
Concept explainers
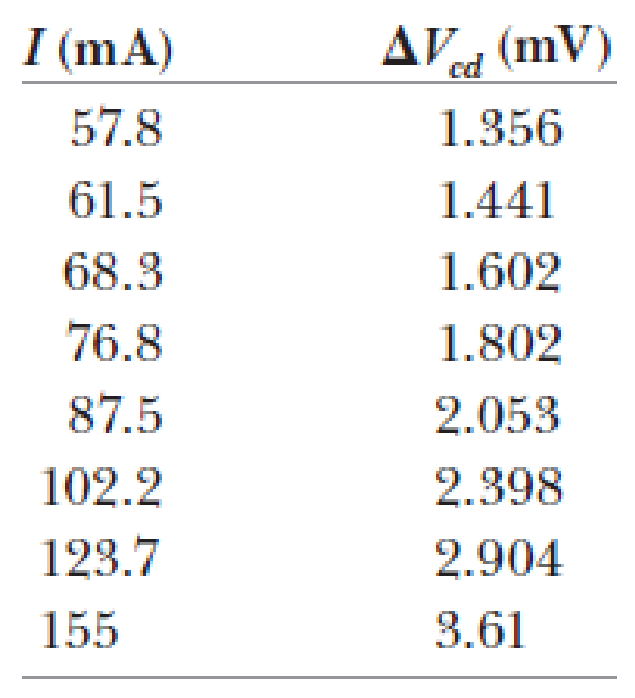
A direct and relatively simple demonstration of zero DC resistance can be carried out using the four-point probe method. The probe shown in Figure P43.52 consists of a disk of YBa2Cu3O7 (a high-Tc superconductor) to which four wires are attached. Current is maintained through the sample by applying a DC voltage between points a and b, and it is measured with a DC ammeter. The current can be varied with the variable resistance R. The potential difference ΔVcd between c and d is measured with a digital voltmeter. When the probe is immersed in liquid nitrogen, the sample quickly cools to 77 K, below the critical temperature of the material, 92 K. The current remains approximately constant, but ΔVcd drops abruptly to zero, (a) Explain this observation on the basis of what you know about superconductors. (b) The data in the accompanying table represent actual values of ΔVcd for different values of I taken on the sample at room temperature in the senior author’s laboratory. A 6-V battery in series with a variable resistor R supplied the current. The values of R ranged from 10 Ω to 100 Ω. Make an I-ΔV plot of the data and determine whether the sample behaves in a linear manner, (c) From the data, obtain a value for the DC resistance of the sample at room temperature. (d) At room temperature, it was found that ΔVcd = 2.234 mV for I = 100.3 mA, but after the sample was cooled to 77 K, ΔVcd = 0 and I = 98.1 mA. What do you think might have caused the slight decrease in current?
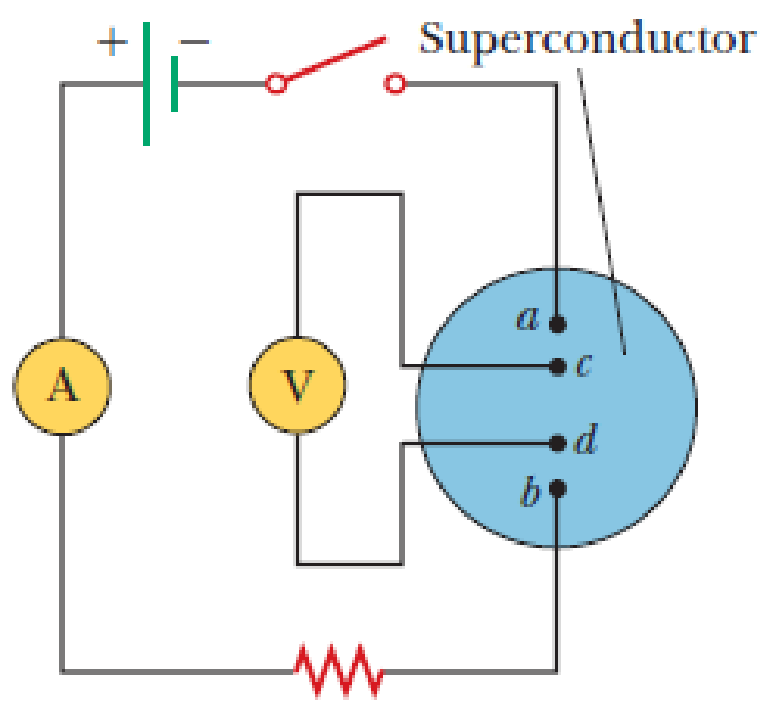
Figure P43.52
Current Versus Potential Difference ΔVcd Measured in a Bulk Ceramic Sample of YBa2Cu3O7−δ at Room Temperature
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 43 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern, Revised Hybrid (with Enhanced WebAssign Printed Access Card for Physics, Multi-Term Courses)
- Two objects get pushed by the same magnitude of force. One object is 10x more massive. How does the rate of change of momentum for the more massive object compare with the less massive one? Please be able to explain why in terms of a quantitative statement found in the chapter.arrow_forwardA box is dropped on a level conveyor belt that is moving at 4.5 m/s in the +x direction in a shipping facility. The box/belt friction coefficient is 0.15. For what duration will the box slide on the belt? In which direction does the friction force act on the box? How far will the box have moved horizontally by the time it stops sliding along the belt?arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardA toy car speeds up at 1.0 m/s2 while rolling down a ramp, and slows down at a rate of 2.0 m/s2 while rolling up the same ramp. What is the slope of the ramp in degrees? Grade in %? The friction coefficient?arrow_forwardPlz solution should be complete No chatgpt pls will upvote .arrow_forward
- A box with friction coefficient of 0.2 rests on a 12 foot long plank of wood. How high (in feet) must one side of the plank be lifted in order for the box to begin to slide?arrow_forwardWhat is a good general rule to follow in order to find the best choice of coordinate system to solve a dynamics problem?arrow_forwardWhat is the meaning of a first order approximation?arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning





