
College Physics
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781285737027
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 4, Problem 72AP
A rope with mass m, is attached to a block with mass mb, as in Figure P4.72. Both the rope and the block rest on a horizontal, frictionless surface. The rope does not stretch. The free end of the rope is pulled to the right with a horizontal force F. (a) Draw free-body diagrams for the rope and the block, noting that the tension in the rope is not uniform, (b) Find the acceleration of the system in terms of mb, mT, and F. (c) Find the magnitude of the force the rope exerts on the block, (d) What happens to the force on the block as the rope’s mass approaches zero? What can you state about the tension in a light cord joining a pair of moving objects?
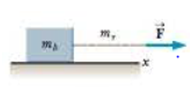
Figure P4.72
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
How would partial obstruction of an air intake port of an air-entrainment mask effect FiO2 and flow?
14
Z
In figure, a closed surface with q=b=
0.4m/
C =
0.6m
if the left edge
of the closed surface at position X=a,
if E is non-uniform and is given by
€ = (3 + 2x²) ŷ N/C, calculate the
(3+2x²)
net electric flux leaving the closed
surface.
No chatgpt pls will upvote
Chapter 4 Solutions
College Physics
Ch. 4.3 - Which of the following statements are true? (a) An...Ch. 4.3 - Which has greater value, a newton of gold on Earth...Ch. 4.3 - Respond to each statement, true or false: (a) No...Ch. 4.4 - A small sports car collides head-on with a massive...Ch. 4.5 - Consider the two situations shown in Figure 4.30,...Ch. 4.5 - For the woman being pulled forward on the toboggan...Ch. 4.6 - If you press a book flat against a vertical wall...Ch. 4.6 - A crate is sitting in the center of a flatbed...Ch. 4.6 - Suppose your friend is sitting on a sled and asks...Ch. 4 - Physics Review A hockey player strikes a puck,...
Ch. 4 - Four forces act on an object, given by A = 40.0 N...Ch. 4 - A force of 30.0 N is applied in the positive...Ch. 4 - What would be the acceleration of gravity at the...Ch. 4 - Two monkeys are holding onto a single vine of...Ch. 4 - Two identical strings making an angle of = 30.0...Ch. 4 - Calculate the normal force on a 15.0 kg block in...Ch. 4 - A horizontal force of 95.0 N is applied to a...Ch. 4 - Prob. 9WUECh. 4 - A block of mass 12.0 kg is sliding at an initial...Ch. 4 - A man exerts a horizontal force of 112 N on a...Ch. 4 - An Atwoods machine (Fig. 4.38) consists of two...Ch. 4 - A block of mass m1= 10 kg is on a frictionless...Ch. 4 - A passenger sitting in the rear of a bus claims...Ch. 4 - A space explorer is moving through space far from...Ch. 4 - (a) If gold were sold by weight, would you rather...Ch. 4 - If you push on a heavy box that is at rest, you...Ch. 4 - A ball is held in a persons hand. (a) Identify all...Ch. 4 - A weight lifter stands on a bathroom scale. (a) As...Ch. 4 - (a) What force causes an automobile to move? (b) A...Ch. 4 - If only one force acts on an object, can it be in...Ch. 4 - In the: motion picture It Happened One Night...Ch. 4 - Analyze the motion of a rock dropped in water in...Ch. 4 - Identify the action-reaction pairs in the...Ch. 4 - Draw a free-body diagram for each of the following...Ch. 4 - In a tug-of-war between two athletes, each pulls...Ch. 4 - Suppose you are driving a car at a high speed. Why...Ch. 4 - As a block slides down a frictionless incline,...Ch. 4 - A crate remains stationary after it has been...Ch. 4 - In Figure 4.4, a locomotive has broken through the...Ch. 4 - If an object is in equilibrium, which of the...Ch. 4 - A truck loaded with sand accelerates along a...Ch. 4 - A large crate of mass m is placed on the back of a...Ch. 4 - Which of the following statements are true? (a) An...Ch. 4 - The heaviest invertebrate is the giant squid,...Ch. 