
a.
Find the displacement when
a.
Answer to Problem 101E
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The displacement from equilibrium of an oscillating weight suspended by a spring and subject to the damping effect of friction is given by
Calculation:
Consider that in Harmonic Motion the displacement from equilibrium of an oscillating weight suspended by a spring and subjrct to the damping effect of friction is given by
Here
Consider the following figure
Substitute
Because
Hence, displacement is
b.
Find the displacement when
b.
Answer to Problem 101E
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The displacement from equilibrium of an oscillating weight suspended by a spring and subject to the damping effect of friction is given by
Calculation:
Consider that in Harmonic Motion the displacement from equilibrium of an oscillating weight suspended by a spring and subjrct to the damping effect of friction is given by
Here
Consider the following figure
 Substitute
Substitute
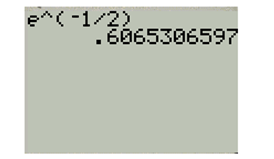
Evaluate value of cosine function using TI-83 calculator as shown below,
First set the calculator at radian mode then enter the function as below,
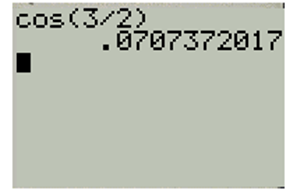
And
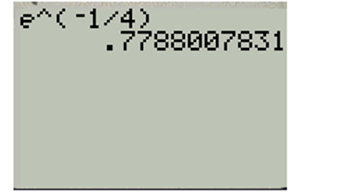
Hence,
Hence, the displacement is
c.
Find the displacement when
c.
Answer to Problem 101E
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The displacement from equilibrium of an oscillating weight suspended by a spring and subject to the damping effect of friction is given by
Calculation:
Consider that in Harmonic Motion the displacement from equilibrium of an oscillating weight suspended by a spring and subjrct to the damping effect of friction is given by
Here
Consider the following figure
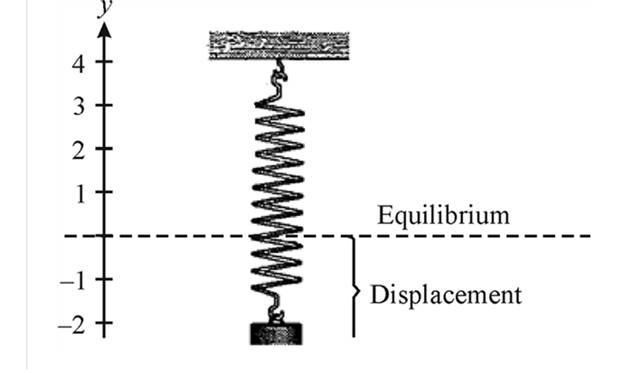
Substitute
Evaluate value of cosine function using TI-83 calculator as shown below,
First set the calculator at radian mode then enter the function as below,
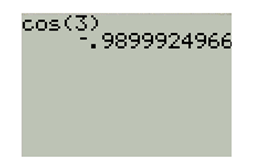
And
Hence,
Hence, the displacemnet is
Chapter 4 Solutions
EBK PRECALCULUS W/LIMITS
- #2arrow_forward2. We want to find the inverse of f(x) = (x+3)² a. On the graph at right, sketch f(x). (Hint: use what you know about transformations!) (2 points) b. What domain should we choose to get only the part of f (x) that is one- to-one and non-decreasing? Give your answer in inequality notation. (2 points) - c. Now use algebra to find f¯¹ (x). (2 points) -4- 3- 2 1 -4 -3 -2 -1 0 1 -1- -2- --3- -4 -N- 2 3 4arrow_forward1. Suppose f(x) = 2 4 == x+3 and g(x) = ½-½. Find and fully simplify ƒ(g(x)). Be sure to show all x your work, write neatly so your work is easy to follow, and connect your expressions with equals signs. (4 points)arrow_forward
- Find the one sided limit Tim f(x) where f(x)= (2x-1 X>1+ *arrow_forwardFind the limit lim X-700 4 13x-15 3x4+x³-12arrow_forwardFind the slope of the line secant to the curve F(x) = 13-x³ (from x=1 to x=2]arrow_forwardFind the ONe sided limit lim 2x X-2 1-xarrow_forwardFor each function, identify all points of discontinuity and label them as removable, jump, or infinite. A) f(x) = x-4 (X+15)(x-4) B) f(x) = (x²-1 x ≤2 14-2x 2arrow_forwardFind the one sided limit 2 lim Flx) where f(x) = (x²-4_xarrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_iosRecommended textbooks for you
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage LearningTrigonometry - Harmonic Motion - Equation Setup; Author: David Hays;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BPrZnn3DJ6Q;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BYSimple Harmonic Motion - An introduction : ExamSolutions Maths Revision; Author: ExamSolutions;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tH2vldyP5OE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage LearningTrigonometry - Harmonic Motion - Equation Setup; Author: David Hays;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BPrZnn3DJ6Q;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BYSimple Harmonic Motion - An introduction : ExamSolutions Maths Revision; Author: ExamSolutions;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tH2vldyP5OE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY