b of the...Ch. 4 - The Norton resistance RN is exactly equal to the...Ch. 4 - Which pair of circuits in Fig. 4.68 are...Ch. 4 - A load is connected to a network. At the terminals...Ch. 4 - The source is supplying the maximum power to the...Ch. 4 - Calculate the current io in the circuit of Fig....Ch. 4 - Using Fig. 4.70, design a problem to help other...Ch. 4 - (a) In the circuit of Fig. 4.71, calculate vo and...Ch. 4 - Use linearity to determine io in the circuit of...Ch. 4 - For the circuit in Fig. 4.73, assume vo = 1 V, and...Ch. 4 - For the linear circuit shown in Fig. 4.74, use...Ch. 4 - Use linearity and the assumption that Vo = 1 V to...Ch. 4 - Using superposition, find Vo in the circuit of...Ch. 4 - Given that I = 6 amps when Vs = 160 volts and Is =...Ch. 4 - Using Fig. 4.78, design a problem to help other...Ch. 4 - Use the superposition principle to find io and vo...Ch. 4 - Determine vo in the circuit of Fig. 4.80 using the...Ch. 4 - Use superposition to find vo in the circuit of...Ch. 4 - Apply the superposition principle to find vo in...Ch. 4 - For the circuit in Fig. 4.83, use superposition to...Ch. 4 - Given the circuit in Fig. 4.84, use superposition...Ch. 4 - Use superposition to obtain vx in the circuit of...Ch. 4 - Use superposition to find Vo in the circuit of...Ch. 4 - Use superposition to solve for vx in the circuit...Ch. 4 - Use source transformation to reduce the circuit...Ch. 4 - Using Fig. 4.89, design a problem to help other...Ch. 4 - For the circuit in Fig, 4.90, use source...Ch. 4 - Referring to Fig. 4.91, use source transformation...Ch. 4 - Use source transformation to find the voltage Vx...Ch. 4 - Obtain vo in the circuit of Fig. 4.93 using source...Ch. 4 - Use source transformation to find io in the...Ch. 4 - Apply source transformation to find vx in the...Ch. 4 - Use source transformation to find Io in Fig. 4.96....Ch. 4 - Use source transformation to find vo in the...Ch. 4 - Use source transformation on the circuit shown in...Ch. 4 - Determine vx in the circuit of Fig. 4.99 using...Ch. 4 - Use source transformation to find ix in the...Ch. 4 - Determine the Thevenin equivalent circuit, shown...Ch. 4 - Using Fig. 4.102, design a problem that will help...Ch. 4 - Use Thevenins theorem to find vo in Prob. 4.12....Ch. 4 - Solve for the current i in the circuit of Fig....Ch. 4 - Find the Norton equivalent with respect to...Ch. 4 - Apply Thevenins theorem to find Vo in the circuit...Ch. 4 - Obtain the Thevenin equivalent at terminals a-b of...Ch. 4 - Find the Thevenin equivalent at terminals a-b of...Ch. 4 - Find the Thevenin and Norton equivalents at...Ch. 4 - For the circuit in Fig. 4.109, find the Thevenin...Ch. 4 - Find the Thevenin equivalent looking into...Ch. 4 - For the circuit in Fig. 4.111, obtain the Thevenin...Ch. 4 - Find the Thevenin equivalent of the circuit in...Ch. 4 - Using Fig. 4.113, design a problem to help other...Ch. 4 - Obtain the Thevenin and Norton equivalent circuits...Ch. 4 - Determine the Norton equivalent at terminals a-b...Ch. 4 - Find the Norton equivalent looking into terminals...Ch. 4 - Obtain the Norton equivalent of the circuit in...Ch. 4 - Given the circuit in Fig. 4.117, obtain the Norton...Ch. 4 - For the transistor model in Fig. 4.118, obtain the...Ch. 4 - Find the Norton equivalent at terminals a-b of the...Ch. 4 - Find the Thevenin equivalent between terminals a-b...Ch. 4 - Obtain the Norton equivalent at terminals a-b of...Ch. 4 - Use Nortons theorem to find Vo in the circuit of...Ch. 4 - Obtain the Thevenin and Norton equivalent circuits...Ch. 4 - The network in Fig. 4.124 models a bipolar...Ch. 4 - Determine the Thevenin and Norton equivalents at...Ch. 4 - For the circuit in Fig. 4.126, find the Thevenin...Ch. 4 - Obtain the Thevenin and Norton equivalent circuits...Ch. 4 - Find the Thevenin equivalent of the circuit in...Ch. 4 - Find the Norton equivalent for the circuit in Fig....Ch. 4 - Obtain the Thevenin equivalent seen at terminals...Ch. 4 - For the circuit shown in Fig. 4.131, determine the...Ch. 4 - Find the maximum power that can be delivered to...Ch. 4 - The variable resistor R in Fig. 4.133 is adjusted...Ch. 4 - Consider the 30- resistor in Fig. 4.134. First...Ch. 4 - Find the maximum power transferred to resistor R...Ch. 4 - Determine the maximum power delivered to the...Ch. 4 - For the circuit in Fig. 4.137, what resistor...Ch. 4 - (a) For the circuit in Fig. 4.138, obtain the...Ch. 4 - Determine the maximum power that can be delivered...Ch. 4 - For the bridge circuit shown in Fig. 4.140, find...Ch. 4 - For the circuit in Fig. 4.141, determine the value...Ch. 4 - Solve Prob. 4.34 using PSpice or MultiSim. Let V =...Ch. 4 - Use PSpice or MultiSim to solve Prob. 4.44. For...Ch. 4 - Use PSpice or MultiSim to solve Prob. 4.52.Ch. 4 - Obtain the Thevenin equivalent of the circuit in...Ch. 4 - Use PSpice or MultiSim to find the Thevenin...Ch. 4 - For the circuit in Fig. 4.126, use PSpice or...Ch. 4 - An automobile battery has an open circuit voltage...Ch. 4 - The following results were obtained from...Ch. 4 - When connected to a 4- resistor, a battery has a...Ch. 4 - The Thevenin equivalent at terminals a-b of the...Ch. 4 - A black box with a circuit in it is connected to a...Ch. 4 - A transducer is modeled with a current source Is...Ch. 4 - Consider the circuit in Fig. 4.144. An ammeter...Ch. 4 - Consider the circuit in Fig. 4.145. (a) Replace...Ch. 4 - The Wheatstone bridge circuit shown in Fig. 4.146...Ch. 4 - (a) In the Wheatstone bridge circuit of Fig. 4.147...Ch. 4 - Consider the bridge circuit of Fig. 4.148. Is the...Ch. 4 - The circuit in Fig. 4.149 models a common-emitter...Ch. 4 - An attenuator is an interface circuit that reduces...Ch. 4 - A dc voltmeter with a sensitivity of 10 k/V is...Ch. 4 - A resistance array is connected to a load resistor...Ch. 4 - A common-emitter amplifier circuit is shown in...Ch. 4 - For Practice Prob. 4.18, determine the current...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Describe the principle of operation of a lin- ear induction motor.arrow_forwardName the principal components of an in- duction motor. Explain how a revolving field is set up in a 3-phase induction motor.arrow_forwardAnswer all the questions (a) How much power is the wind farm generating? (b) How much power is the solar farm generating? (c) Find the power delivered to the AC motor. (d) If the AC motor requires at least 45 kW of power, is the system able to provide that power? If not, how many additional series PV modules should be added to each string (we want to keep the same number of modules in each string)? If so, how many modules can be removed from each string while still meeting the requirements?arrow_forward
- An open-circuit voltage of 240 V appears across the slip-rings of a wound-rotor in- duction motor when the rotor is locked. The stator has 6 poles and is excited by a 60 Hz source. If the rotor is driven by a variable-speed dc motor, calculate the open-circuit voltage and frequency across the slip-rings if the dc motor turns a. At 600 r/min, in the same direction as the rotating field b. At 900 r/min, in the same direction as the rotating field c. At 3600 r/min, opposite to the rotating fieldarrow_forwardIf we double the number of poles on the stator of an induction motor, will its syn- chronous speed also double? The rotor of an induction should never be locked while full voltage is being applied to the stator. Explain. Why does the rotor of an induction motor turn slower than the revolving field?arrow_forwarda. Calculate the synchronous speed of a 3-phase, 12-pole induction motor that is excited by a 60 Hz source. b. What is the nominal speed if the slip at full-load is 6 percent?arrow_forward
- A 3-phase, 75 hp, 440 V induction motor has a full-load efficiency of 91 percent and a power factor of 83 percent. Calculate the nominal current per phase.arrow_forwardPlease answer all the questions a) What is the minimum required transformer rating for each transformer in kVA? b) Find the voltage required at Bus 1. c) The loadcentre is to be powered by PV panels that have the same I-V curve (ISC = 120 A, VOC = 60 V). Identify the configuration that uses the minimum number of panels to provide enough power to Bus 1. You can assume that the inverter converts the power at 95% efficiency and requires V DC input to generate the same VRMS AC output.arrow_forwardWhat happens to the rotor speed and rotor current when the mechanical load on an in- duction motor increases? Would you recommend using a 50 hp in- duction motor to drive a 10 hp load? Explain. Give two advantages of a wound-rotor mo- tor over a squirrel-cage motor. Both the voltage and frequency induced in the rotor of an induction motor decrease as the rotor speeds up. Explain.arrow_forward
- Please provide explainations and detailed working. thank youarrow_forwardPlease provide explainations and detailed working. thank youarrow_forwardThe excitation of a three-phase synchronous motor connected in parallel with a load of 500 kW operating at 0-85 p.f. lagging is adjusted to improve the overall p.f. of the system to 0.95 lagging. If the mechanical load on the motor is 120 kW, calculate the kVA input to the synchronous motor and its p.f.?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Norton's Theorem and Thevenin's Theorem - Electrical Circuit Analysis; Author: The Organic Chemistry Tutor;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-kkvqr1wSwA;License: Standard Youtube License