
(a)
Prove that the reflection coefficient for the given condition is
(a)
Answer to Problem 59CP
Proof for the reflection coefficient for the given condition is
Explanation of Solution
Write the Schrodinger’s equation.
Here,
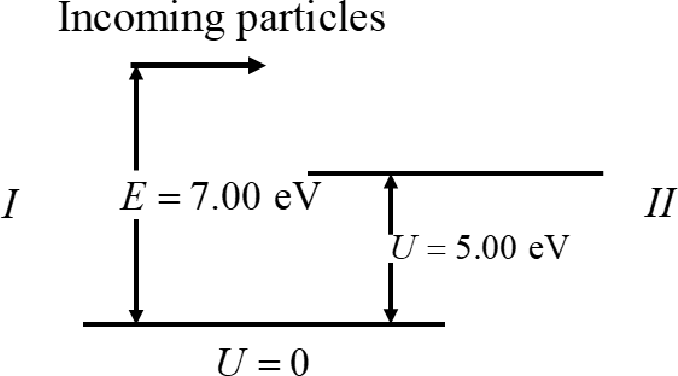
The solutions of the equation I for the region I in the above figure is
The solutions of the equation I for the region II in the above figure is
Here,
Check the solution for the region I satisfies the equation I.
The above equation will be true only if the
Here,
Rewrite the above equation to find the value of
Therefore the equation I is satisfied for the region I.
Check the equation I for the region II.
The above equation will be true only if the
Rewrite the above equation to find the value of
Therefore the equation I is satisfied for the region II.
Then apply the boundary conditions such as matching the function and derivatives at x=0.
From the above equations,
Write the equation for probability.
Conclusion:
Substitute equation VI in VII.
Therefore, the proof for the reflection coefficient for the given condition is
(b)
Find the probability of particle being reflected.
(b)
Answer to Problem 59CP
The probability of particle being reflected is
Explanation of Solution
Write the equation for ration of
Conclusion:
Substitute
Substitute
Therefore, the probability of particle being reflected is
(c)
Find the probability of particle being transmitted.
(c)
Answer to Problem 59CP
The probability of particle being transmitted is
Explanation of Solution
Write the equation for probability of transmitted.
Conclusion:
Substitute
Therefore, the probability of particle being transmitted is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 41 Solutions
Bundle: Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics, Loose-leaf Version, 9th + WebAssign Printed Access Card, Multi-Term
- Which of the following best describes how to calculate the average acceleration of any object? Average acceleration is always halfway between the initial acceleration of an object and its final acceleration. Average acceleration is always equal to the change in velocity of an object divided by the time interval. Average acceleration is always equal to the displacement of an object divided by the time interval. Average acceleration is always equal to the change in speed of an object divided by the time interval.arrow_forwardThe figure shows the velocity versus time graph for a car driving on a straight road. Which of the following best describes the acceleration of the car? v (m/s) t(s) The acceleration of the car is negative and decreasing. The acceleration of the car is constant. The acceleration of the car is positive and increasing. The acceleration of the car is positive and decreasing. The acceleration of the car is negative and increasing.arrow_forwardWhich figure could represent the velocity versus time graph of a motorcycle whose speed is increasing? v (m/s) v (m/s) t(s) t(s)arrow_forward
- Unlike speed, velocity is a the statement? Poisition. Direction. Vector. Scalar. quantity. Which one of the following completesarrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvote Already got wrong chatgpt answerarrow_forward3.63 • Leaping the River II. A physics professor did daredevil stunts in his spare time. His last stunt was an attempt to jump across a river on a motorcycle (Fig. P3.63). The takeoff ramp was inclined at 53.0°, the river was 40.0 m wide, and the far bank was 15.0 m lower than the top of the ramp. The river itself was 100 m below the ramp. Ignore air resistance. (a) What should his speed have been at the top of the ramp to have just made it to the edge of the far bank? (b) If his speed was only half the value found in part (a), where did he land? Figure P3.63 53.0° 100 m 40.0 m→ 15.0 marrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Modern PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781111794378Author:Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. MoyerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Modern PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781111794378Author:Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. MoyerPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax
University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill





