
Follow the directions of Question 7 for solutions of the following:
(a) silver nitrate and sodium chloride
(b) cobalt(II) nitrate and sodium hydroxide
(c) ammonium phosphate and potassium hydroxide
(d) copper(II) sulfate and sodium carbonate
(e) lithium sulfate and barium hydroxide
(a)
Interpretation:
Whether a precipitate will form when the given solutions are mixed should be determined along with the net ionic equation should be written, if precipitate will form.
Silver nitrate and sodium chloride
Concept introduction:
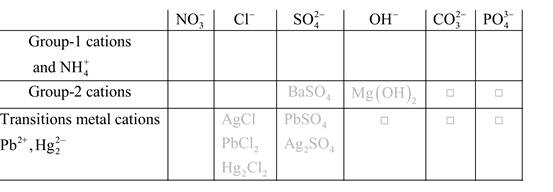
Solubility of any compound is predicted by above solubility chart.
Blank boxes indicate no precipitate formation occurs which means soluble in dilute solution.
Boxes with grey small box will form precipitate from dilute solutions and boxes where formula is written this is a cation-anion combination that will form precipitate.
Precipitation reactions: It is a type of chemical reactions where two soluble salts react with each other and formed different products, out of which one product must be insoluble in solution which is known as precipitate.
A chemical equation which shows only the species that are participated in the reaction is said to be net ionic equation.
Answer to Problem 8QAP
Precipitation occurs
The net ionic equation is:
Explanation of Solution
Silver nitrate:
Sodium chloride:
Reaction for the solution of silver nitrate and sodium chloride is written as:
Reactants:
Ions in solution:
Ions in solution:
Products:
Ions in solution:
Ions in solution:
Now,
So, the equation will be:
Now, cancelling out the ions which appear on both sides of the equation (
(b)
Interpretation:
Whether a precipitate will form when the given solutions are mixed should be determined along with the net ionic equation should be written, if precipitate will form.
Cobalt(II) nitrate and sodium hydroxide
Concept introduction:
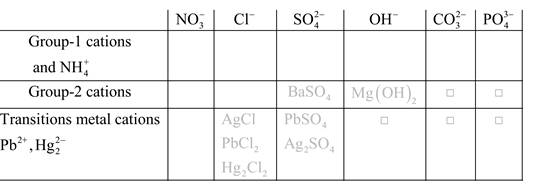
Solubility of any compound is predicted by above solubility chart.
Blank boxes indicate no precipitate formation occurs which means soluble in dilute solution.
Boxes with grey small box will form precipitate from dilute solutions and boxes where formula is written this is a cation-anion combination that will form precipitate.
Precipitation reactions: It is a type of chemical reactions where two soluble salts react with each other and formed different products, out of which one product must be insoluble in solution which is known as precipitate.
A chemical equation which shows only the species that are participated in the reaction is said to be net ionic equation.
Answer to Problem 8QAP
Precipitation occurs
The net ionic equation is:
Explanation of Solution
Cobalt(II) nitrate:
Sodium hydroxide:
Reaction for the solution of cobalt(II) nitrate and sodium hydroxide is written as:
Reactants:
Ions in solution:
Ions in solution:
Products:
Ions in solution:
Ions in solution:
Now,
So, the equation will be:
Now, cancelling out the ions which appear on both sides of the equation (
(c)
Interpretation:
Whether a precipitate will form when the given solutions are mixed should be determined along with the net ionic equation should be written, if precipitate will form.
Ammonium phosphate and potassium hydroxide
Concept introduction:
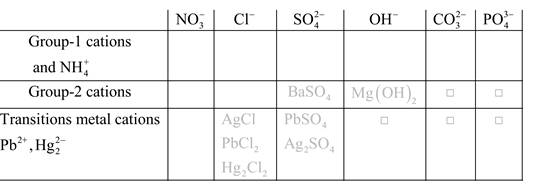
Solubility of any compound is predicted by above solubility chart.
Blank boxes indicate no precipitate formation occurs which means soluble in dilute solution.
Boxes with grey small box will form precipitate from dilute solutions and boxes where formula is written this is a cation-anion combination that will form precipitate.
Precipitation reactions: It is a type of chemical reactions where two soluble salts react with each other and formed different products, out of which one product must be insoluble in solution which is known as precipitate.
A chemical equation which shows only the species that are participated in the reaction is said to be net ionic equation.
Answer to Problem 8QAP
No precipitation occurs.
Explanation of Solution
Ammonium phosphate:
Potassium hydroxide:
Reaction for the solution of ammonium phosphate and potassium hydroxide is written as:
Reactants:
Ions in solution:
Ions in solution:
Products:
Ions in solution:
Ions in solution:
Now,
(d)
Interpretation:
Whether a precipitate will form when the given solutions are mixed should be determined along with the net ionic equation should be written, if precipitate will form.
Copper(II) sulfate and sodium carbonate
Concept introduction:
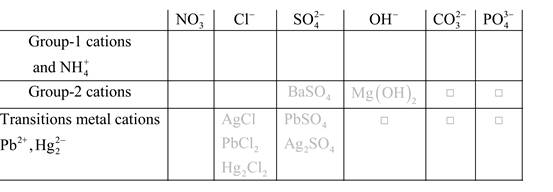
Solubility of any compound is predicted by above solubility chart.
Blank boxes indicate no precipitate formation occurs which means soluble in dilute solution.
Boxes with grey small box will form precipitate from dilute solutions and boxes where formula is written this is a cation-anion combination that will form precipitate.
Precipitation reactions: It is a type of chemical reactions where two soluble salts react with each other and formed different products, out of which one product must be insoluble in solution which is known as precipitate.
A chemical equation which shows only the species that are participated in the reaction is said to be net ionic equation.
Answer to Problem 8QAP
Precipitation occurs
The net ionic equation is:
Explanation of Solution
Copper(II) sulfate:
Sodium carbonate:
Reaction for the solution of copper(II) sulfate and sodium carbonate is written as:
Reactants:
Ions in solution:
Ions in solution:
Products:
Ions in solution:
Ions in solution:
Now,
So, the equation will be:
Now, cancelling out the ions which appear on both sides of the equation (
(e)
Interpretation:
Whether a precipitate will form when the given solutions are mixed should be determined along with the net ionic equation should be written, if precipitate will form.
Lithium sulfate and barium hydroxide
Concept introduction:
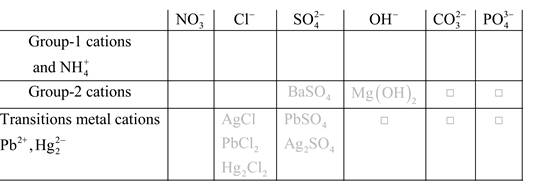
Solubility of any compound is predicted by above solubility chart.
Blank boxes indicate no precipitate formation occurs which means soluble in dilute solution.
Boxes with grey small box will form precipitate from dilute solutions and boxes where formula is written this is a cation-anion combination that will form precipitate.
Precipitation reactions: It is a type of chemical reactions where two soluble salts react with each other and formed different products, out of which one product must be insoluble in solution which is known as precipitate.
A chemical equation which shows only the species that are participated in the reaction is said to be net ionic equation.
Answer to Problem 8QAP
Precipitation occurs
The net ionic equation is:
Explanation of Solution
Lithium sulfate:
Barium hydroxide:
Reaction for the solution of lithium sulfate and barium hydroxide is written as:
Reactants:
Ions in solution:
Ions in solution:
Products:
Ions in solution:
Ions in solution:
Now,
So, the equation will be:
Now, cancelling out the ions which appear on both sides of the equation (
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
- What is the final product when D-galactose reacts with hydroxylamine?arrow_forwardIndicate the formula of the product obtained by reacting methyl 5-chloro-5-oxopentanoate with 1 mole of 4-penten-1-ylmagnesium bromide.arrow_forwardIn the two chair conformations of glucose, the most stable is the one with all the OH groups in the equatorial position. Is this correct?arrow_forward
- please help me with my homeworkarrow_forwardhelparrow_forwardThe temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forward
- QUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forwardpressure (atm) 3 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 0 0 200 temperature (K) 400 аarrow_forwarder your payment details | bar xb Home | bartleby x + aleksogi/x/isl.exe/1o u-lgNskr7j8P3jH-1Qs_pBanHhviTCeeBZbufuBYT0Hz7m7D3ZcW81NC1d8Kzb4srFik1OUFhKMUXzhGpw7k1 O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 1 3- 0- 0 200 Explanation Check temperature (K) 400 X Q Search L G 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved Terms of Use Privacy Cearrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning





