
Concept explainers
Two forces
Figure P4.7
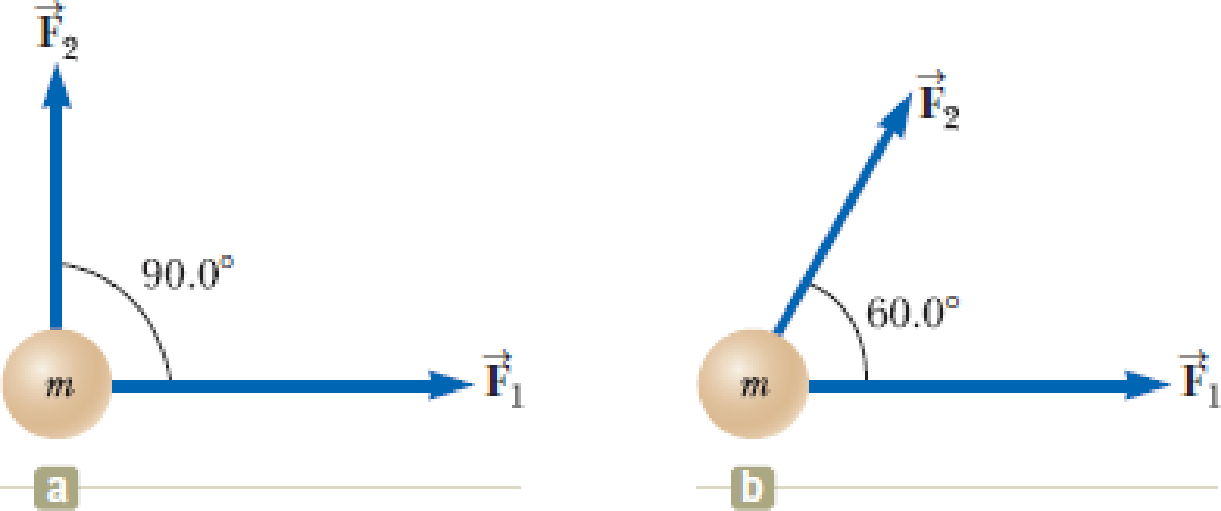
(a)
The acceleration of the object.
Answer to Problem 7P
The acceleration of the object is
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for net force.
Here,
Write the expression for acceleration by using equation (I).
Here,
Write the expression for the direction of the acceleration.
Here,
Write the expression for the magnitude of the acceleration.
Here,
Conclusion:
Substitute,
Substitute,
Substitute,
Thus, the acceleration of the object is
(b)
The acceleration of the object.
Answer to Problem 7P
The acceleration of the object is
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for net force.
Here,
Write the expression for acceleration by using equation (I).
Here,
Write the expression for the direction of the acceleration.
Here,
Write the expression for the magnitude of the acceleration.
Here,
Conclusion:
Substitute,
Substitute,
Substitute,
Thus, the acceleration of the object is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
- Mick and Rick are twins born on Earth in the year 2175. Rick grows up to be an Earth-bound robotics technician while Mick becomes an intergalactic astronaut. Mick leaves the Earth on his first space mission in the year 2200 and travels, according to his clock, for 10 years at a speed of 0.75c. Unfortunately, at this point in his journey, the structure of his ship undergoes mechanical breakdown and the ship explodes. How old is Rick when his brother dies?arrow_forwardHi, I have canceled, why did you charge me again?arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