4 - A football punter accelerates a football from rest...Ch. 4 - A 6.0-kg object undergoes an acceleration of 2.0...Ch. 4 - One or more external forces are exerted on each...Ch. 4 - A bag of sugar weighs 5.00 lb on Earth. What would...Ch. 4 - A freight train has a mass of 1.5 107 kg. If the...Ch. 4 - A 75-kg man standing on a scale in an elevator...Ch. 4 - Consider a solid metal sphere (S) a few...Ch. 4 - As a fish jumps vertically out of the water,...Ch. 4 - A 5.0-g bullet leaves the muzzle of a rifle with a...Ch. 4 - A boat moves through the water with two forces...Ch. 4 - Two forces are applied to a car in an effort to...Ch. 4 - A 970.-kg car starts from rest on a horizontal...Ch. 4 - An object of mass m is dropped from the roof of a...Ch. 4 - After falling from rest from a height of 30.0 m, a...Ch. 4 - The force exerted by the wind on the sails of a...Ch. 4 - (a) Find the tension in each cable supporting the...Ch. 4 - A certain orthodontist uses a wire brace to align...Ch. 4 - A 150-N bird feeder is supported by three cables...Ch. 4 - The leg and cast in Figure P4.40 weigh 220 N (w1)....Ch. 4 - Two blocks each of mass m are fastened to the top...Ch. 4 - Two blocks each of mass m = 3.50 kg are fastened...Ch. 4 - The distance between two telephone poles is 50.0...Ch. 4 - The systems shown in Figure P4.58 are in...Ch. 4 - A 5.0-kg bucket of water is raised from a well by...Ch. 4 - A crate of mass m = 32 kg rides on the bed of a...Ch. 4 - Two blocks of masses m and 2m are held in...Ch. 4 - Two packing crates of masses 10.0 kg and 5.00 kg...Ch. 4 - Assume the three blocks portrayed in Figure P4.59...Ch. 4 - A block of mass m = 5.8 kg is pulled up a = 25...Ch. 4 - A setup similar to the one shown in Figure P4.53...Ch. 4 - Two blocks of masses m1 and m2 (m1 m2) are placed...Ch. 4 - A 276-kg glider is being pulled by a 1 950-kg jet...Ch. 4 - In Figure P4.63, the light, taut, unstretchable...Ch. 4 - (a) An elevator of mass m moving upward has two...Ch. 4 - An object with mass m1 = 5.00 kg rests on a...Ch. 4 - A 1.00 103 car is pulling a 300.-kg trailer....Ch. 4 - Two objects with masses of 3.00 kg and 5.00 kg are...Ch. 4 - A dockworker loading crates on a ship finds that a...Ch. 4 - In Figure P4.64, m1 = 10. kg and m2 = 4.0 kg. The...Ch. 4 - A 1.00 103-N crate is being pushed across a level...Ch. 4 - A block of mass 3m is placed on a frictionless...Ch. 4 - Consider a large truck carrying a heavy load, such...Ch. 4 - A crate of mass 45.0 kg is being transported on...Ch. 4 - Objects with masses m1 = 10.0 kg and m2 = 5.00 kg...Ch. 4 - A hockey puck struck by a hockey stick is given an...Ch. 4 - The coefficient of static friction between the...Ch. 4 - A student decides to move a box of books into her...Ch. 4 - An object falling under the pull of gravity is...Ch. 4 - A car is traveling at 50.0 km/h on a flat highway....Ch. 4 - A 3.00-kg block starts from rest at the top of a...Ch. 4 - A 15.0-lb block rests on a horizontal floor, (a)...Ch. 4 - To meet a U.S. Postal Service requirement,...Ch. 4 - Objects of masses m1 = 4.00 kg and m2 = 9.00 kg...Ch. 4 - The person in Figure P4.49 weighs 170. lb. Each...Ch. 4 - As a protest against the umpires calls, a baseball...Ch. 4 - Three objects are connected on a table as shown in...Ch. 4 - The force exerted by the wind on a sailboat is...Ch. 4 - (a) What is the resultant force exerted by the two...Ch. 4 - (a) What is the minimum force of friction required...Ch. 4 - A boy coasts down a hill on a sled, reaching a...Ch. 4 - A woman at an airport is towing her 20.0-kg...Ch. 4 - A box rests on the back of a truck. The...Ch. 4 - Three objects are connected by light strings as...Ch. 4 - A frictionless plane is 10.0 m long and inclined...Ch. 4 - A high diver of mass 70.0 kg steps off a board...Ch. 4 - A 2.00-kg aluminum block and a 6.00-kg copper...Ch. 4 - An object of mass m1 hangs from a string that...Ch. 4 - Two boxes of fruit on a frictionless horizontal...Ch. 4 - Measuring coefficients of friction A coin is...Ch. 4 - A fisherman poles a boat as he searches for his...Ch. 4 - A rope with mass m, is attached to a block with...Ch. 4 - A car accelerates down a hill (Fig. P4.87), going...Ch. 4 - Prob. 74APCh. 4 - The parachute on a race car of weight 8 820 N...Ch. 4 - On an airplanes takeoff, the combined action of...Ch. 4 - The board sandwiched between two other boards in...Ch. 4 - A sled weighing 60.0 N is pulled horizontally...Ch. 4 - A 72-kg man stands on a spring scale in an...Ch. 4 - A magician pulls a tablecloth from under a 200-g...Ch. 4 - An inventive child wants to reach an apple in a...Ch. 4 - A fire helicopter carries a 620-kg bucket of water...Ch. 4 - A crate of weight Fg is pushed by a force P on a...Ch. 4 - In Figure P1.84, the pulleys and the cord are...Ch. 4 - What horizontal force must ho applied to a large...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- suggest a reason ultrasound cleaning is better than cleaning by hand?arrow_forwardCheckpoint 4 The figure shows four orientations of an electric di- pole in an external electric field. Rank the orienta- tions according to (a) the magnitude of the torque on the dipole and (b) the potential energy of the di- pole, greatest first. (1) (2) E (4)arrow_forwardWhat is integrated science. What is fractional distillation What is simple distillationarrow_forward
- 19:39 · C Chegg 1 69% ✓ The compound beam is fixed at Ę and supported by rollers at A and B. There are pins at C and D. Take F=1700 lb. (Figure 1) Figure 800 lb ||-5- F 600 lb بتا D E C BO 10 ft 5 ft 4 ft-—— 6 ft — 5 ft- Solved Part A The compound beam is fixed at E and... Hình ảnh có thể có bản quyền. Tìm hiểu thêm Problem A-12 % Chia sẻ kip 800 lb Truy cập ) D Lưu of C 600 lb |-sa+ 10ft 5ft 4ft6ft D E 5 ft- Trying Cheaa Những kết quả này có hữu ích không? There are pins at C and D To F-1200 Egue!) Chegg Solved The compound b... Có Không ☑ ||| Chegg 10 וחarrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardair is pushed steadily though a forced air pipe at a steady speed of 4.0 m/s. the pipe measures 56 cm by 22 cm. how fast will air move though a narrower portion of the pipe that is also rectangular and measures 32 cm by 22 cmarrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- 13.87 ... Interplanetary Navigation. The most efficient way to send a spacecraft from the earth to another planet is by using a Hohmann transfer orbit (Fig. P13.87). If the orbits of the departure and destination planets are circular, the Hohmann transfer orbit is an elliptical orbit whose perihelion and aphelion are tangent to the orbits of the two planets. The rockets are fired briefly at the depar- ture planet to put the spacecraft into the transfer orbit; the spacecraft then coasts until it reaches the destination planet. The rockets are then fired again to put the spacecraft into the same orbit about the sun as the destination planet. (a) For a flight from earth to Mars, in what direction must the rockets be fired at the earth and at Mars: in the direction of motion, or opposite the direction of motion? What about for a flight from Mars to the earth? (b) How long does a one- way trip from the the earth to Mars take, between the firings of the rockets? (c) To reach Mars from the…arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwarda cubic foot of argon at 20 degrees celsius is isentropically compressed from 1 atm to 425 KPa. What is the new temperature and density?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:9780534408961
Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Drawing Free-Body Diagrams With Examples; Author: The Physics Classroom;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3rZR7FSSidc;License: Standard Youtube License